Understanding AIDS
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is the most severe phase of infection caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). HIV impairs the immune system by targeting white blood cells, leading to an increased risk of diseases, such as tuberculosis, infections, and certain types of cancer. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines Advanced HIV Disease (AHD) as having a CD4 cell count of less than 200 cells/mm3 or being at WHO stage 3 or 4 for adults and adolescents. All HIV-positive children under the age of 5 are deemed to have AHD[1].
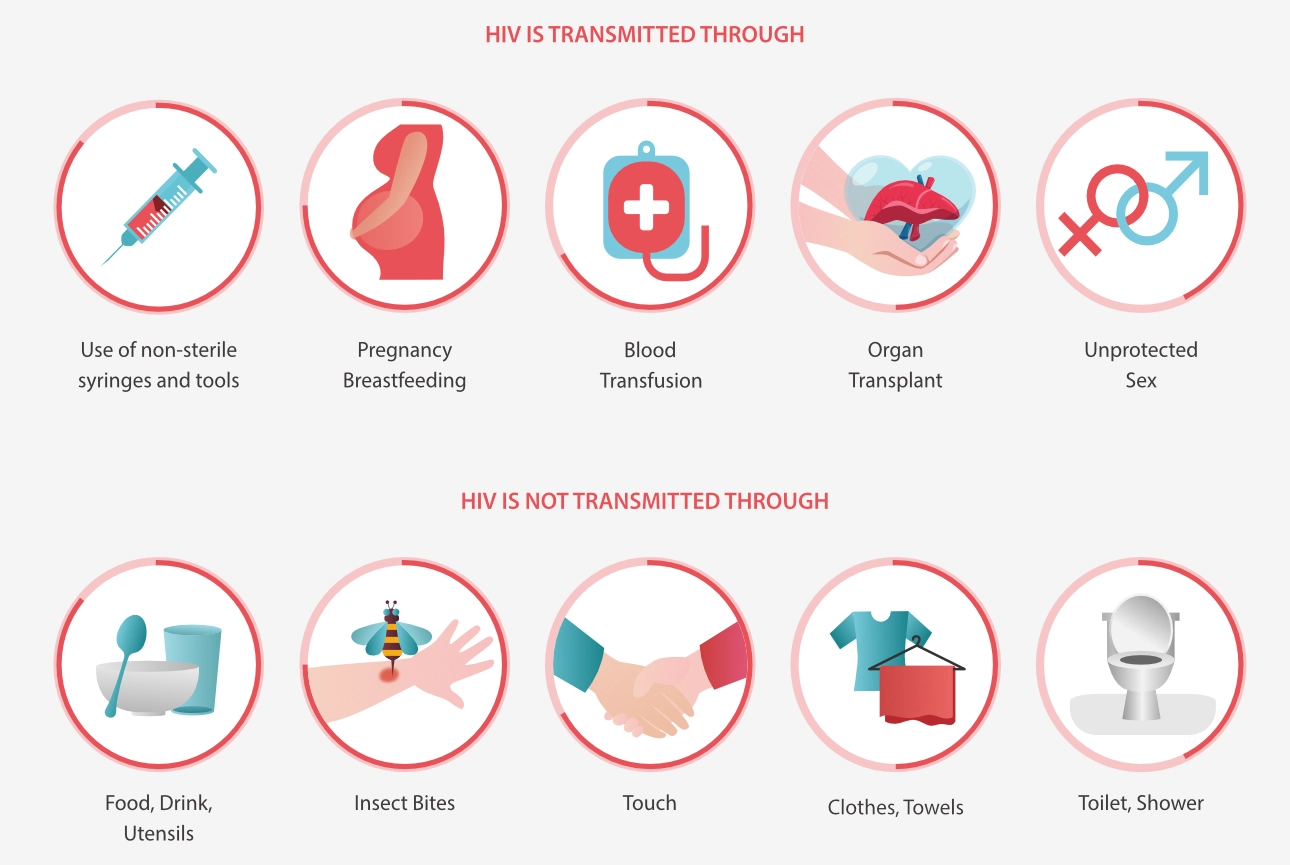
Transmission Pathways of HIV
HIV spreads via the body fluids of an infected individual, including blood, breast milk, semen, and vaginal fluids. It is not transmitted through casual contact such as kissing, hugging, or sharing meals. However, it can be transferred from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding. The virus is most commonly contracted through unprotected sexual intercourse and the sharing of needles or syringes associated with drug use.
Global HIV Prevalence
As of the end of 2022, there were approximately 39.0 million [33.1–45.7 million] individuals living with HIV worldwide, with two-thirds (25.6 million) of this population residing in the African Region (according to WHO data).
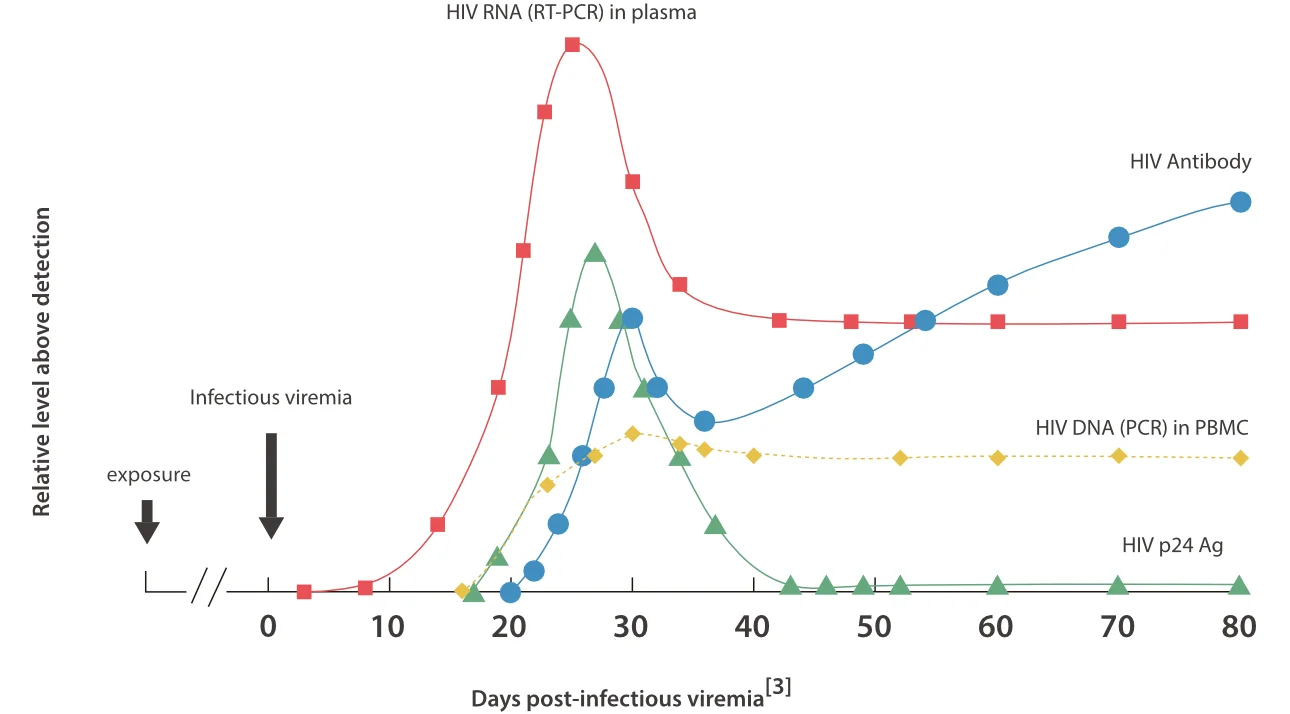
HIV Infection and Detection Biomarkers
Two strains of HIV have been identified: HIV-1, which is the more aggressive and the primary cause of global infections; and HIV-2, which is mainly confined to West Africa. After exposure to HIV, it takes 1–2 weeks for the virus to replicate in the mucosa/lymphoid tissue before entering circulation, with no biomarkers detectable during this initial phase. RNA assays can detect the initial viremia as early as 10 days after infection, while P24 antigen or DNA assays may yield positive results 15 days after infection, and antibodies are detectable 20–30 days after infection [2].
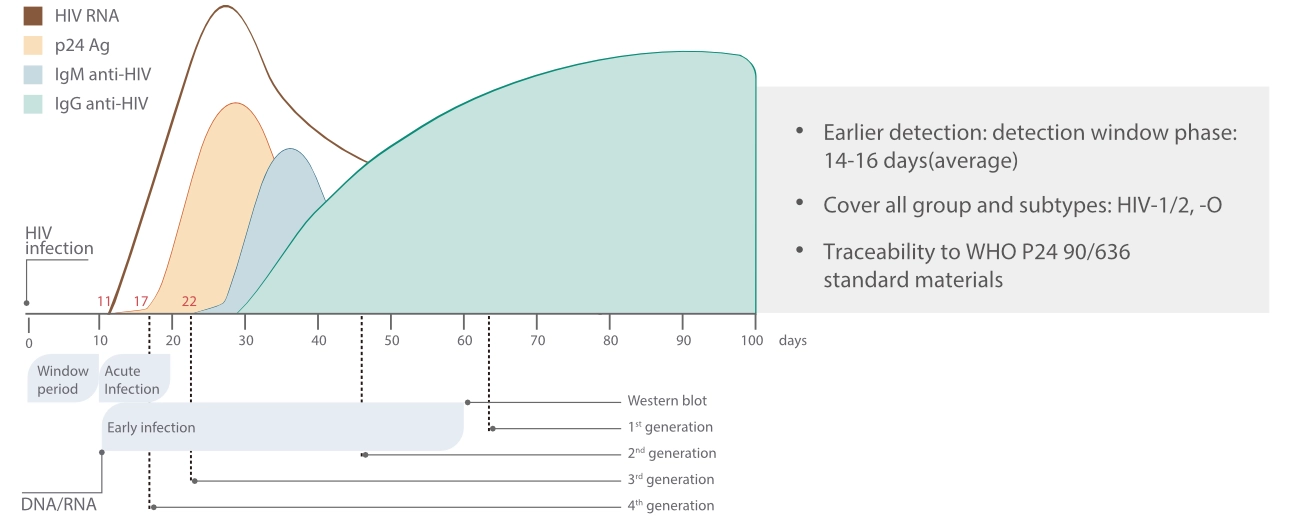
Evolution of HIV Testing Technologies
1st-generation HIV antibody tests:
- Detect only the IgG anti-HIV-1;
- Detection window phase of 12 weeks or more;
2nd and 3rd-generation HIV tests:
- Uses recombinant antigens, specifically HIV-1 p24;
- Can identify both HIV-2 and HIV-1 group O antibodies;
- Shorten the detection window phase to 4–6 weeks;
- Third-generation HIV tests include IgM detection, reducing the detection window phase to 3 weeks. Additionally, the p24 antigen detection ELISA can detect the virus as early as 2 weeks after infection.
4th-generation HIV tests:
- Integrated detection of both antibodies and antigens, covering P24 antigen and HIV-1/2 antibodies;
- Further reduce the window period to approximately 2 weeks;
- Provide a unified test result, not distinguishing between the presence of HIV-1 p24 antigen and HIV-1/2 antibodies.
Mindray 4th-Generation HIV Test
- Detection window phase of 14-16 days;
- Traceability to WHO P24 90/636 standard materials;
- Received CE List A Certificate.
References
[1] HIV and AIDS (who.int)
[2] Busch MP, Satten GA. Time course of viremia and antibody seroconversion following human immunodeficiency virus exposure. Am J Med. 1997 May 19;102(5B):117-24; discussion 125-6. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(97)00077-6. PMID: 9845513.2
[3] https://depts.washington.edu/uwviro/hiv-diagnostic-and-mol ecular-testing/







