Professor Fred Apple Reveals Another Significant Progress with Mindray in Cardiac Biomarkers at ADLM 2025
2025-08-01

At the Association for Diagnostics & Laboratory Medicine (ADLM, formerly AACC) conference, Professor Fred Apple (Former Chair of IFCC Committee on Clinical Application of Cardiac Biomarkers (C-CB)), as an invited speaker, made a significant announcement and interpretation of his key research on Mindray's high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) - (Mindray-hs-cTnI Assay: Analytical and Clinical Evaluation for the Diagnosis and Risk Assessment of Myocardial Infarction).
Currently, cTn testing still faces the key challenge of "being unable to distinguish the causes of acute and chronic myocardial injury through a single test". Professor Apple presented prospective explorations that are expected to enable the differentiation of acute and chronic injuries, and further help distinguish between type 1 and type 2 myocardial infarction. He stated that Mindray’s innovative reagents targeting specific troponin complexes have shown promising and unique advantages.
Mindray's hs-cTnI analytical performance has been certified by Fred Apple's laboratory
Professor Fred Apple's team released the results of an in-depth evaluation of the analytical performance of Mindray's hs-cTnI. The report points out that Mindray's hs-cTnI shows an extremely high detection rate in healthy populations and can achieve accurate quantification at extremely low concentrations. Its excellent sensitivity and specificity are the core foundations for its application in clinical practice, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of results.

Looking Ahead: Exploring the Diagnostic and Triage Efficacy of Troponin Complexes for Acute Myocardial Infarction in Emergency Scenarios
In the summary of the report, Professor Fred Apple pointed out that based on a profound understanding of the complexity of myocardial injury biomarkers, Mindray’s innovative detection reagents targeting specific troponin complexes have shown promising and unique advantages. [1,2]
Notably, Professor Fred Apple is conducting in-depth collaborative research with Mindray's team. This collaboration is pioneering and systematically exploring the diagnostic and triage efficacy of troponin complexes for acute myocardial infarction in emergency scenarios.
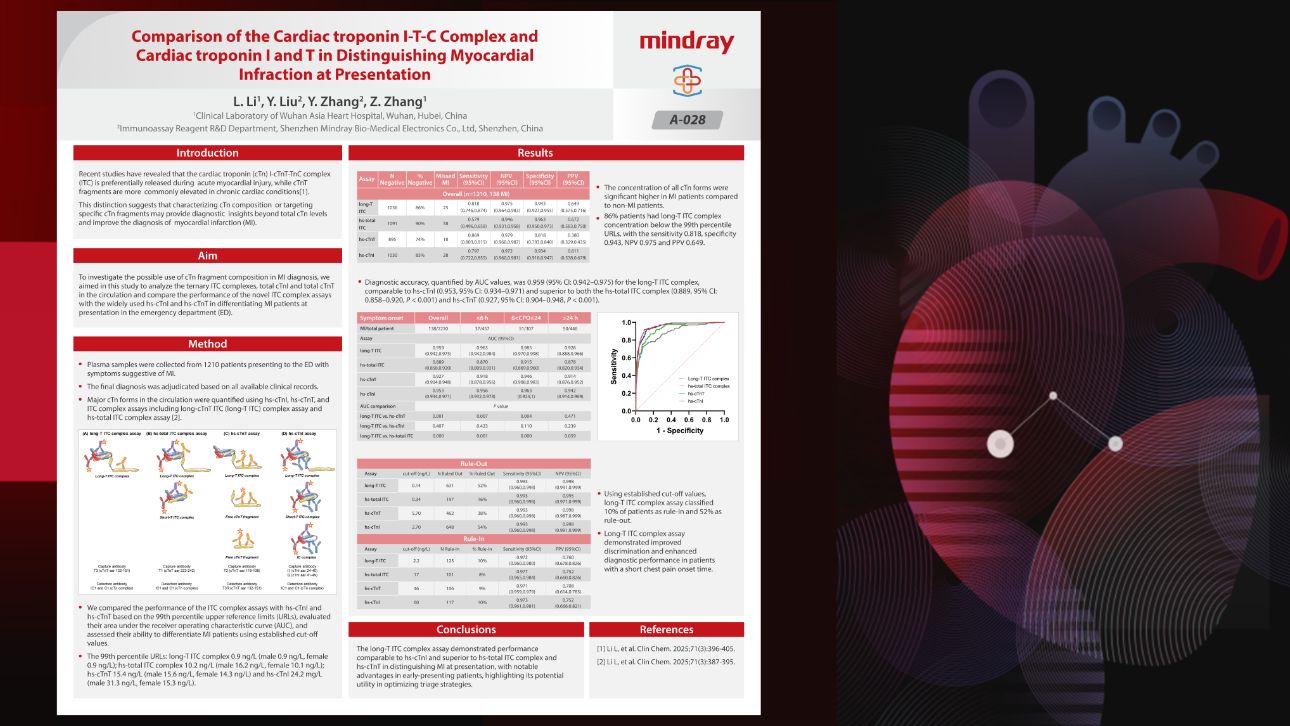
Exploring Complex Interference Patterns Guided by Clinical Needs to Propel Anti - interference to a New "Cardiac" Height
Subsequently, Dr. Zhang Yi, the manager of Mindray's Immunoassay Reagent Development Department, centered on the original reagent design, introduced the development concept and technological breakthroughs of Mindray's hs-cTnI, as well as the latest research results on troponin complexes.
Research has shown that enhancing the sensitivity of hs-cTn makes it easier to detect transient myocardial injuries, and also ensures greater safety when ruling out the risk of myocardial infarction at a single point. [3-5] Therefore, higher sensitivity has become the pursuit of the entire industry.

cTn Complexes as Rapid-Response Indicators of Myocardial Injury: Promising for Single-Point Early Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction
Previous studies [6] have shown that when a patient experiences a myocardial infarction, cTnI is released into the bloodstream in the form of ITC complexes. Subsequently, cTnI and cTnT within the ITC complexes gradually degrade, forming low-molecular-weight ITC complexes. As cTnT further dissociates from the ITC complexes, IC complexes are eventually formed. Although various forms of cTn complexes exist in the patient's blood as the myocardial infarction progresses, studies have found that cTnI remains bound to TnC, and no free cTnI has been detected.
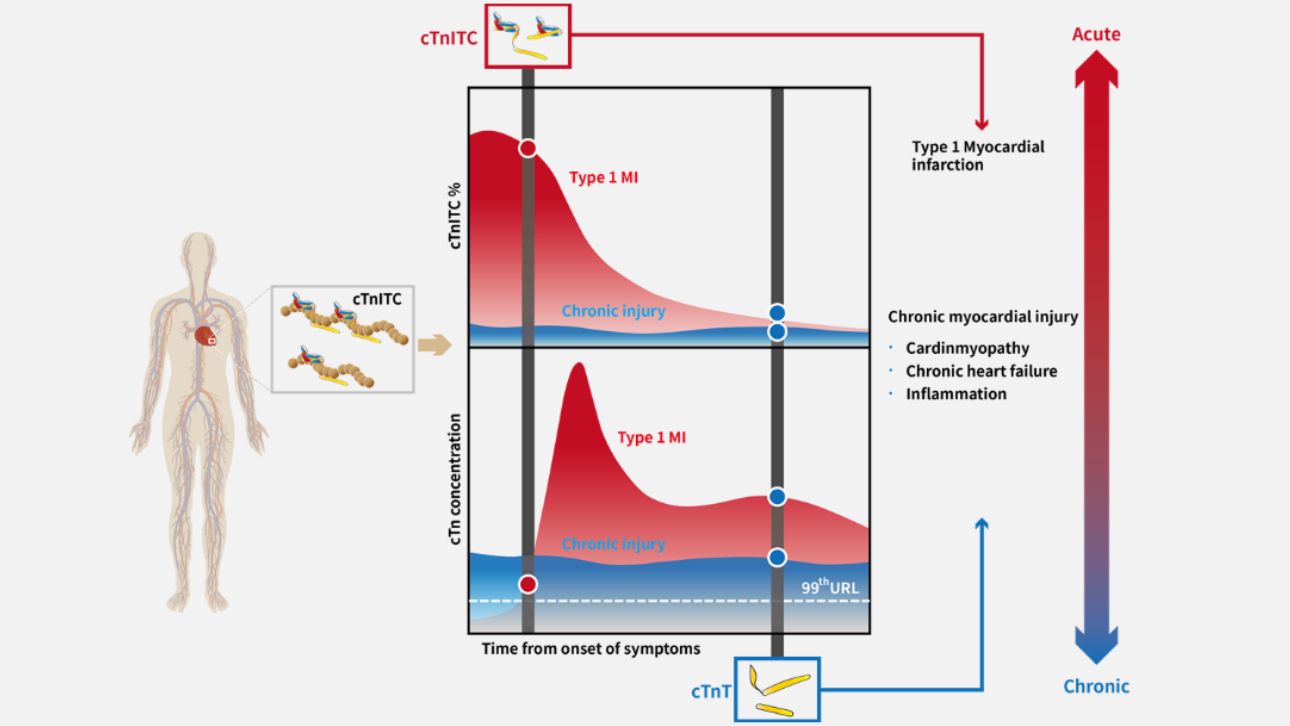
Based on this, Mindray has designed a variety of reagents to detect different forms of cTn. The latest results show that in cases of acute myocardial injury (such as early myocardial infarction and post - cardiac surgery), Long - T ITC is rapidly released into the bloodstream, with its concentration and proportion increasing significantly; in patients with chronic heart disease, the main existing form of cTn is the free fragment of cTnT. Therefore, the concentration and proportion characteristics of Long - T ITC can serve as key indicators for distinguishing between acute and chronic injuries.
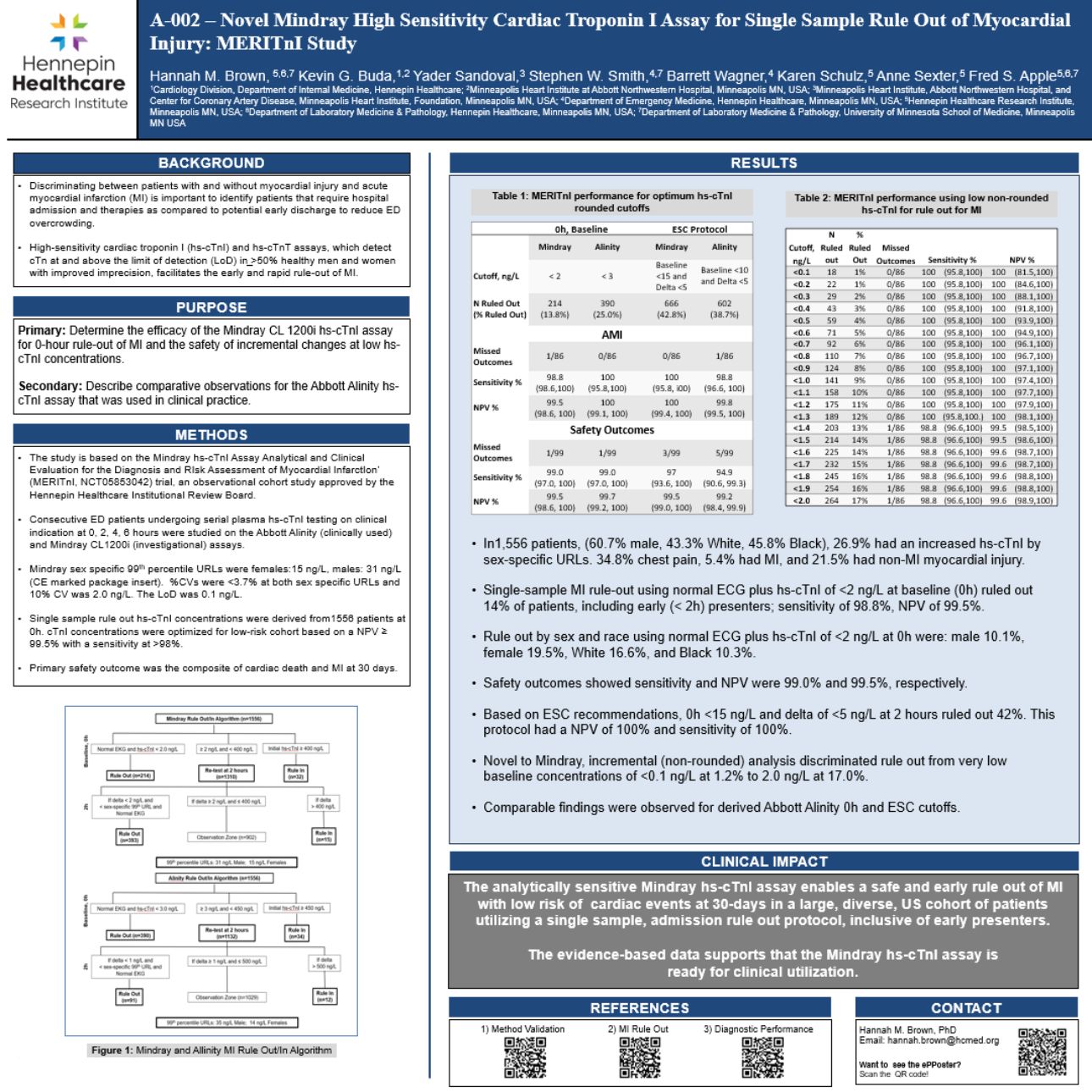
The report at this conference is an authoritative affirmation of the excellent performance of Mindray's hs-cTnI in the rapid and accurate diagnosis of myocardial infarction. The impressive results of the MERITnI study not only verify the outstanding clinical performance and safety of Mindray's products, but also demonstrate the forward-looking nature of cooperation with top international research teams.
References:
[1]. Westermann D, Neumann JT, Sörensen NA, Blankenberg S. High-sensitivity assays for troponin in patients with cardiac disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017;14(8):472-483. doi:10.1038/nrcardio.2017.48
[2]. Apple FS. A new season for cardiac troponin assays: it's time to keep a scorecard. Clin Chem. 2009;55(7):1303-1306. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2009.128363
[3]. Lowry MTH, Doudesis D, Boeddinghaus J, et al. Troponin in early presenters to rule out myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(30):2846-2858. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehad376
[4]. Thygesen K, Mair J, Giannitsis E, et al. How to use high-sensitivity cardiac troponins in acute cardiac care. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(18):2252-2257. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehs154
[5]. Vylegzhanina AV, Kogan AE, Katrukha IA, et al. Full-Size and Partially Truncated Cardiac Troponin Complexes in the Blood of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. Clin Chem. 2019;65(7):882-892. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2018.301127
[6]. Vylegzhanina AV, Kogan AE, Katrukha IA, et al. Full-Size and Partially Truncated Cardiac Troponin Complexes in the Blood of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. Clin Chem. 2019;65(7):882-892. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2018.301127