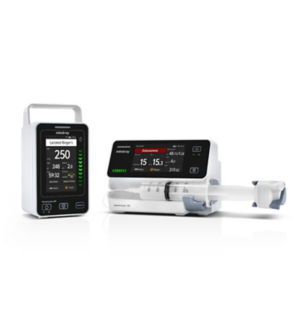
Optimizing Chemotherapy with Smart Infusion Pump Innovation: Addressing Clinical Needs for Chrono-Chemotherapy
2023-05-12

Global cancer rates on the rise: what can we do?
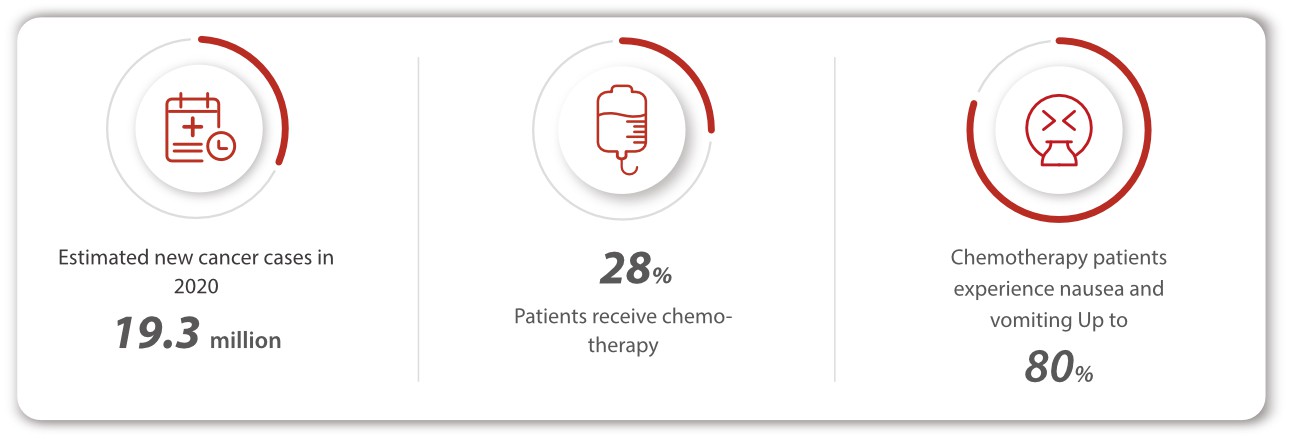
Cancer remains a significant global health challenge, as an estimated 19.3 million new cases were recorded in 2020 alone [1]. Over the years, chemotherapy has been a widely used treatment option for cancer patients, with approximately 28% of them receiving this therapy to combat the disease [2]. However, despite its effectiveness, chemotherapy can cause severe side effects like nausea and vomiting in up to 80% of patients [3], which can render the treatment unbearable. As global cancer rates continue to rise, it's essential to explore new, innovative approaches to improve patient outcomes while minimizing adverse side effects.
Chromo-chemotherapy: a more caring cancer treatment method
This is where chromo-chemotherapy comes in as an emerging approach to enhance the safety and efficacy of chemotherapy while reducing drug toxicity. The concept of chronotherapy has been around since the 1960s but gained popularity in the field of oncology only recently [4]. Chromo-chemotherapy involves administering drugs according to a patient’s circadian rhythm. Circadian rhythms are the body's natural 24-hour cycles that regulate various physiological functions such as sleep-wake cycles, hormone secretion, metabolism, and immune function [5].
Multiple studies have illustrated the potential benefits of chromo-chemotherapy for enhancing response rates and minimizing toxicity as compared to standard chemotherapy. In a recent study evaluating the use of chronomodulated irinotecan in combination with 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer, the results showed that this approach led to a higher response rate and longer progression-free survival compared to conventional chemotherapy [6].
Similarly, in another study conducted on patients with advanced pancreatic cancer, the researchers found that chronomodulated administration of gemcitabine resulted in significantly lower rates of toxicities such as neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and fatigue [7].
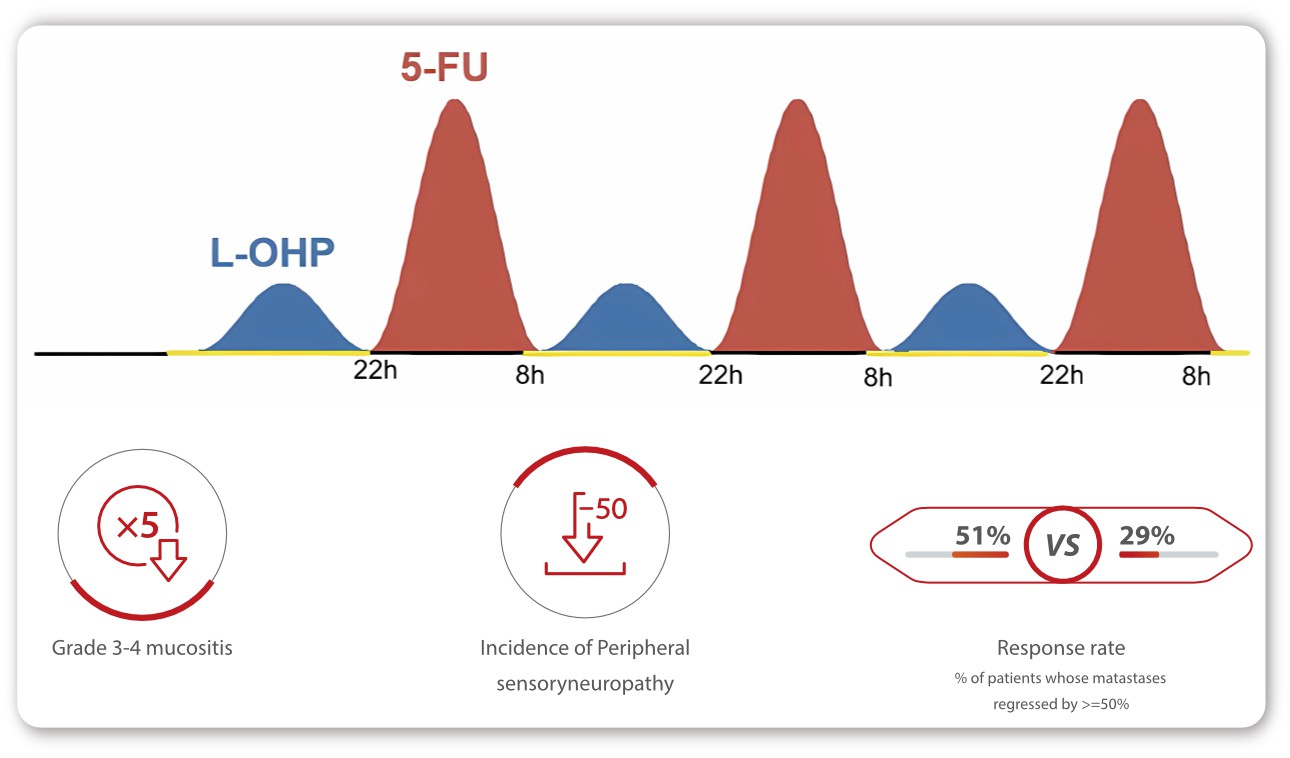
A clinical trial involving 278 patients with metastatic colorectal cancer evaluated the efficacy of chrono-modulated delivery of 5-fluoracil and oxaliplatin compared to non-circadian-based administration. The results revealed that the chrono-modulated delivery led to a significant reduction in grade 3-4 mucositis and peripheral sensory neuropathy (by half), as well as an almost twofold increase in response rate [8].
Medical professionals require an optimal solution for administering cancer drugs with chrono-thermotherapy via infusion pumps. While providing treatment, it is essential to align the medication delivery rate intelligently with the human circadian rhythm, instead of delivering medication at a fixed speed. Furthermore, oncology medical staff also demand a better solution to avoid potential complications caused by manual transfer of the infusion and initiation of the infusion at the precise time. Meeting these needs will not only enhance the quality of chrono-chemotherapy but also increase patient satisfaction levels and boost the work efficiency.
Mindray's innovative solution: Rhythm DoseTM infusion mode
To help optimize the chrono-chemotherapy infusion, Mindray has incorporated an innovative infusion mode called Rhythm DoseTM in their latest BeneFusion i/u series. This feature enables healthcare professionals to administer continuous intravenous infusions of multiple drugs used in chemotherapy at varying rates. With Rhythm DoseTM, clinicians can create more personalized treatment plans.
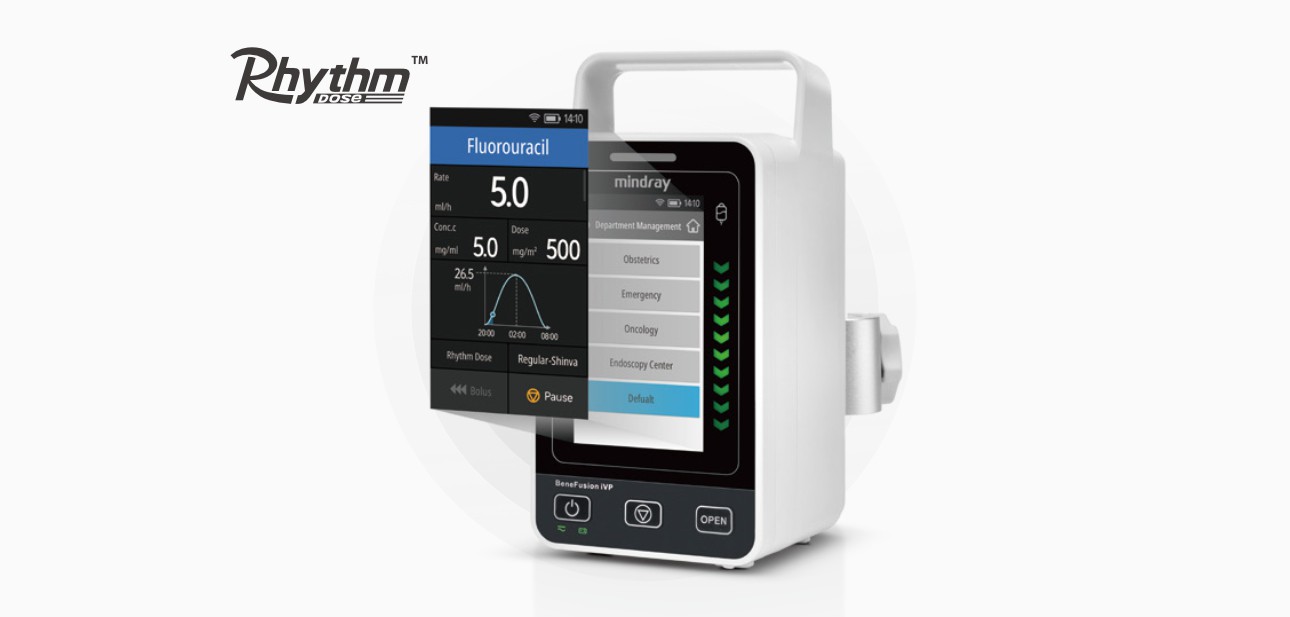

The Rhythm DoseTM mode applies chromo-chemotherapy to drug delivery and offers a choice of two modes depending on the specific drug: Constant Rhythm Infusion and Sin Rhythm Infusion (Sinusoidal wave).
Constant Rhythm Infusion delivers medication at a steady rate over a pre-set specific period of time, whereas Sin Rhythm Infusion delivers medication at varying flow rates over a set period of time to mimic the body’s circadian rhythms and improve patient outcomes while reducing side effects [9]. Studies have found evident benefits of this mode in a range of drugs including fluorouracil (5-FU), cyclophosphamide (CTX), and oxaliplatin [8] [10].
With Mindray's Rhythm DoseTM solution, healthcare providers have a safe and efficient way to deliver medication to patients undergoing chromo-chemotherapy.
Future application of chromo-chemotherapy
The field of chromo-chemotherapy offers promising possibilities for improving cancer treatment outcomes by optimizing drug delivery based on a patient's circadian rhythm. Although further research is required to validate these findings, the initial results are encouraging and suggest the potential for a new approach to cancer treatment. By continuing to investigate the application of chrono-chemotherapy and the timing of treatment, healthcare professionals have the opportunity to improve the lives of cancer patients worldwide.
Reference
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7-30. doi:10.3322/caac.21590
[2] Cancer Research UK. Treatment statistics. Accessed April 21, 2023. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/treatment#heading-Four
[3] Asbestos.com. Chemotherapy side effects. Accessed April 21, 2023. https://www.asbestos.com/treatment/chemotherapy/statistics/
[4] Levi F, Schibler U. Circadian rhythms: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:593-628.
[5] Innominato, P. F., Focan, C., Gorlia, T., Moreau, T., Garufi, C., Waterhouse, J., ... & Bjarnason, G. A. (2019). Chronotherapy in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a randomised feasibility study of maintenance fluorescent light and sleep–wake cycle interventions. BMC cancer, 19(1), 43.
[6] López-Briz, E., Ruiz-García, V., Cabello, J. B., Bort-Martínez, A., Carbonell-Sanchis, R., Gonzálvez-Perales, J. L., ... & Bonfill Cosp, X. (2018). Chronotherapy with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin in metastatic colorectal cancer: a systematic review. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 11, CD007052.
[7] Lévi, F., Boige, V., Hebbar, M., Smith, D., Lepère, C., Focan, C., ... & Ducreux, M. (2013). Chronomodulated irinotecan, oxaliplatin, and leucovorin-modulated 5-fluorouracil as ambulatory salvage therapy in patients with irinotecan- and oxaliplatin-resistant metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer, 119(13), 2329-2337.
[8] Giacchetti, S., Bjarnason, G. A., Garufi, C., Genet, D., Iacobelli, S., Tampellini, M., ... & Lévi, F. (2012). Phase III trial comparing 4-day chronomodulated therapy versus 2-day conventional delivery of fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin as first-line chemotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer: the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Chronotherapy Group
[9] Kucukarslan, S.N., Peters, M., Mlynarek, M., Nafziger, D.A., & Christensen, D.B. (2003). Sine wave infusion: A new approach to infusing medications. Journal of Pharmacy Technology, 19(1), 8-13.
[10] Wallace, E., & Swainston Harrison, T. (2010). Fluorouracil: a review of its use in the treatment of solid tumours. Drugs, 70(14), 1885-1922.