Infection is common in people of all ages and around the globe. However, the signs of infection are not always noticeable and differentiating them accurately can be a challenge.

To address the rising burden of infectious disease on hospitals, Mindray has developed sCD14-ST, a biomarker that is sensitive and accurate for the detection of infection.
sCD14-ST, a soluble subtype of CD14, is a glycoprotein fragment derived from monocytes and macrophages. It is a biomarker indicating the activation of innate immune cell response to an invading pathogen [1-3].

As a result of such response, CD14 will be expressed on the surface of various immune cells. CD14 then binds to the LPS/LBP complex and activates TLR4. Then, it initiates innate immune response to infectious agents. After that, sCD14 is cleaved by cathepsin D and other proteases. The N-terminal fragments of CD14 are released and sCD14-ST is formed [1-3].
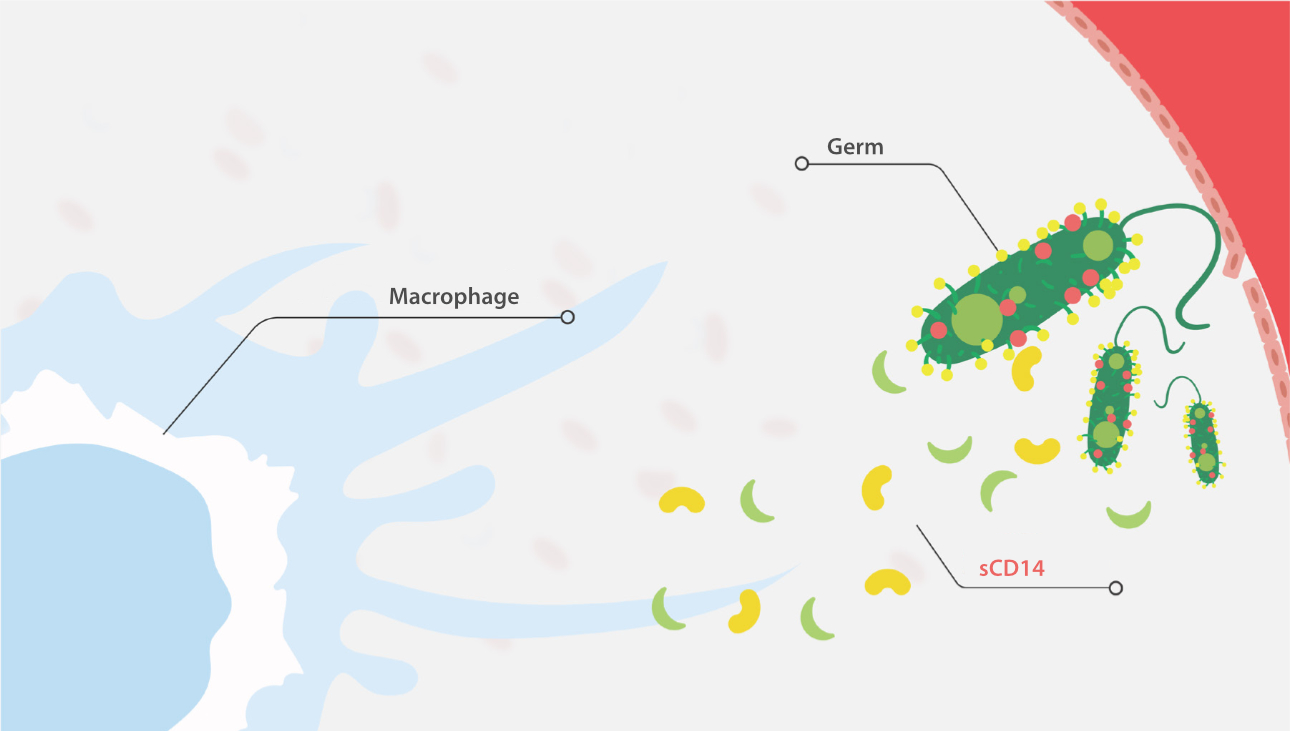
Compared to PCT induced by cytokines after bacterial phagocytosis, sCD14-ST is a more direct infectious biomarker, which is mediated by pathogens [1-2].

Pathological studies and clinical trials have revealed that sCD14-ST is important for the clinical management of infectious diseases or related conditions, such as neonatal sepsis, prosthetic joint infection (PJI), febrile neutropenia (FN), sepsis, and early infection in trauma.

sCD14-ST shows high specificity and sensitivity for some special scenarios such as prosthetic joint infection (PJI) and febrile neutropenia (FN) for which there is always a lack of ideal diagnostic methods.
Prosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a tremendous burden for individual patients as well as the global health care industry [4]. The nature of implant-related infections is complex. Currently, there is no definitive test for PJI and its diagnosis remains challenging despite recent developments [5]. While a small minority of joint arthroplasties will become infected, appropriate recognition and management are critical to preserve or restore adequate function and prevent excess morbidity [4].

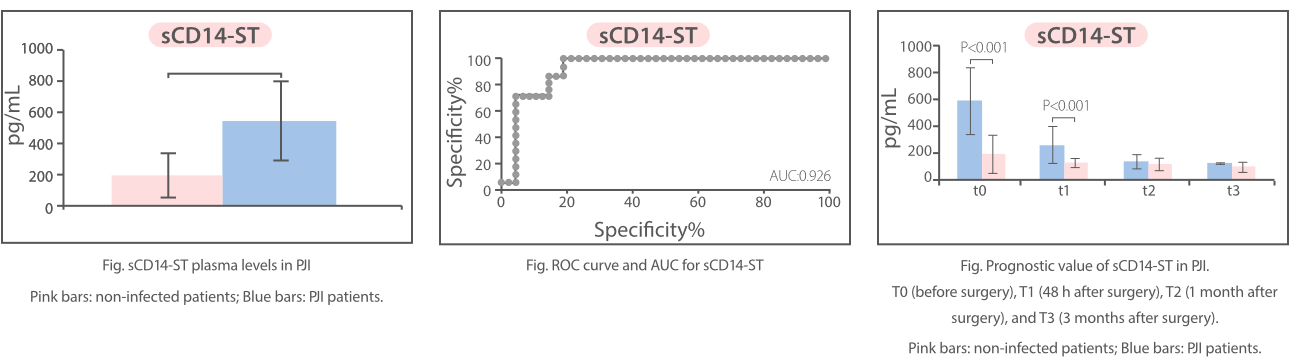
sCD14-ST is found to be a potential inflammation biomarker for PJI diagnosis and prognosis. Research has revealed that its level is significantly higher in PJI patients than controls. In PJI patients after surgery, the sCD14-ST level is significantly higher, which means a longer recovery time; in non-infected patients, however, the sCD14-ST level is significantly lower [6].
Febrile neutropenia (FN) is the most common life-threatening complication of cancer therapy. It is defined as a single oral temperature measurement of >101°F (>38.3°C) or a temperature of ≥100.4°F (≥38.0°C) sustained over 1 hour, with an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of <500 cells/microliter, or an ANC that is expected to decrease to <500 cells/microliter over the next 48 hours [7].
Traditional methods such as liver function tests and blood cultures for bacteria can be used to support the first investigation of FN, but they all have some drawbacks.

From researches, sCD14-ST is considered to be an early diagnostic marker of FN in hematologic malignancy patients. According to studies on FN cases, the sCD14-ST level elevates one day prior to CRP. Plasma sCD14-ST level is a reliable marker of FN even in extremely low WBC counts. Besides, evaluation of sCD14-ST level increase helps with the early diagnosis of FN in both myeloid and lymphoid disorders. Close monitoring of this molecule could prevent infection-associated deaths in hematologic malignancy cases [8].

In such special scenarios, sCD14-ST can be used as a novel biomarker for disease management.
In series 2, we will introduce more clinical applications of sCD14-ST in other commonly seen diseases such as sepsis and bacterial infection.
If you have interest in this inflammation biomarker, please register to watch Mindray IPS (IL-6, PCT and sCD14-ST) online launch event on 1st December, 2022: https://www.mindray.com/en/events/webinar-on-il-6-scd14-st
References
[1] Bas S, Gauthier B R, Spenato U, et al. CD14 is an acute-phase protein[J]. J Immunol, 2004, 172(7): 4470-9.
[2] Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity[J]. Immunity, 2011, 34(5): 637-50
[3] "Presepsin (sCD14-ST), an innate immune response marker in sepsis." Clinica Chimica Acta 450(2015):97-103.
[4] Aaron J. Tandea, and Robin Patelcorresponding authora,b, Prosthetic Joint Infection, Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014 Apr; 27(2): 302–345. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00111-13
[5] Seung-Ju Kim, MD, PhDcorresponding author and Yun Jae Cho, MD, Current Guideline for Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Review Article. Hip Pelvis.2021 Mar; 33(1): 11–17. 2021 Mar 2. doi: 10.5371/hp.2021.33.1.11
[6] Monica Gioia Marazzi, et al. Presepsin: A potential biomarker of PJI.A comparative analysis with known and new infection biomarkers. DOI: 10.1177/0394632017749356
[7] https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-us/950
[8] Koizumi et al. Plasma presepsin level is an early diagnostic marker of severe febrile neutropenia in hematologic malignancy patients.BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:27