Prevalence
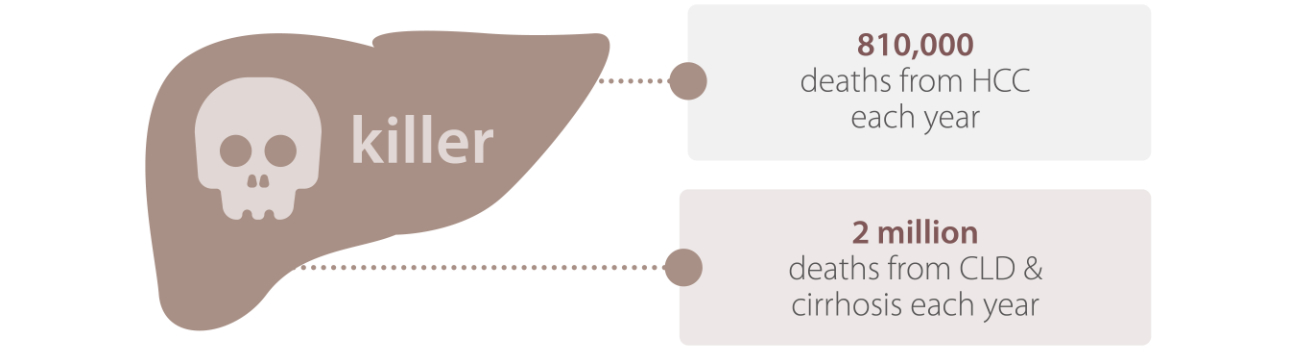
Globally, chronic liver disease (CLD) and cirrhosis accounts for 2 million deaths each year. In addition, there are estimated 810,000 incidents of liver cancer-related deaths worldwide. Patients with cirrhosis from any etiology are at high risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). These diseases have increased the global burden and health costs.
Common etiologies
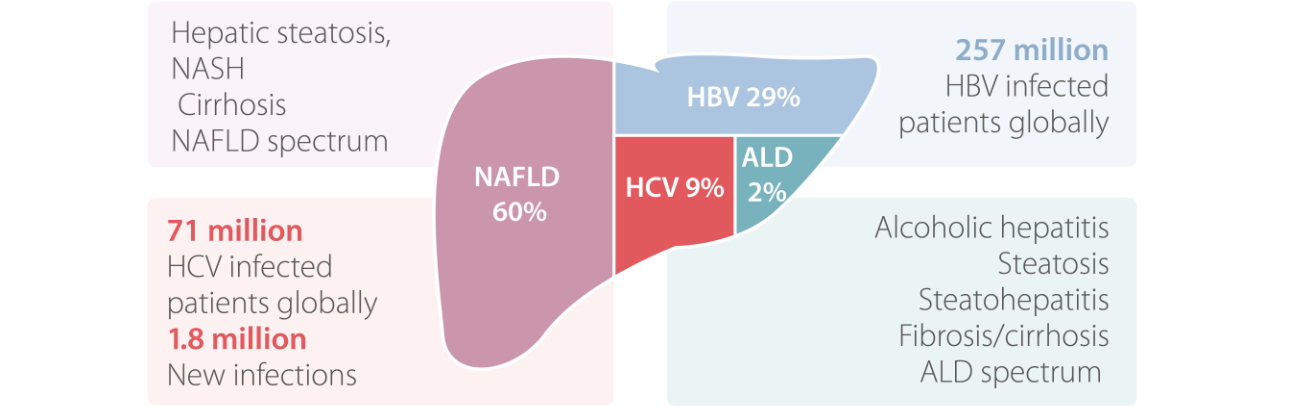
The most common etiologies of CLD and cirrhosis are due to chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), alcohol-related liver disease (ALD), and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD and ALD encompass a spectrum including hepatic steatosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis. To date, there are 325 million viral hepatitis B and C infected cases globally.
Trend shifting
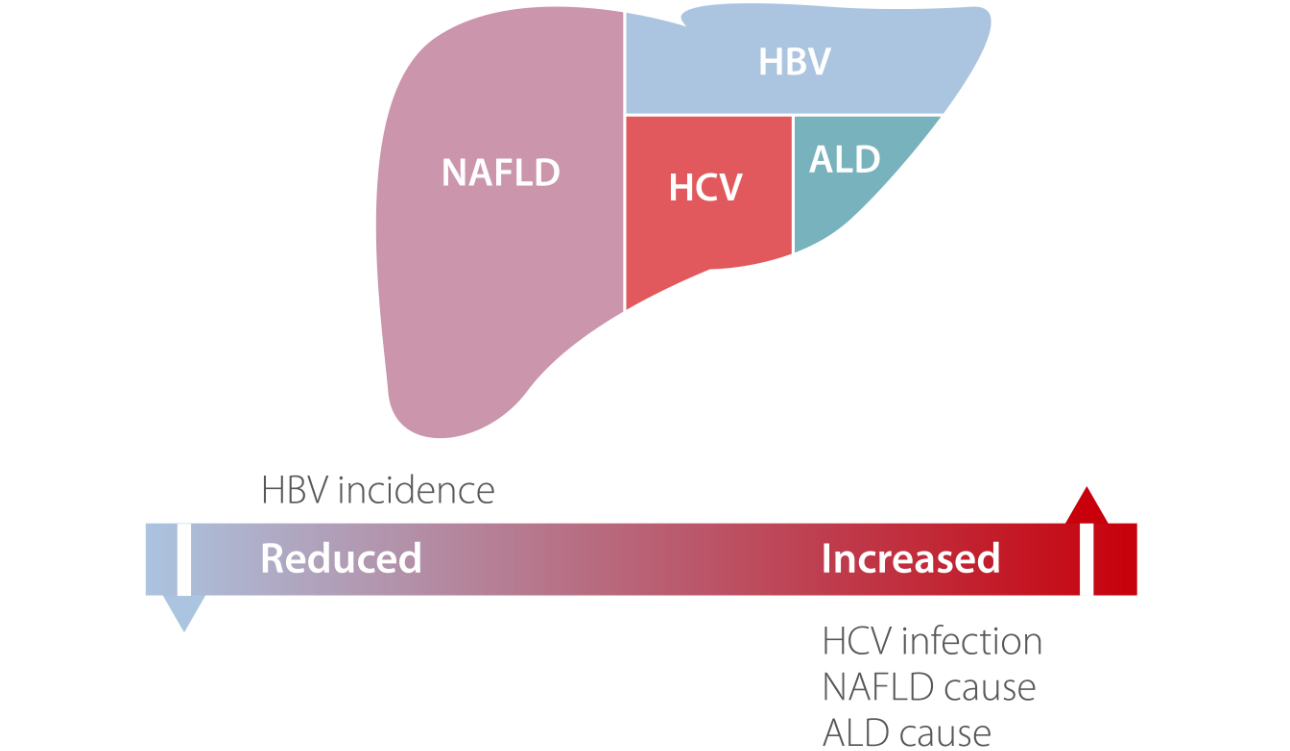
However, the trend is shifting now. The relative contribution of viral hepatitis B to CLD is reduced because of widespread vaccination and anti-viral treatment programs. In contrast, HCV infection, NAFLD and ALD are more commonly the causes of CLD due to epidemic trends, obesity, metabolic syndrome and alcohol consumption.
Complications of CLD & cirrhosis
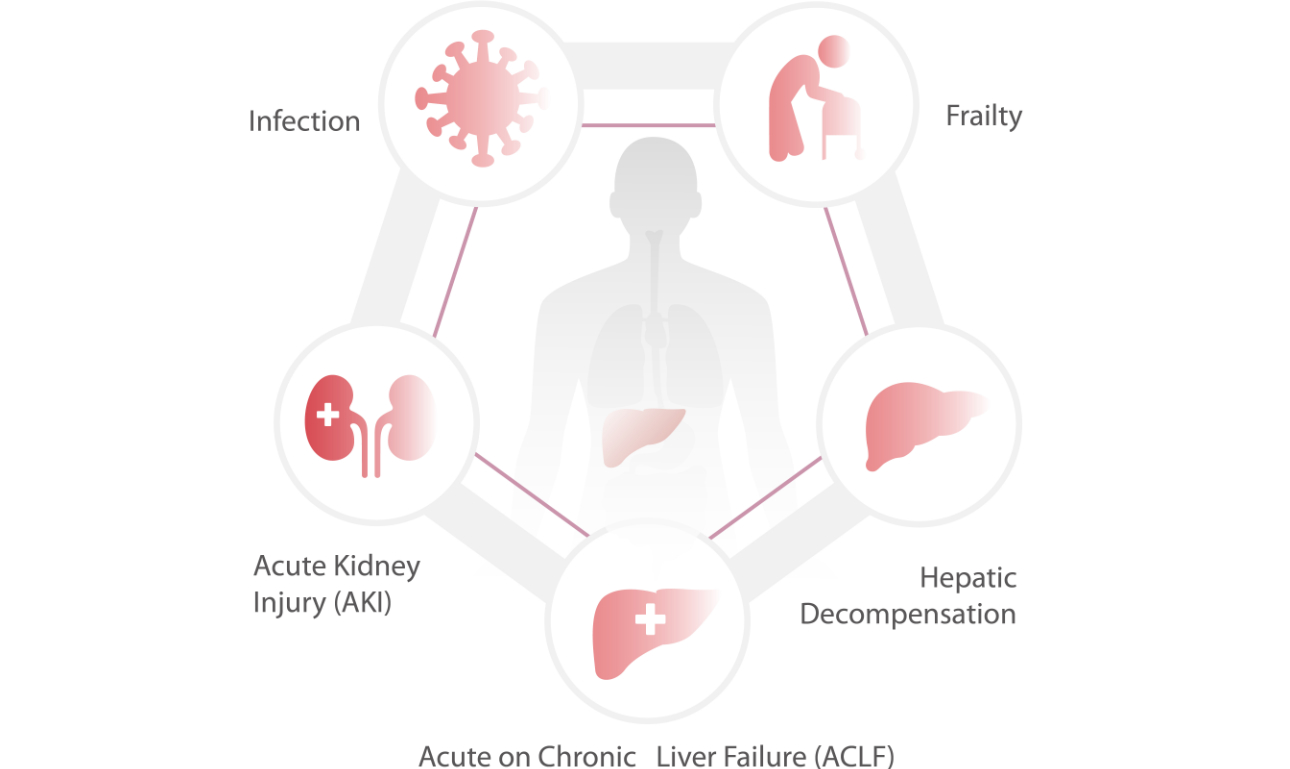
The burden of CLD and cirrhosis is also evident due to the large number of patients with complications which demand extensive healthcare resources for diagnosis and treatment.
Testing methods
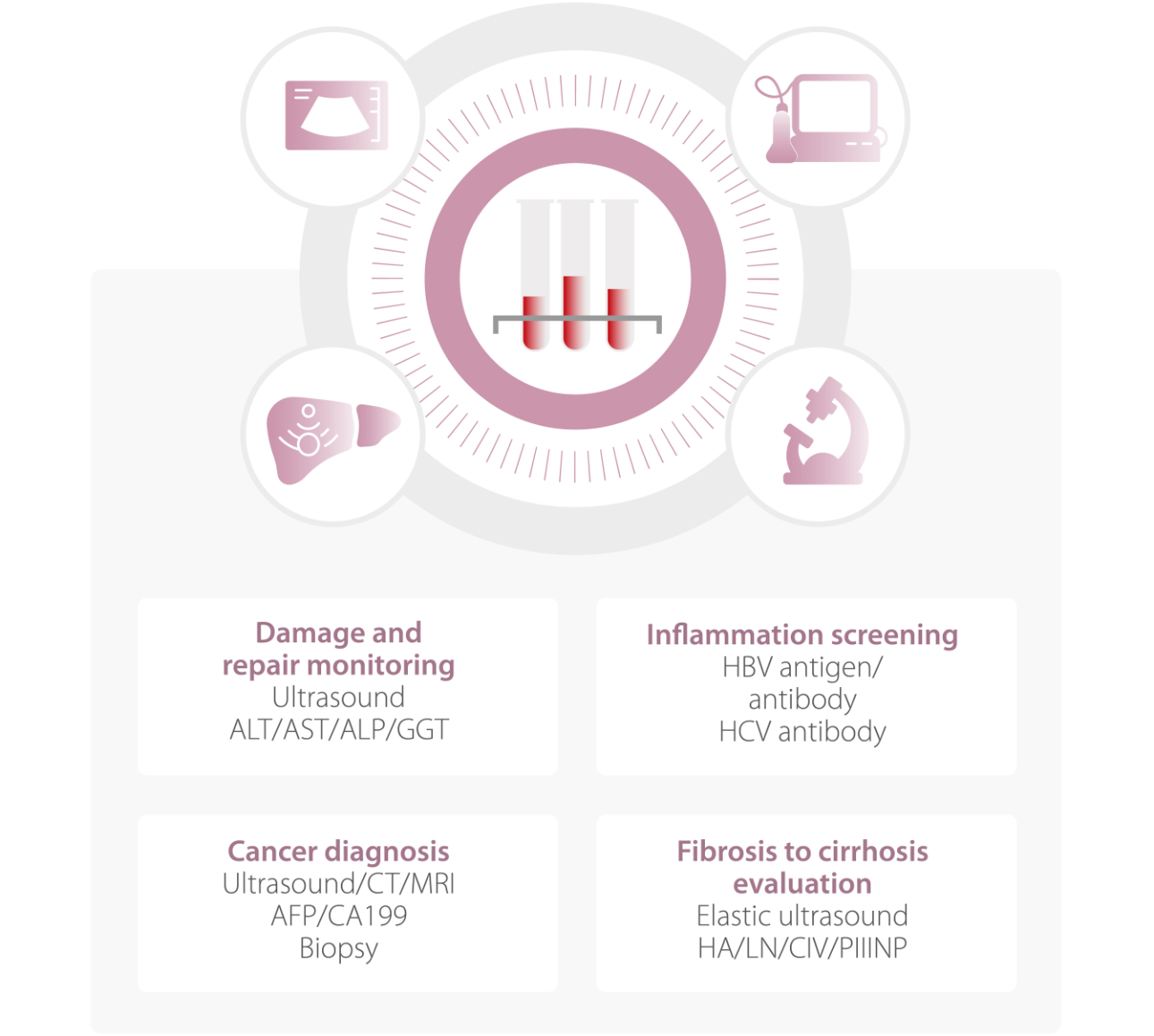
Everyone who is at risk of CLD should have access to testing, so they can benefit from screening, and different clinical values can be monitored and diagnosed.
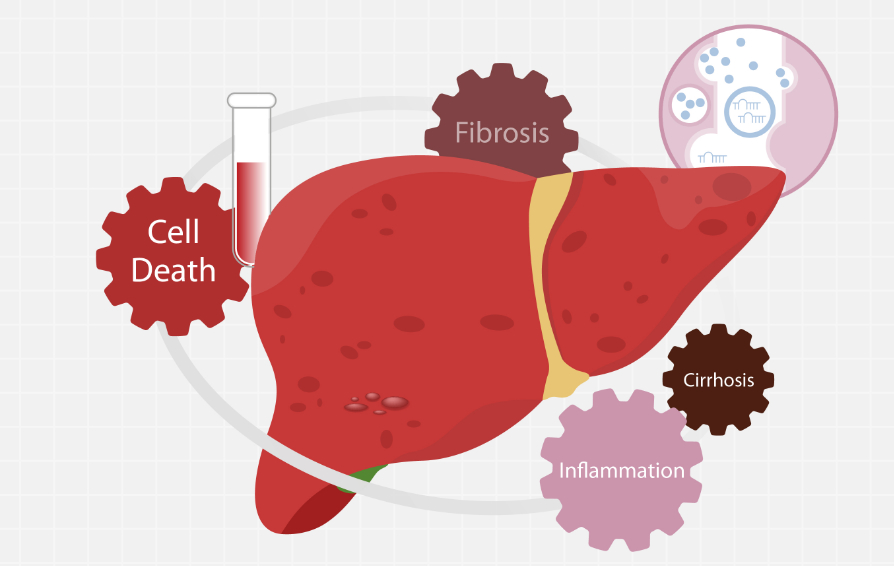
Liver fibrosis mechanism
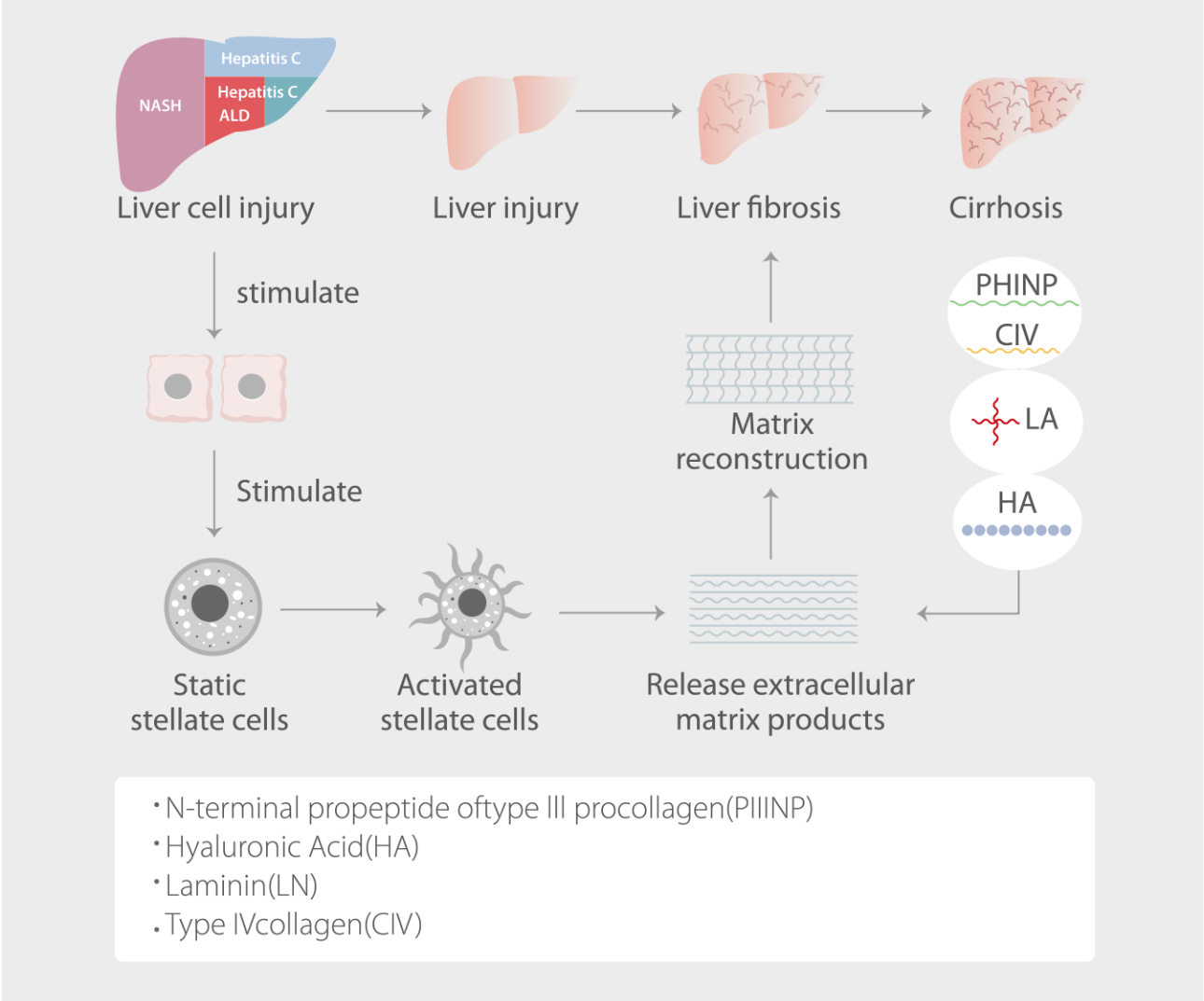
HBV, HCV, and AFP are the most widely studied and known screening tests used as serum biomarkers for liver condition evaluation.
Recent studies have shown that HA, LN, CIV, and PIIINP are correlated with advanced fibrosis.
Study results revealed that CIV, PIIINP, HA, and LN are significantly correlated with the severity of liver inflammation and hold better predictive values for differentiating moderate to severe inflammation in patients with CHB.
Mindray Liver Disease Solution
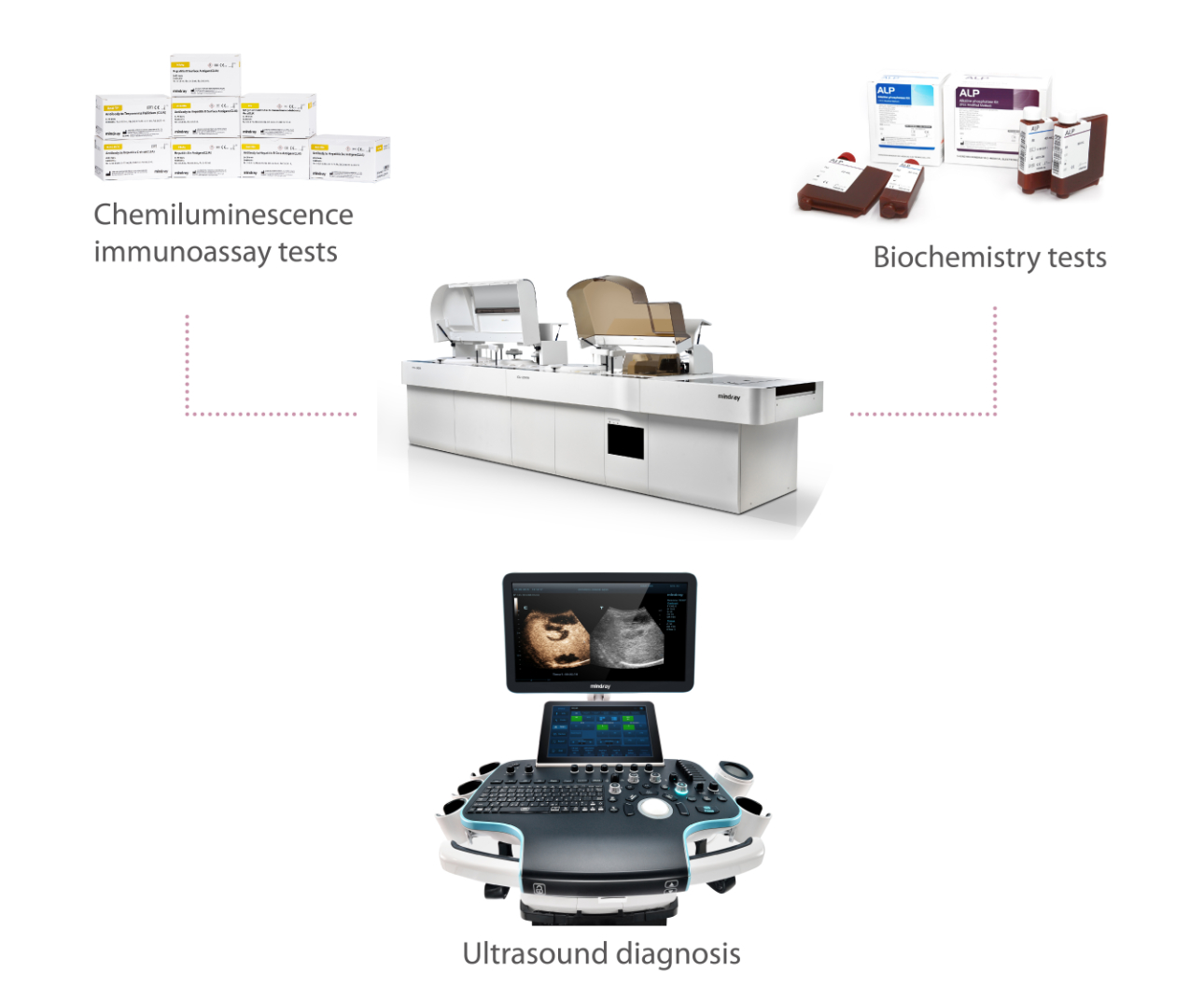
Some guidelines also emphasize that serum testing and ultrasound imaging should be combined to improve the accuracy of the noninvasive diagnosis. Mindray provides a comprehensive solution for liver disease diagnosis and management, helping doctors to deliver reliable diagnosis and treatment options with accurate serum tests and ultrasound imaging.
References:
[1]Andrew M. Moon, Contemporary Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 November;18(12): 2650–2666.
[2]S D Ryder, Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in adults, Gut 2003; 52(Suppl III):iii1–iii8
[3]WHO 2021