Mindray Wins ADLM Distinguished Abstracts Award
In July 2025, the global laboratory medicine community turned its attention to McCormick Place in Chicago for ADLM 2025 (formerly AACC Annual Meeting) – a top-tier event with a 70-year history, covering 110 countries and gathering over 20,000 professionals! Mindray Medical made history by winning the Academy Distinguished Abstracts Awards for its groundbreaking research in cardiac troponin testing, marking further international recognition of Chinese innovative strength in the high-end diagnostic field!

One in a Thousand: Recognition from the World's Highest Stage
The ADLM Distinguished Abstracts Awards, selected by the Academy for Diagnostic & Laboratory Medicine under the association, is one of the most influential academic honors in the field of laboratory medicine. The award selects only 19 papers out of thousands of unpublished manuscripts submitted globally, truly "one in a hundred." The selection is based on three core criteria: scientific excellence, methodological rigor, and clinical value, making it highly prestigious.
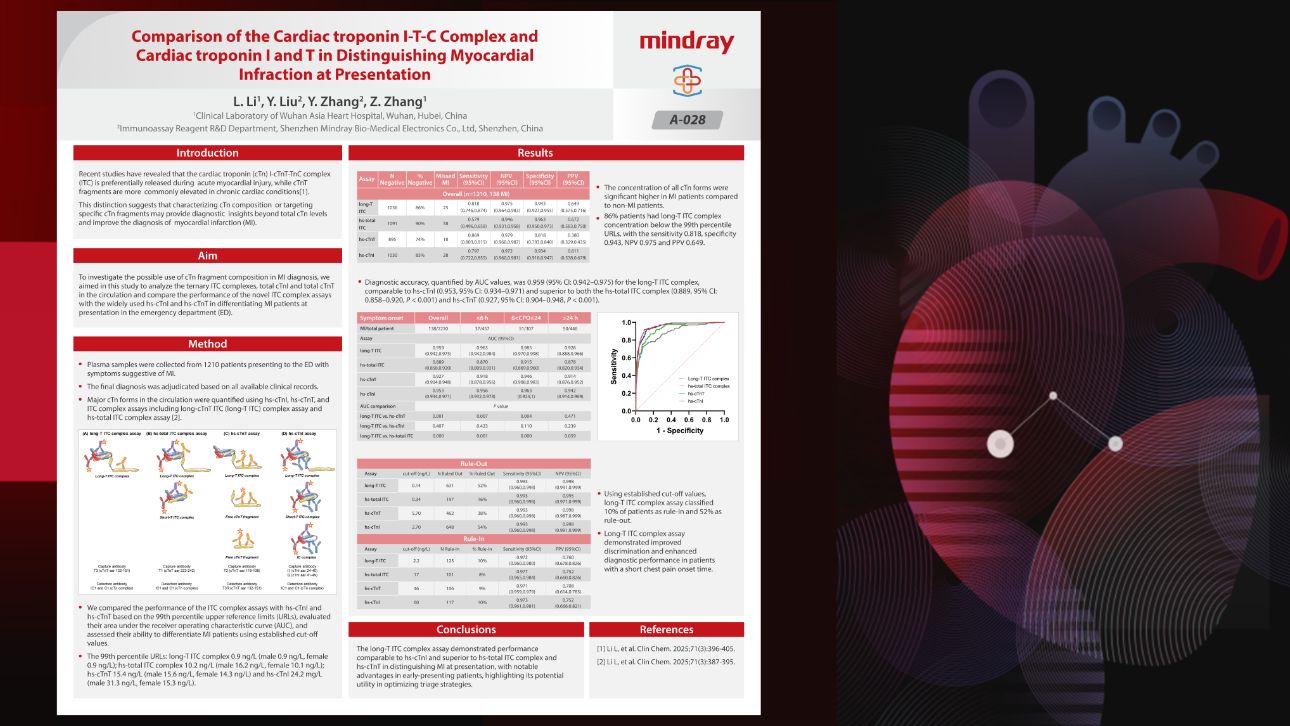
The paper "Comparison of the Cardiac troponin I-T-C Complex and Cardiac troponin I and T in Distinguishing Myocardial Infarction at Presentation" by Dr. Yi Zhang's team from Mindray received this honor. What's more, Mindray's award-winning research was among only 4 oral presentations at the conference.

Key Breakthrough: New Clinical Progress in Myocardial Research
In this presentation, Dr. Yi Zhang mainly shared the research results and clinical validation of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin.
The study confirmed that the Long-T ITC test has excellent diagnostic performance, with an AUC value of 0.959, which is comparable to hs-cTnI (AUC 0.953) and significantly better than hs-total ITC (AUC 0.889) and hs-cTnT (AUC 0.927). Based on a single test result, Long-T ITC can safely rule out 52% of patients (sensitivity 0.993, negative predictive value NPV 0.998), which is comparable to hs-cTnI. In patients who seek medical attention early after symptom onset, the Long-T ITC reagent shows stronger discrimination ability and better diagnostic performance. These findings provide key support for the early identification of acute myocardial infarction and a potential solution for optimizing emergency triage processes and achieving faster and more accurate risk stratification of acute myocardial infarction.