The heart is known to be one of the most important organs in humans due to its vital role in maintaining human health. Despite being only slightly larger than a fist, the heart is a powerful, muscular pump responsible for circulating oxygenated blood throughout the entire body. During contraction, the heart expels blood and transports it to every part of the body. If you compare a human being to a machine, then the heart can be regarded as the central component of that machine. Only when the heart operates in a stable condition can the body maintain good overall function.
What is heart failure?
The term "heart failure" may lead one to believe that the heart ceases to function altogether. In fact, heart failure, also known as congestive heart failure, is a condition characterized by the heart’s difficulty in pumping sufficient blood to meet the body's blood and oxygen requirements. This can be attributed to problems with the heart itself or other organs that hinder its normal functionality. Basically, the heart becomes unable to keep up with the workload it is expected to handle.
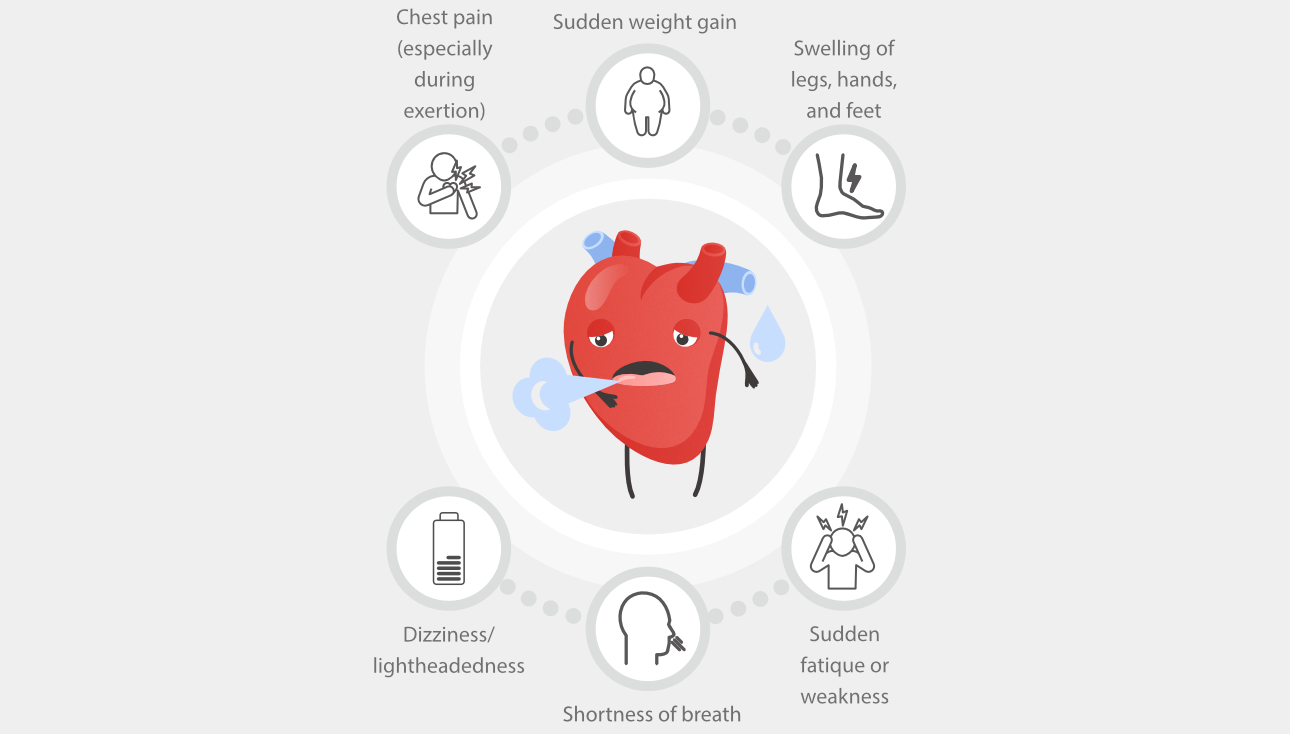
As such, heart failure is a syndrome that manifests as a combination of signs and symptoms caused by the heart’s impaired ability to pump an adequate amount of blood. Typically, the symptoms of heart failure include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The severity of heart failure is primarily evaluated based on ejection fraction, as well as the intensity of its accompanying symptoms.[1]
The role of NT-proBNP in diagnosing heart failure
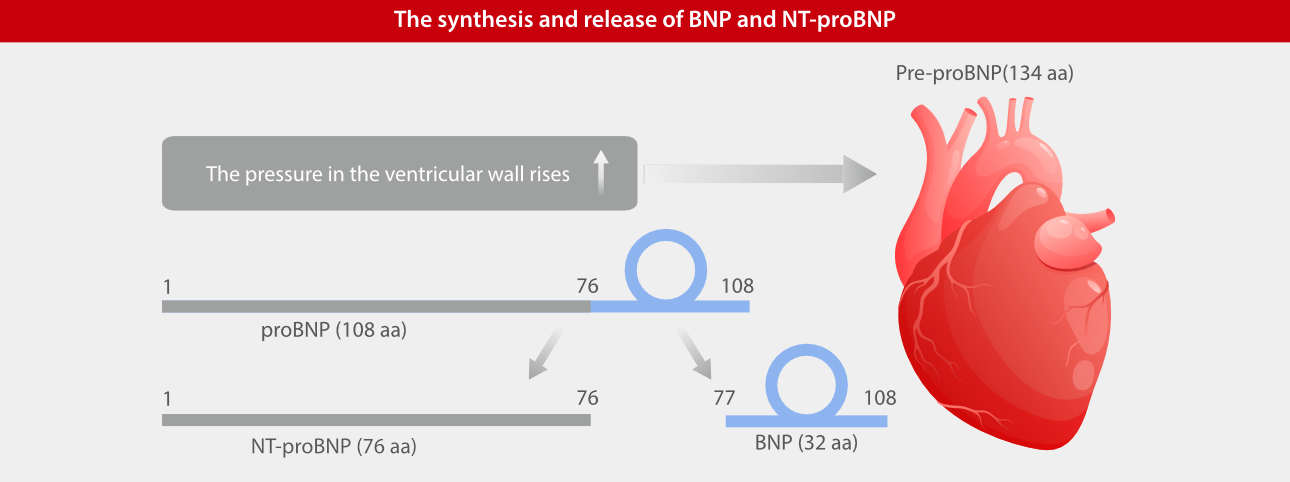
In 1956, researchers began studies aimed at identifying effective markers of heart failure. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) was found to indicate the myocardial function and degree of injury. Compared to BNP, NT-proBNP exhibits a longer half-life, lower biological variability, stability in both serum and plasma, reduced susceptibility to specimen collection, compatibility with a more diverse range of sample types, and improved ease of measurement by laboratory departments [2]. Therefore, NT-proBNP serves as a ideal marker for heart failure in clinical settings. Its utilization allows for a more accurate reference point in clinical diagnosis and treatment decisions.

Diagnostic and prognostic implications in acute heart failure
Acute heart failure (AHF) can occur across various disease conditions and its symptoms may resemble those of many other life-threatening conditions. This introduces a high level of uncertainty to the diagnostic process, especially in emergency situations. NT-proBNP testing can help physicians make more informed decisions in the management of AHF.
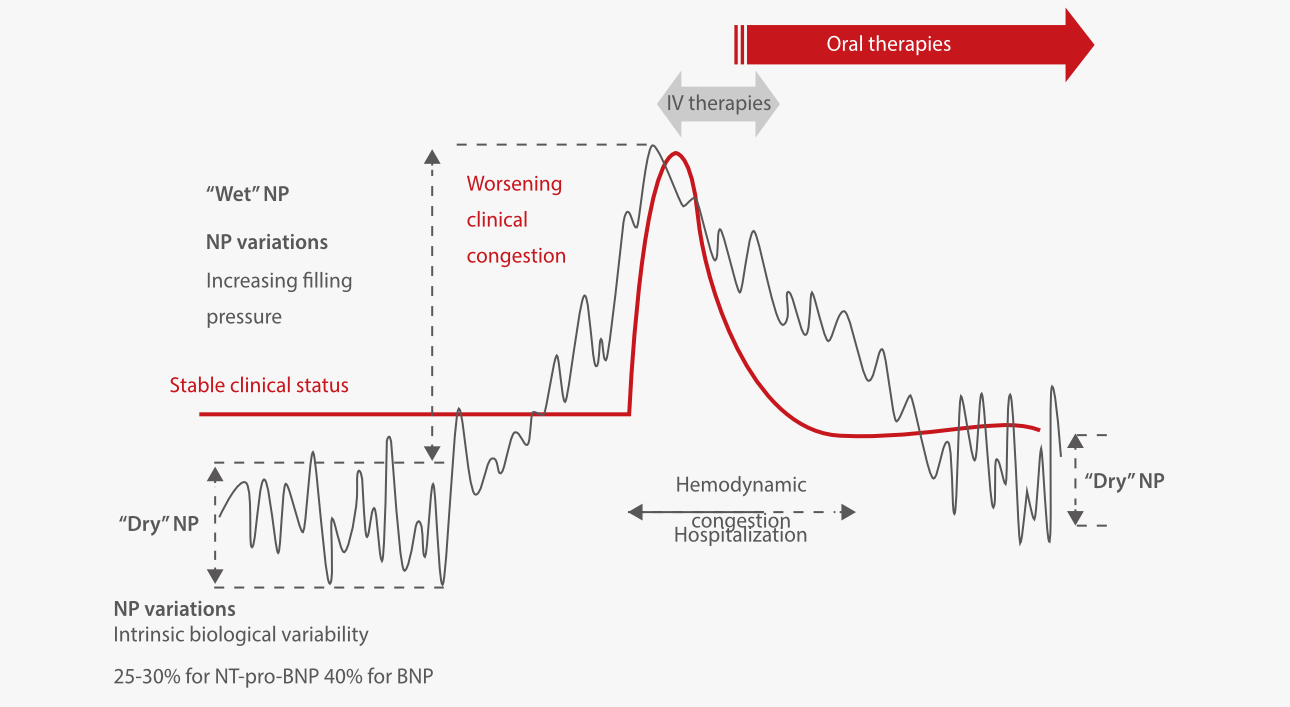
The figure below illustrates the trajectory of natriuretic peptide changes throughout the treatment of AHF.[3]
In the diagnostic work-up of newly presented acute heart failure, an NT-proBNP level greater than 300 pg/mL serves as an appropriate clinical threshold to indicate congestion consistent with AHF.[4]
Diagnostic and prognostic implications in chronic heart failure
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a progressive syndrome that leads to a decreased quality of life for patients and imposes significant financial strain on the healthcare system. Therefore, establishing a prognosis plays a critical role in the optimal management of heart failure. The 2021 ESC guidelines suggest that an NT-proBNP plasma concentration below 125 pg/mL is unlikely to be diagnostic of heart failure. Conversely, higher NT-proBNP levels are associated with a poorer prognosis. [4]
Accurately evaluating the efficacy of ARNi drugs
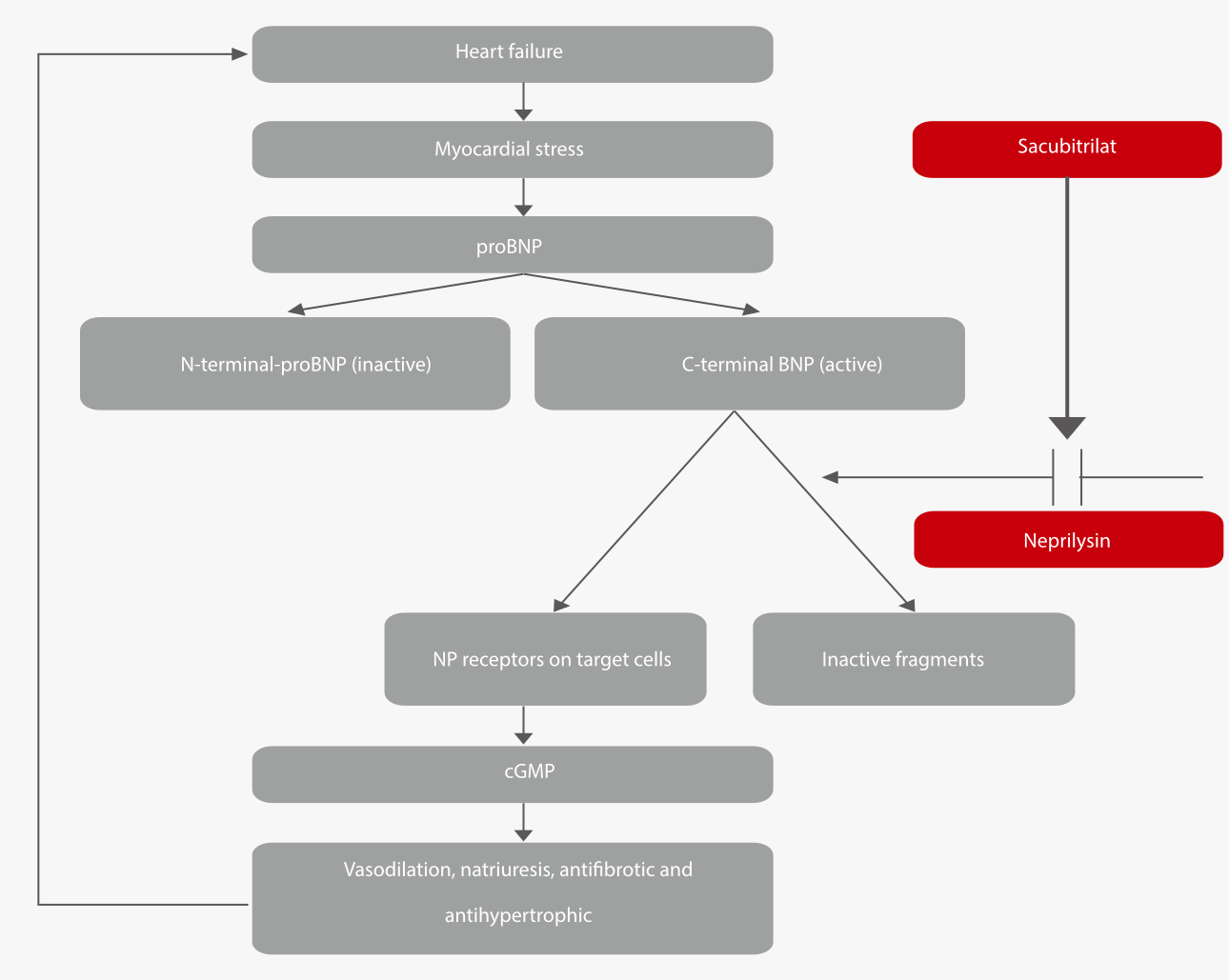
Angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ARNi) have attracted considerable attention in the field of heart failure treatment. ARNi drugs can inhibit renin enzyme (NEP) and block angiotensin type II receptors, thereby hindering the development of heart failure.
The natriuretic peptides (NPs) system and the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) contribute to improved cardiovascular and renal function in patients with heart failure. ARNi therapy is found to be feasible and well tolerated when initiated immediately after the onset of acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF). Patients exhibit significantly lower levels of NT-proBNP at discharge compared to the baseline group. Furthermore, ARNi therapy reduces the degradation of BNP, while NT-proBNP levels remain unaffected. As more drugs that target NPs systems are developed and gain popularity, the clinical applications will expand from BNP to include NT-proBNP in the future. [5]
Conclusion
In summary, NT-proBNP holds important diagnostic and prognostic implications in both AHF and CHF, while also being instrumental in advancing the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure.
By harnessing HyTest’s proven expertise in cardiac marker antibody production and Mindray's innovative capabilities, we have successfully developed a state-of-the-art cardiac assay, NT-proBNP. With the introduction of this assay, Mindray is now equipped to offer a full menu of cardiac assays including hs-cTnI, NT-proBNP, BNP, TnI, CK-MB, and MYO, catering to diverse clinical settings in the immunoassay field.
Reference
[1] Chronic Heart Failure: National Clinical Guideline for Diagnosis and Management in Primary and Secondary Care: Partial Update. National Clinical Guideline Centre.
[2] Natriuretic peptides: their structures, receptors, physiologic functions and therapeutic applications. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology.
[3] NT-ProBNP in acute heart failure: correlation with invasively measured hemodynamic parameters during recompensation. J
[4] 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure.
[5] Natriuretic Peptides: Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Heart Failure Society of America and Japanese Heart Failure Society.







