Ultrasound Journal 23 - Postoperative Ultrasound: A Case Study in Cardiovascular Pathology
2023-12-22
Special thanks to Dr. Ilya Borisovich Metelkov, Head of the Department of Functional Diagnostics of the Republican Cardiological Dispensary of the Ministry of Health of the Chuvash Republic.
Introduction
Ultrasound diagnostics of focal wall delamination in the area of bifurcation of the right common carotid artery with transition to the mouth of the right internal carotid artery (probably formed as a result of dissection) using HD-scope and V-flow technologies.
An example of ultrasound in the postoperative period in a patient with cardiovascular pathology.
Clinical Cases
Patient N. born in 1965 with the diagnosis: generalized atherosclerosis with lesions of the brachiocephalic arteries, arteries of the lower extremities. Condition after carotid endarterectomy in 2010 and 2011 on both sides.
Until 2021, an annual ultrasound examination and examination of a vascular surgeon took place. In 2022, he was not examined due to the COVID-19 pandemic. According to the data of past ultrasound, pathology in the field of surgical intervention was not detected.
In 2023, he came to the next ultrasound control.
Ultrasound was performed on the Resona 7 ultrasound machine (MINDRAY, China) with a linear L9-3U sensor in B-mode, CDK and PW mode, using HD scape and V-flow (Vector Flow) technologies. The following pathology was found in the area of bifurcation of the right common carotid and the mouth of the right internal carotid arteries.
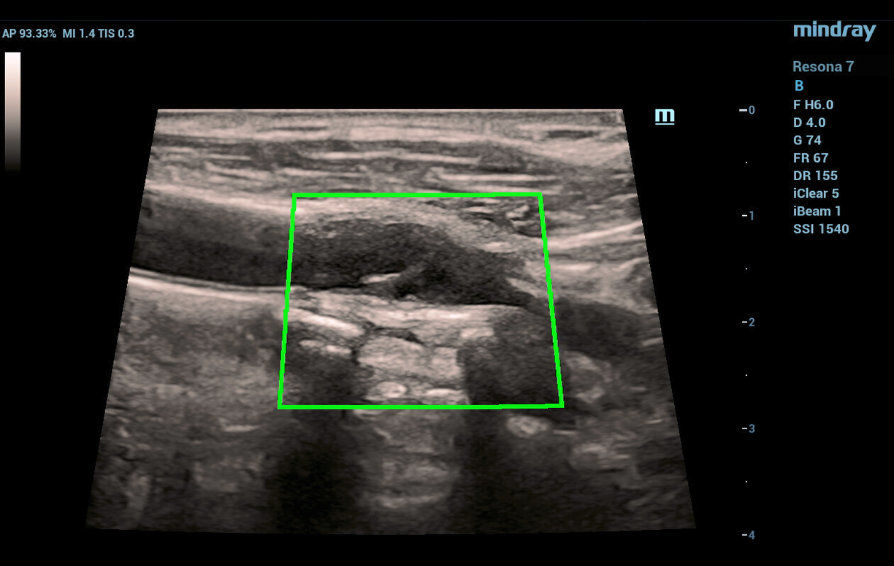
In the area of bifurcation of the right common carotid artery with a transition to the mouth of the internal carotid artery, a spiral-shaped formation of medium echogenicity with a thickness of 1.0 to 2.0 mm, linear in shape, sedentary, dividing the lumen of the mouth of the internal carotid artery into two sections with anterograde blood flow in one section and retrograde flow in the other. The approximate length of the formation is about 12 mm. Turbulence of the flow in the area of education is noted.
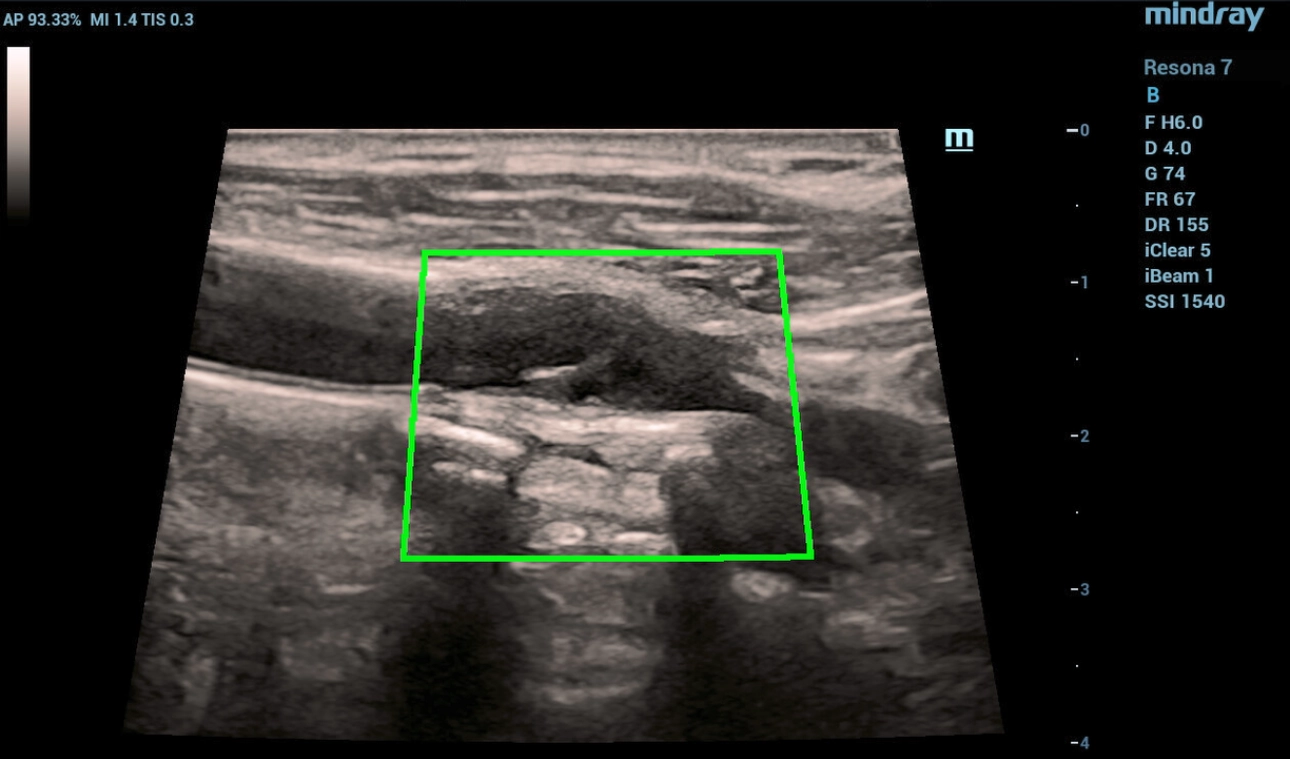
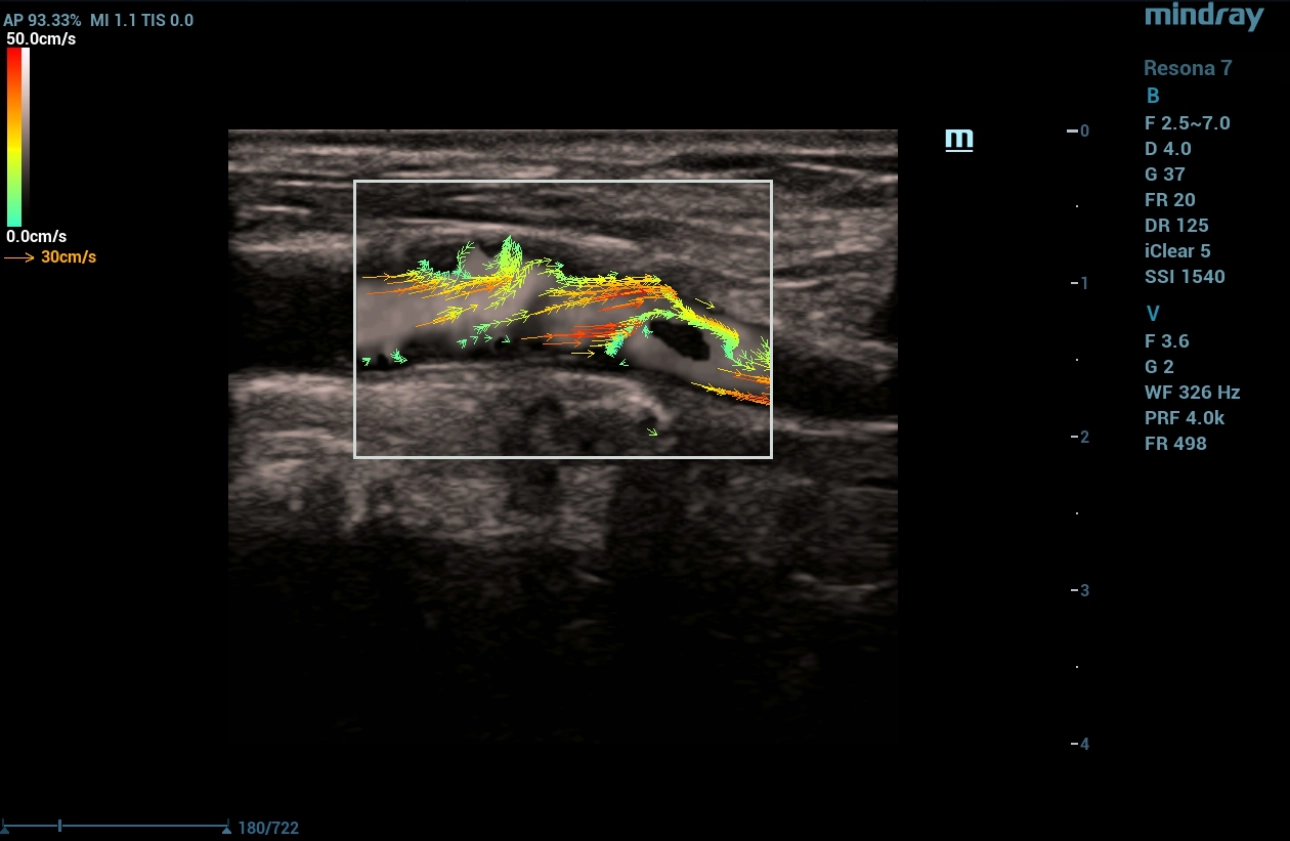
Fig. 1 Ultrasound of the carotid sinus in B-mode with HD Scope, which gives a clearer detail. From the level of bifurcation of the right common carotid artery with a transition to the mouth of the internal carotid artery, a diagonally (helically) located linear structure of average echogenicity with a thickness of 1.0 to 2.0 mm and a length of up to 12 mm.
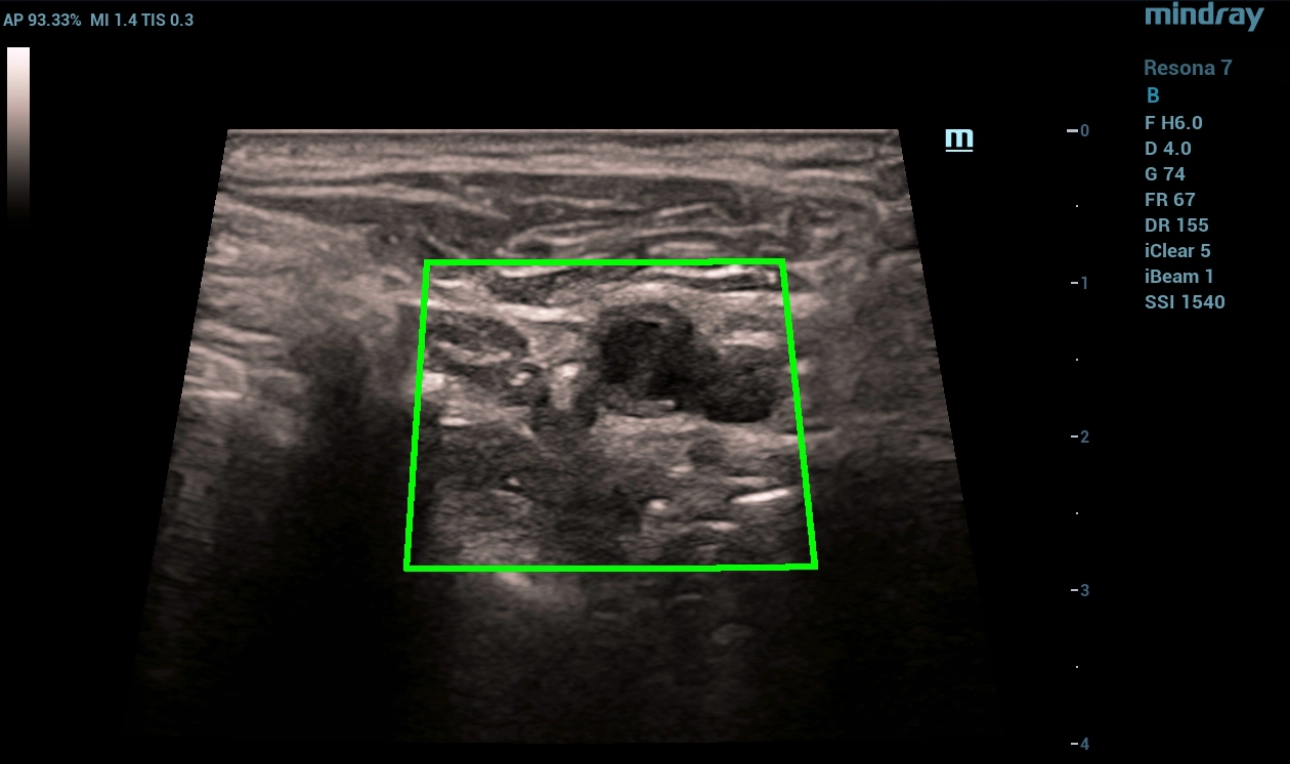
Fig. 2 B-mode using Hd Scape, the transition of the linear structure at the mouth of the internal carotid artery is visualized with the division of the lumen of the internal carotid artery into two channels.
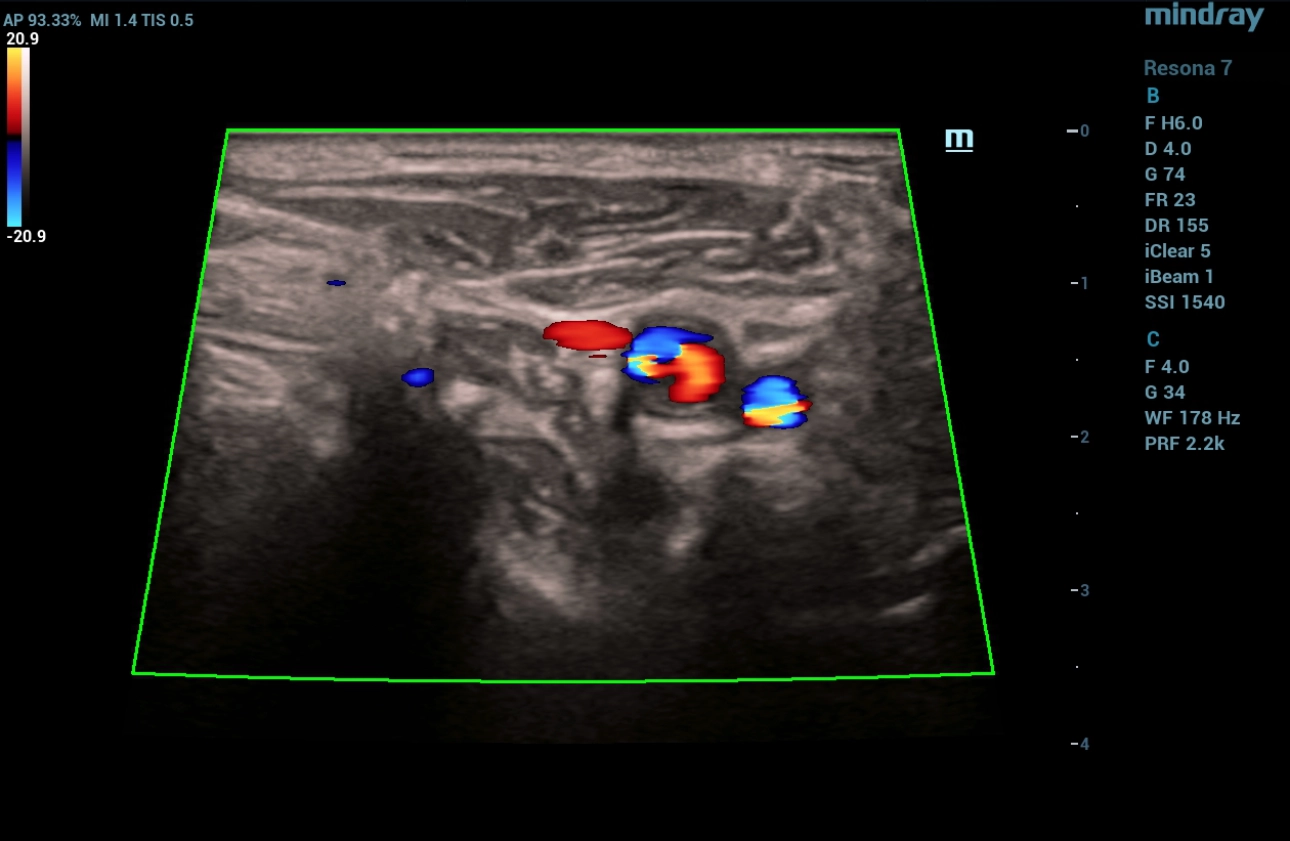
Fig. 3 In the mode of color Doppler mapping, two multidirectional flows are determined at the mouth of the right internal carotid artery (one antegrade flow, the other retrograde). Aliasing effect over the zone no changes were detected.
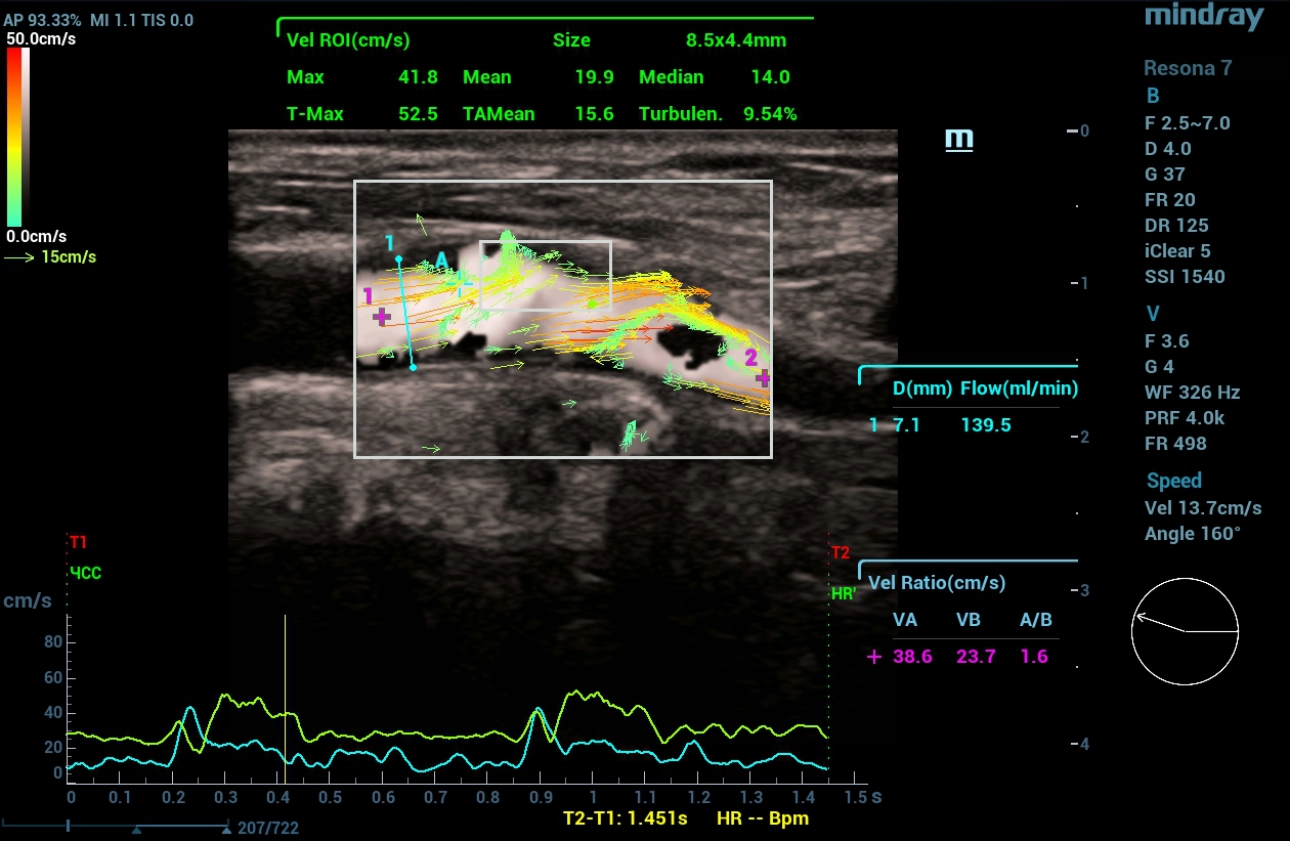
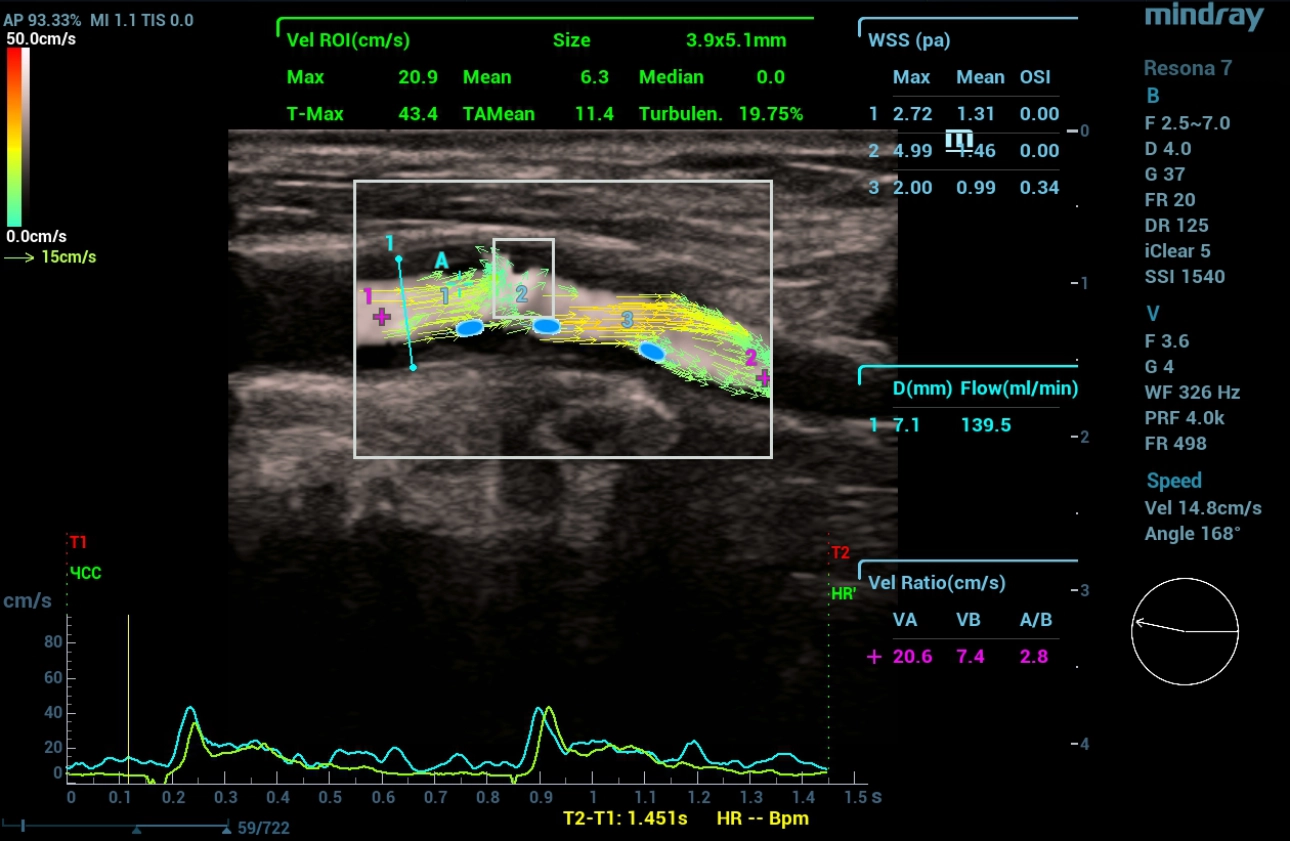
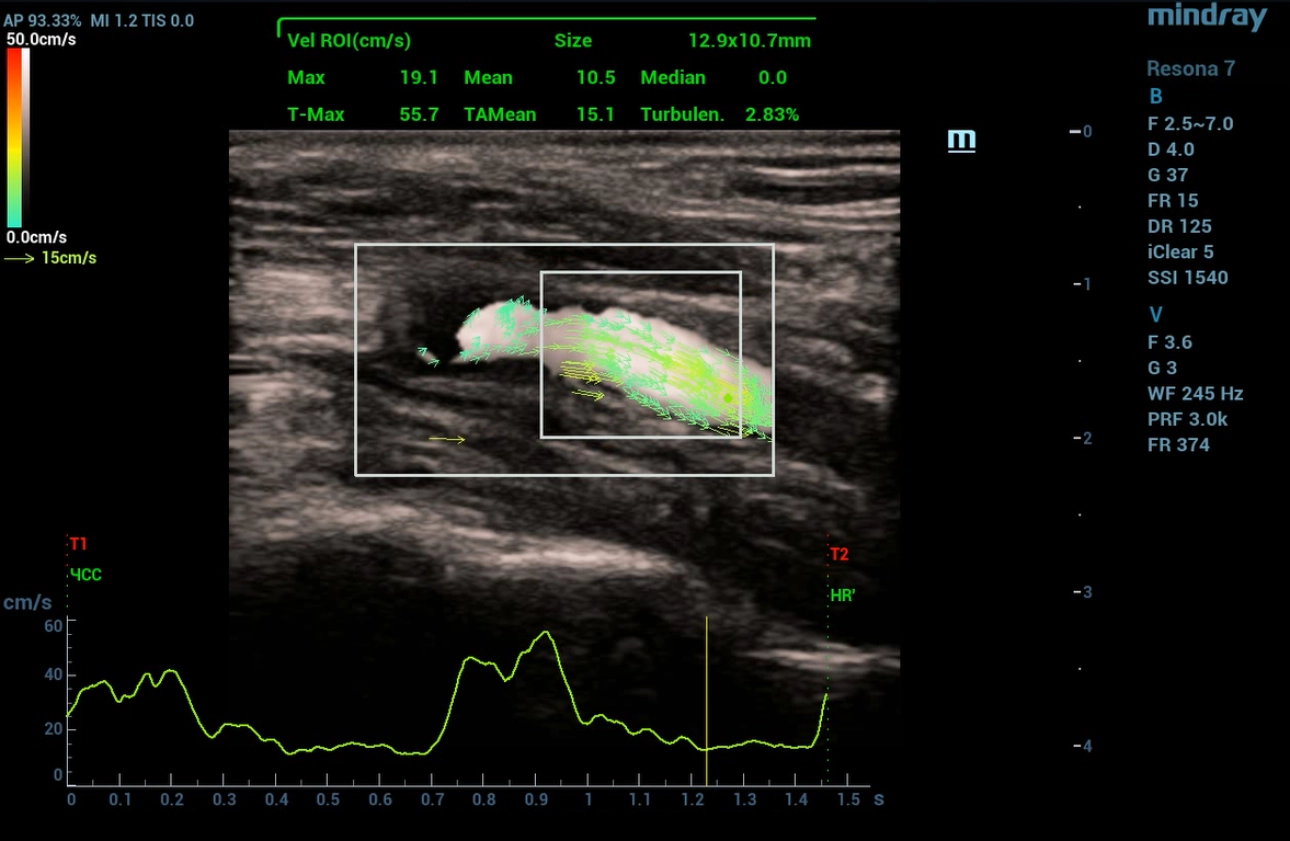
In Figures 4,5,6,7 Ultrasound examination in the mode of vector analysis of blood flow (V Flow).
When the vector analysis mode (V Flow) was activated, a change in the direction of blood flow was clearly traced in front of the linear structure and at the mouth of the internal carotid artery, where the flow had a multidirectional, vortical direction. Behind the linear structure, the flow movement was unidirectional (laminar flow). Turbulence index indices in the carotid sinus area 9.54% in the linear structure area 19.75%, distal to the mouth of the internal carotid artery 0.84%. To clarify the changes detected on ultrasound, the patient underwent computed tomography (CT) angiography of extracranial arteries with intravenous contrast.
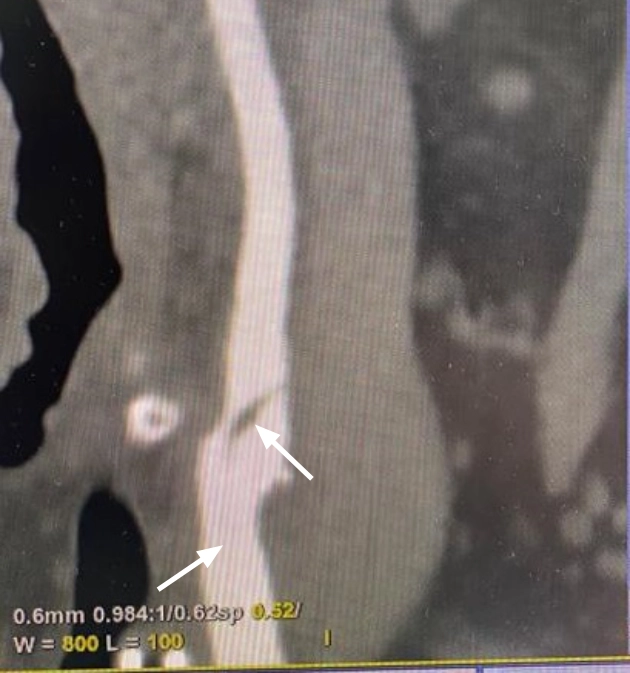
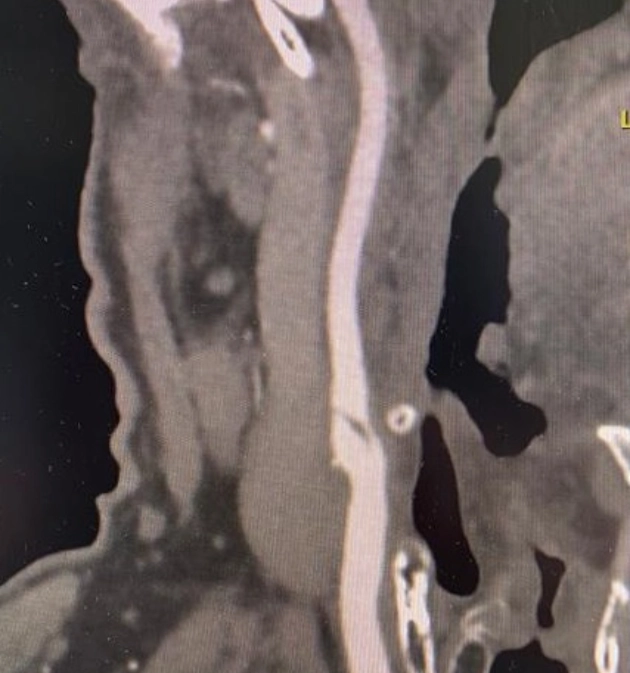
In images 8-9, Computed tomography data: In the area of bifurcation of the right common carotid artery with a transition to the mouth of the internal carotid artery, there is a double lumen of the artery (true and false) for at least 14 mm, then the lumen of the internal carotid artery is filled with a contrast agent without signs of significant stenosis.
Conclusion
Condition after carotid endarterectomy. The CT picture does not exclude focal delamination of the wall in the area of bifurcation of the right common carotid artery with a transition to the mouth of the right internal carotid artery (probably formed as a result of dissection). [1]
According to ultrasound data, using HD-scope and V-flow technologies, a linear structure was revealed in the bifurcation of the right common carotid artery with a transition to the mouth of the internal carotid artery with the division of the lumen into two sections, which could be a sign of intimal detachment and suggest dissection. HD-scope technology made it possible to clearly visualize this formation, its size and insignificant mobility (by the type of flotation).
In the mode of color Doppler mapping, a multidirectional blood flow was determined at the mouth of the internal carotid artery. The V Flow mode made it possible to visually assess the vortex-like and retrograde direction of blood flow in the vessel, as well as the flow rate in this area of interest. An increase in the turbulence index in area of education.
The results of the CT examination confirmed the ultrasound conclusion that the patient has focal wall delamination in area of bifurcation of the right common carotid artery with a transition to the mouth of the right internal carotid artery (probably formed as a result of dissection). [2,3]
References:
[1] Caplan LR. Dissections of brain-supplying arteries. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2008 Jan;4(1):34-42. [PubMed]
[2] Blum CA, Yaghi S. Cervical Artery Dissection: A Review of the Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Outcome. Arch Neurosci. 2015 Oct;2(4) [PMC free article] [PubMed]
[3] Steven D. Goodfriend; Prasanna Tadi; Ron Koury. Carotid Artery Dissection. NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430835/