Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite that infects most species of warm-blooded animals, including humans, and causes toxoplasmosis.
Toxoplasmosis usually occurs after eating undercooked contaminated meat, exposure to infected cat feces, or mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy[1].
Besides pregnant women and infants, AIDS patients and organ transplant recipients are also vulnerable to Toxoplasma gondii.
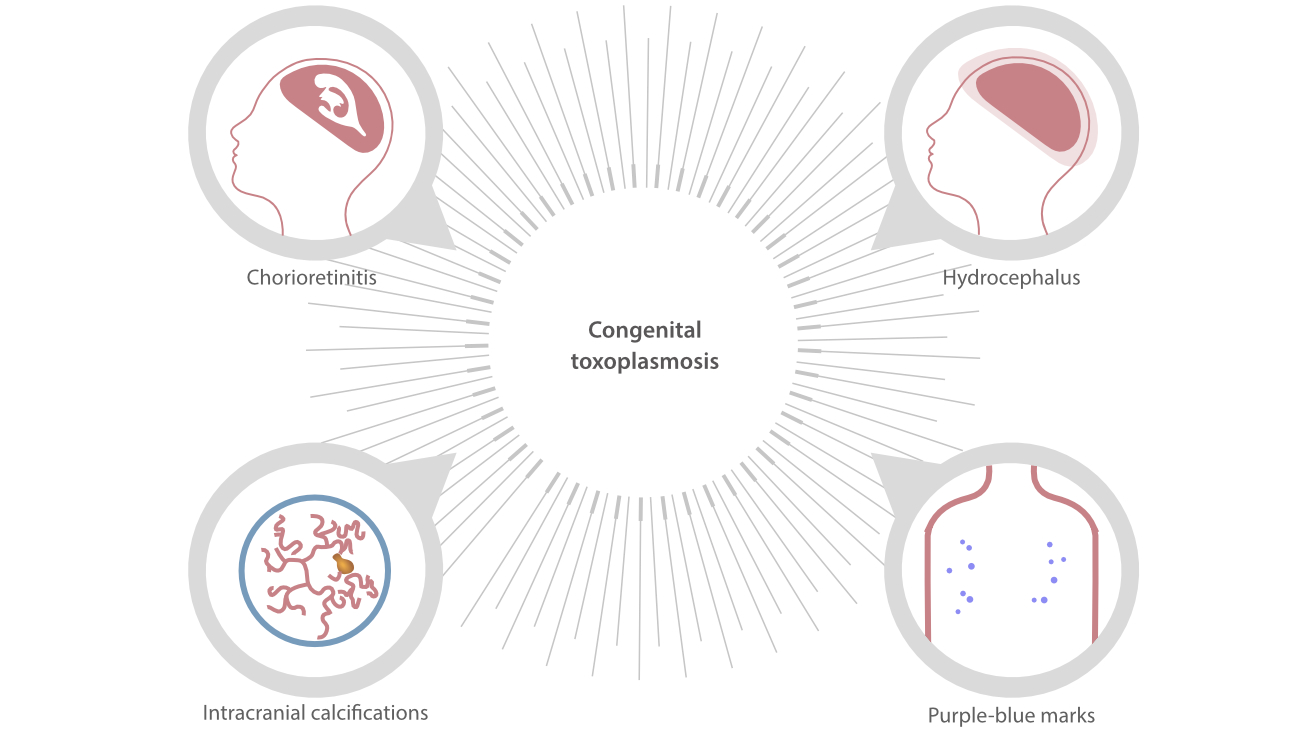
The most common manifestations of congenital toxoplasmosis include chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, and intracranial calcifications. Some babies with congenital toxoplasmosis may exhibit multiple purple-blue marks in the skin.
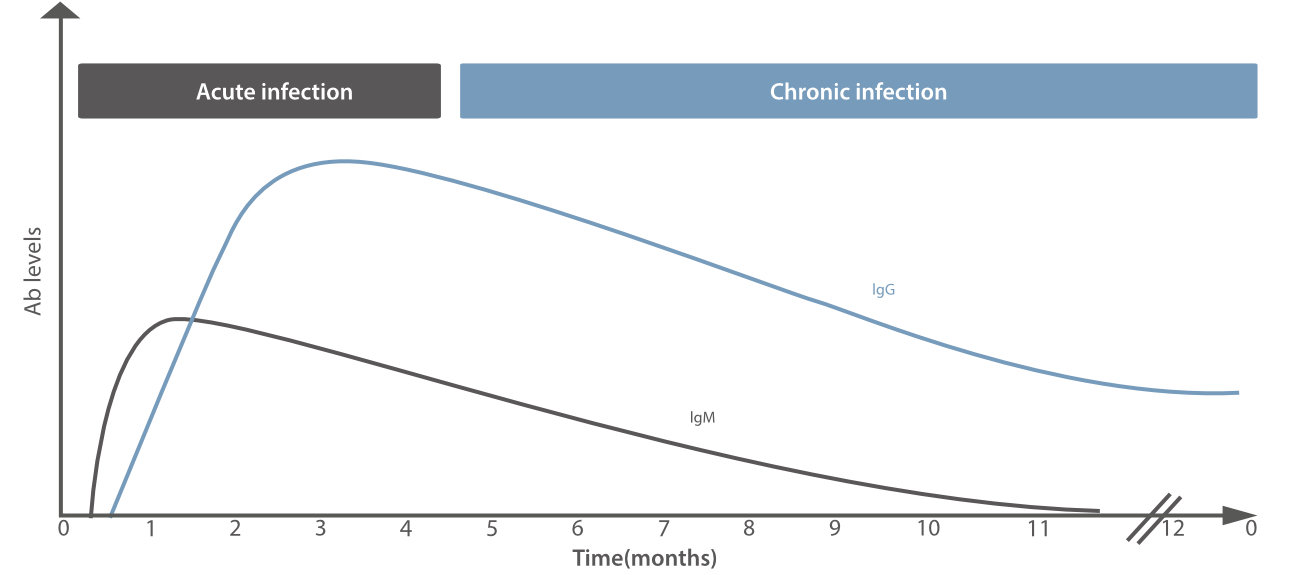
According to CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention), the detection of
Toxoplasma-specific antibodies is a primary diagnostic method to determine infection with Toxoplasma. Newborn infants suspected of congenital toxoplasmosis should be tested by both IgM- and IgA-capture EIA. Also, this detection is recommended for immunocompromised patients, such as AIDS patients[2].
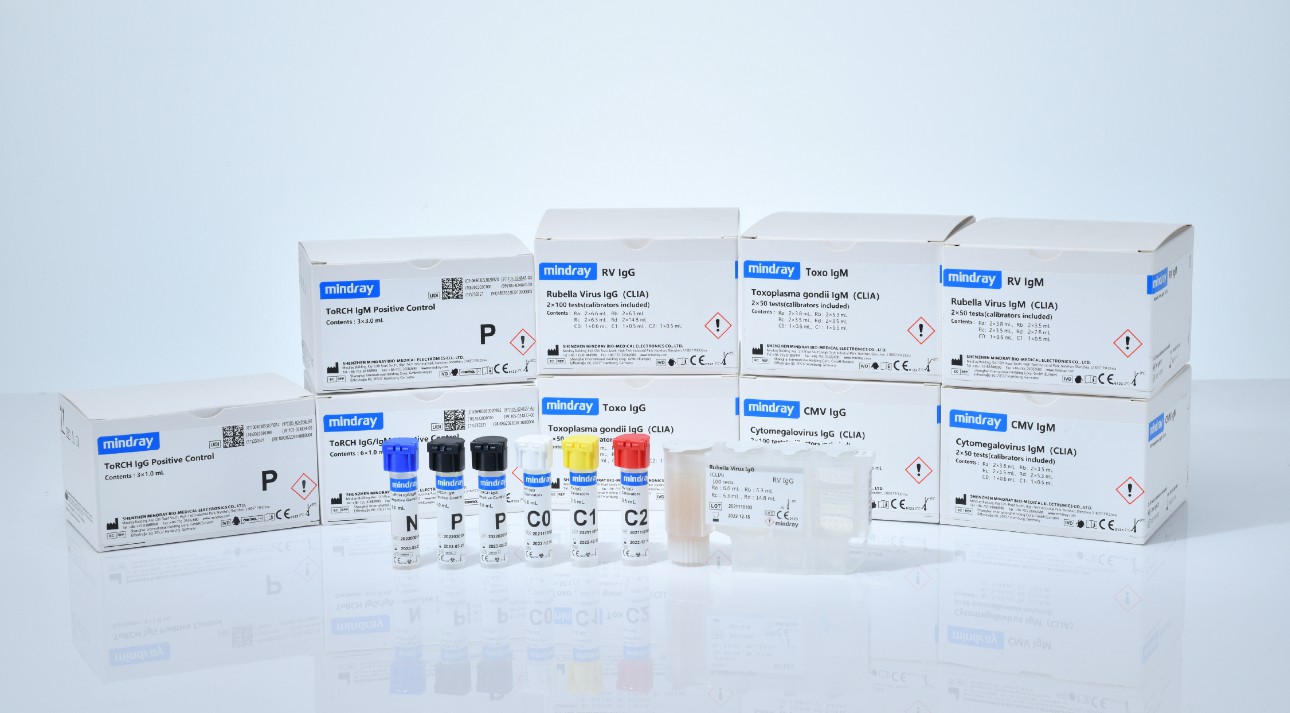
As part of Mindray’s efforts to make healthcare within reach, Mindray has developed reliable ToRCH serological tests with high sensitivity and specificity for our customers. In the meantime, Mindray ToRCH panel has just received CE IVDR certification, which means it's commercially available in the European market.
References
1. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ toxoplasmosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20356249
2. https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/toxoplasmosis/index.html
3. Teimouri, A. , et al. "Role of Toxoplasma gondii IgG avidity testing in discriminating between acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in pregnancy." Journal of Clinical Microbiology (2020).


