An infection is defined as “a pathologic process caused by the invasion of pathogenic or potentially pathogenic microorganisms into normally sterile tissues or fluids or body cavities”. Infections can occur in people of all ages and around the globe. However, the signs of infection are not always obvious. Inappropriate treatment may lead to sepsis, or even death [1-2].
According to statistics, there are approximately 19 million new cases of sepsis each year, with 6 million deaths (more than 1/4 of the total sepsis population); among the survivors, approximately 3 million have experienced serious complications (approximately 1/6 of the total sepsis population)
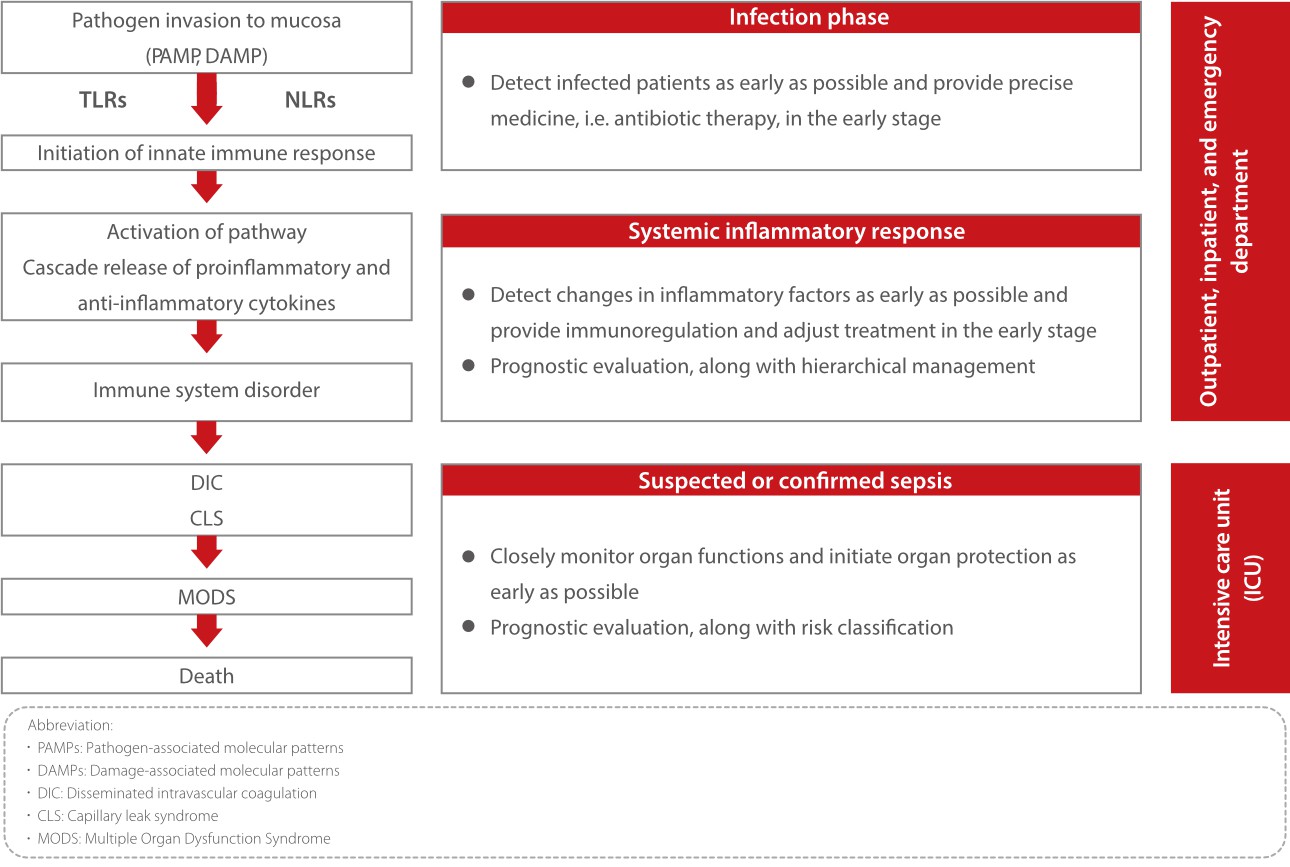
The requirements on infection and inflammation management vary with the clinical situations and stages.
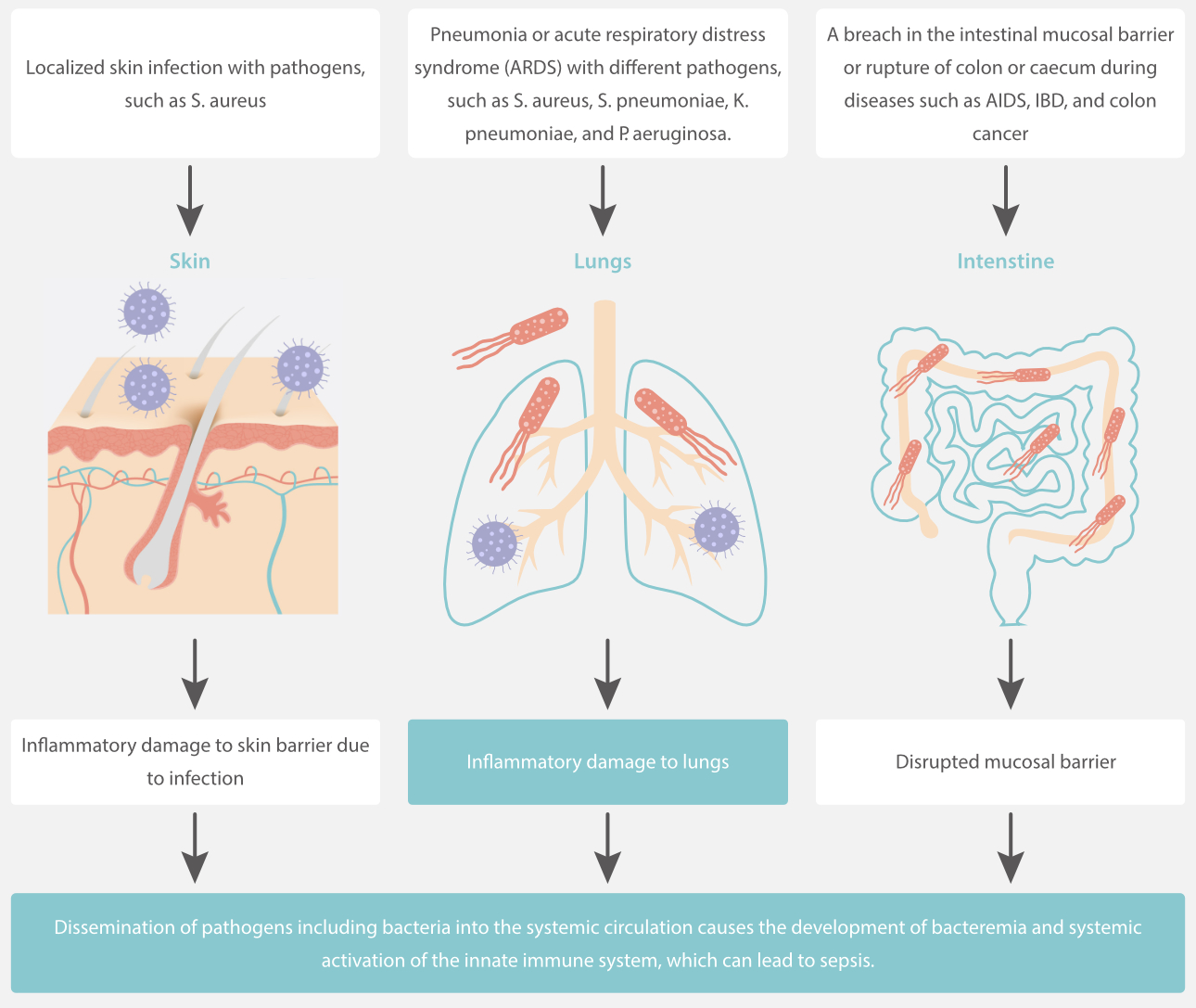
Based on the different physio pathological processes of infection, many biomarkers have been developed and widely used. These biomarkers are expected to have high sensitivity and specificity to help monitor treatment results and assess the prognosis.
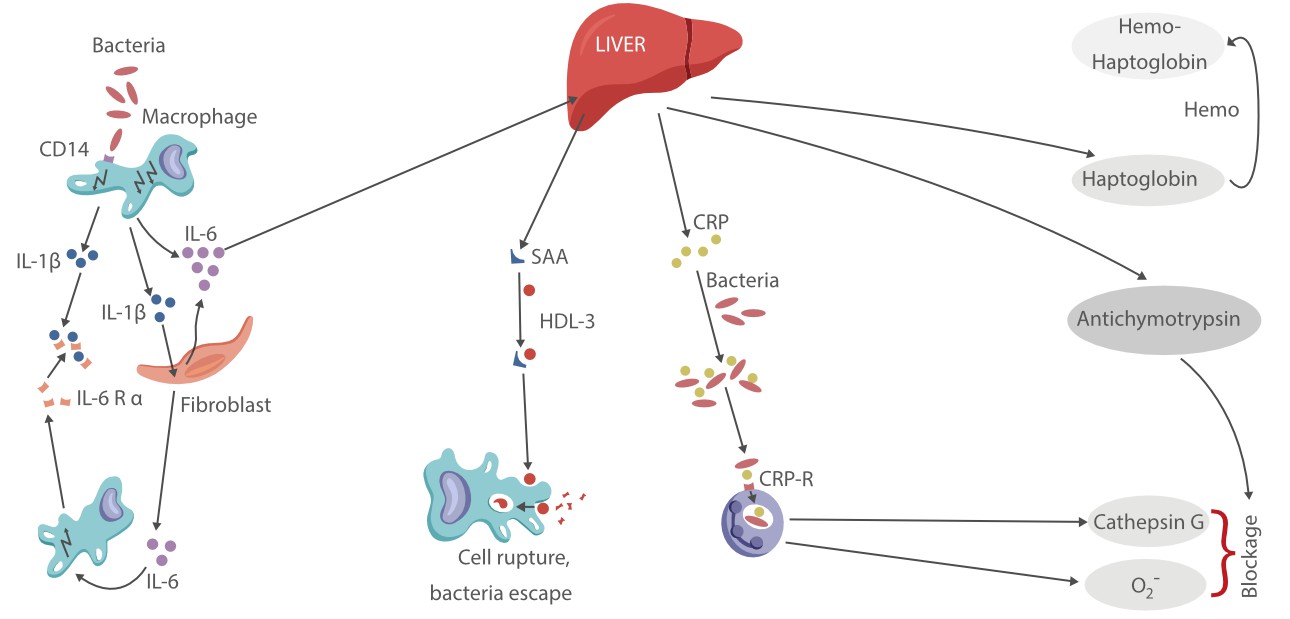
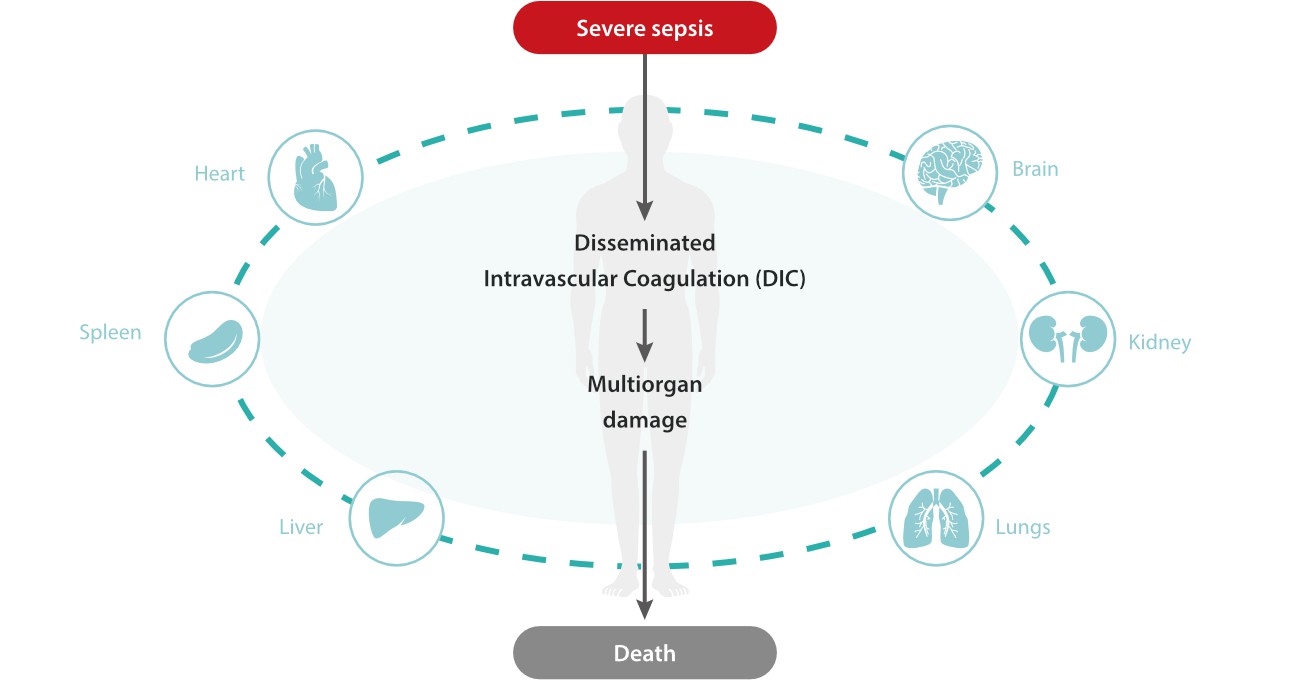
However, conventional inflammatory biomarkers do not provide sufficient diagnostic efficiency. This means the clinical feedback based on them would mislead instructions and in turn causes a delay in both prognostic evaluation and therapy adjustment, posing potential risks to the patient's life.
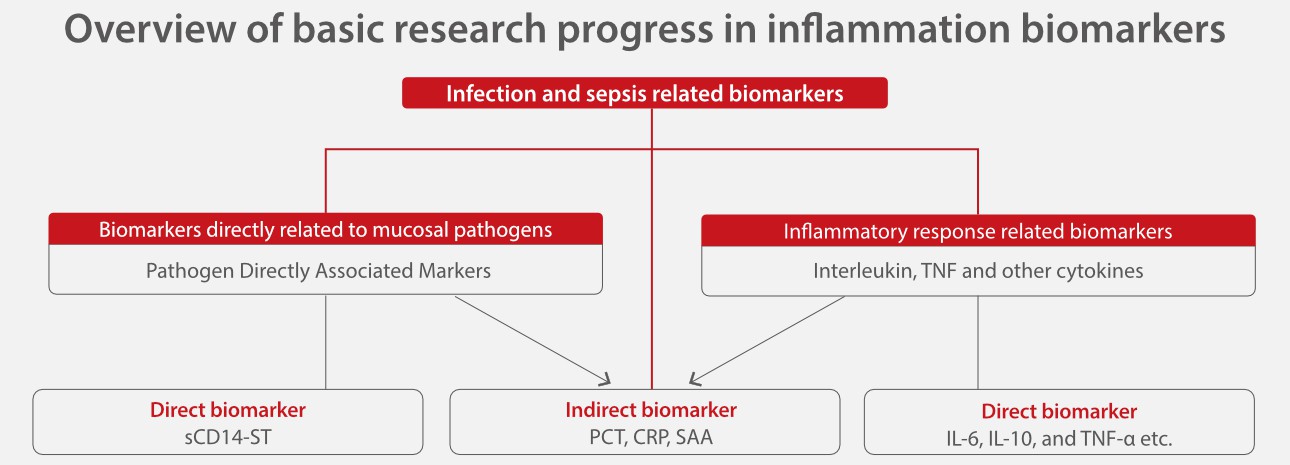
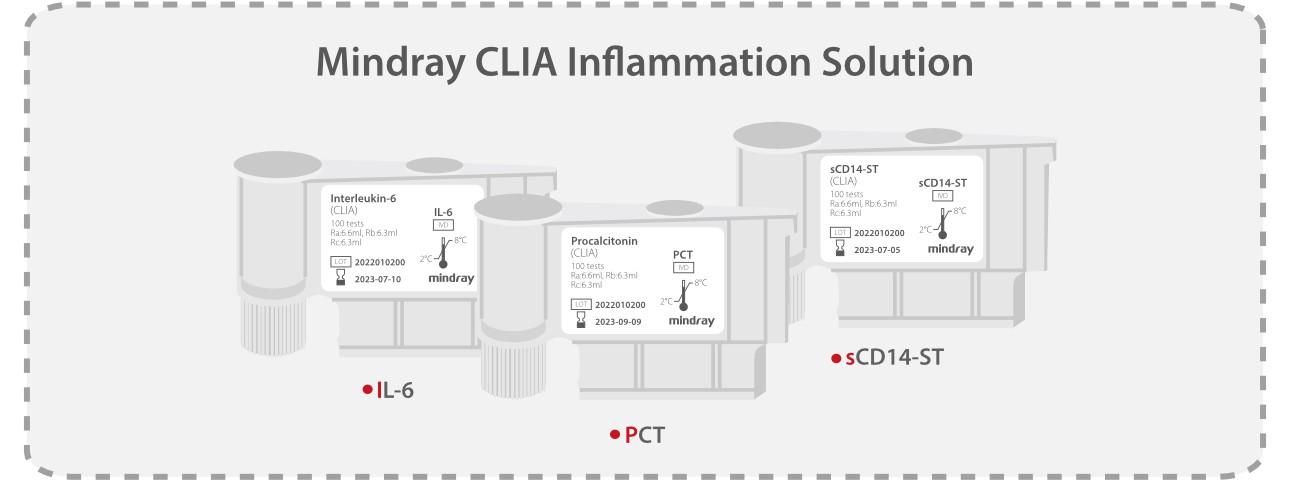
sCD14-ST, IL-6 and PCT each have their advantages and drawbacks and they can compensate for each other.
All the three parameters are developed based on the sandwich immunoassay method, each with a turn-around time (TAT) of 18 mins.
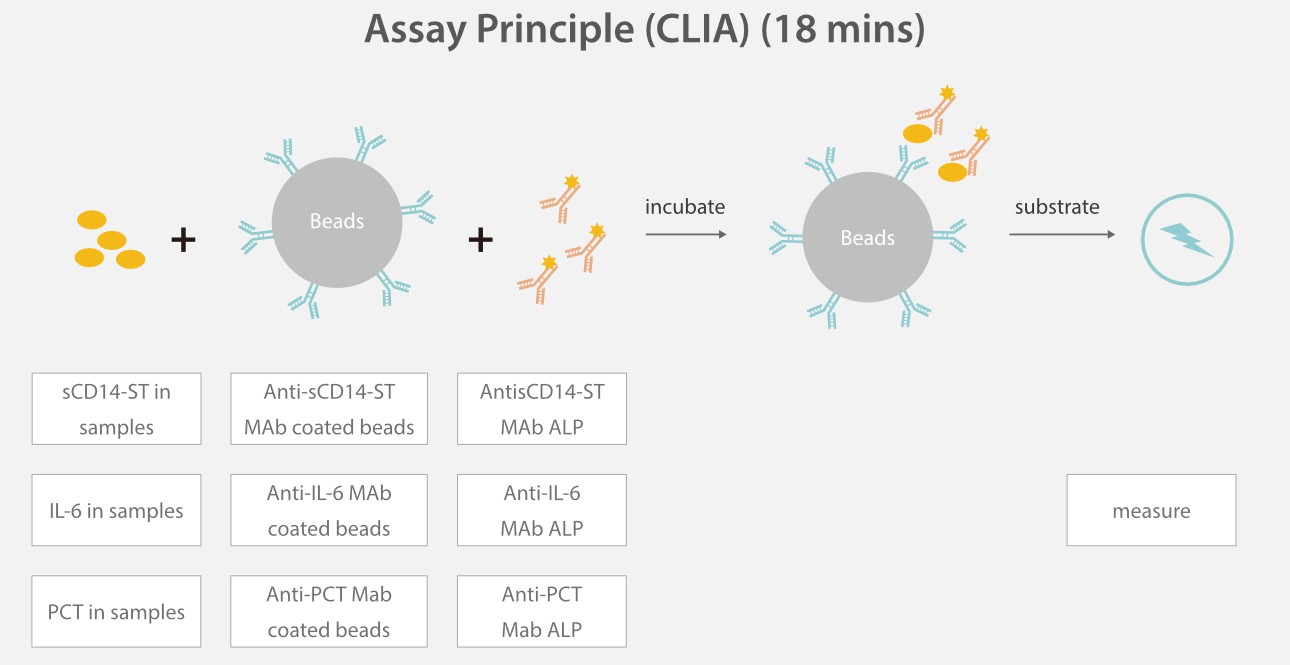
Based on Mindray's CLIA platform, the the inflammation panel is well designed and comprehensively evaluated. All the three assays have high sensitivity, great precision, a wide linearity range, and a good anti-interference ability.
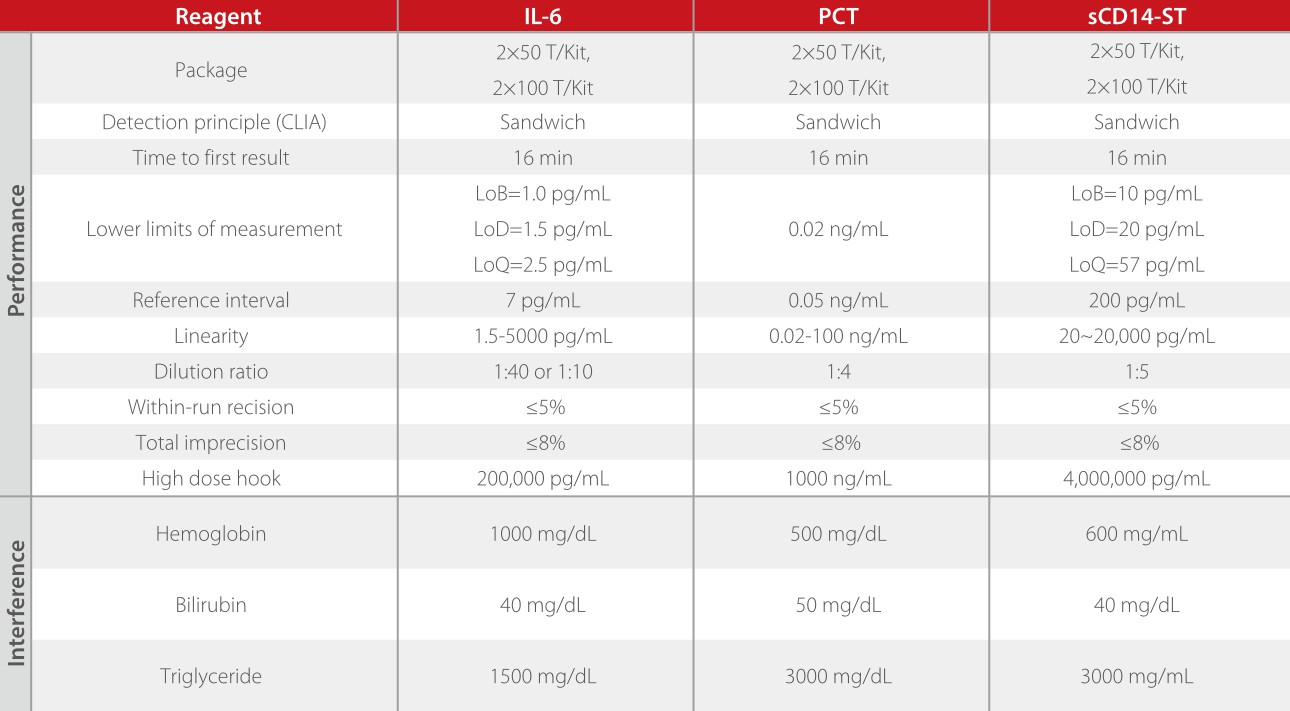
In summary, Mindray's inflammation panel is well designed and developed to provide a comprehensive solution for different clinical settings. Dedicated to advancing academic research and technological development, we will continue to provide high-quality products and solutions that can meet various clinical needs.

References
[1] Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D,Cook D et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med. 2003;31: 1250–1256.
[2] Vincent JL. The Clinical Challenge of Sepsis Identification and Monitoring. PLoS Med. 2016 May 17;13(5):e1002022.
[3] https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S178084
[4] https://www.rndsystems.com/cn/resources/articles/interleukin-6







