The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnostic Imaging
02-03-2026
Clinical teams use ultrasound at the point of care to assess internal anatomy and physiology, and—where applicable—evaluate function. Using transducers that emit and receive high-frequency sound waves, these systems transform the echoes into dynamic images that help support high-quality, timely patient care. Explore why this technology matters in modern healthcare, the role of ultrasound in diagnostics across medical specialties, and its value when combined with other imaging techniques.
Why Clinicians Use Ultrasound for Medical Diagnostics
Ultrasound is widely used in clinical practice for several reasons.
Real-Time Visualization That Enhances Clinical Decision Making
This technology provides real-time visualization of internal anatomy and physiology, allowing teams to observe motion, compressibility, and dynamic responses. Teams can also capture stills and cine loops for documentation and consultation. These capabilities support timely and informed triage, monitoring, and follow-up planning across care settings.
Support for Patient Safety and Comfort
Unlike imaging techniques like X-ray and fluoroscopy, ultrasound does not expose patients to ionizing radiation. Exams are generally painless, and most patients tolerate them well. The imaging typically requires no anesthesia and leaves no surgical wounds, which means there's little to no recovery time necessary. Additionally, ultrasound procedures are generally brief, supporting scheduling flexibility. The lack of ionizing radiation also means clinicians can order serial follow-ups without cumulative dosing concerns.
On a related note, imaging procedures like computed tomography (CT) scans and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) may require the use contrast dye, which some patients may be allergic to. Similar to the risk of radiation exposure due to multiple X-rays, these images cannot be performed repeatedly due to the amount of contrast dye that must be used and the subsequent effect on the kidneys.
Versatility That Supports High Efficiency
Modern ultrasound systems meet imaging needs in various care settings, from point of care applications to private offices. Portable and handheld options enable bedside use, while select configurations include capabilities such as elastography for specific organ assessment, with availability depending on indication. This versatility, combined with short exam time frames, supports high-efficiency workflows and targeted imaging capabilities.
How Ultrasound Is Used in Diagnostic Imaging
Ultrasound has multiple diagnostic imaging applications, offering value in numerous use cases.
Emergency and Critical Care
Ultrasound's real-time imaging capabilities and portability make it well-suited for emergency and critical care settings. Common applications in these environments include:
- Focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST), which is often implemented to detect internal organ damage, specifically in the abdomen and around the heart, or bleeding in response to traumatic impact or injury
- Point of care ultrasound to support the diagnosis and management of cardiac events
- Visualization of vascular systems to assist with line placement and assess blood flow, helping detect and characterize the extent of issues like deep vein thrombosis and arterial disease
- Imaging of lungs to identify effusion
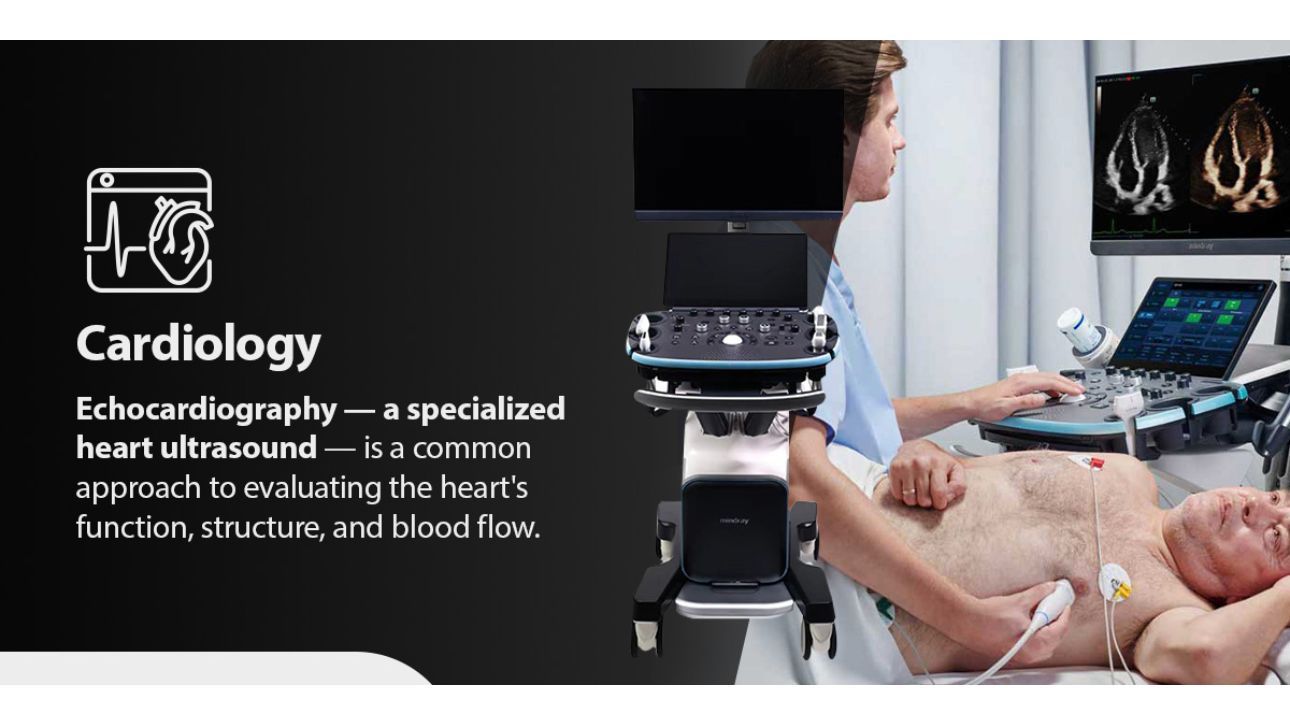
Cardiology
Echocardiography — a specialized heart ultrasound — is a common approach to evaluating the heart's function, structure, and blood flow. This imaging approach can help clinicians detect conditions like:
- Issues with heart valve performance
- Heart disease
- Tumors and blood clots
- Whether the heart is pumping enough blood
- The strength of the heart muscle
Women's Health
Women's health is one of the primary applications for ultrasound, both historically and today. It is widely used in obstetrics to:
- Confirm pregnancy
- Identify the placenta location
- Estimate fetal age
- Monitor fetal growth and development
- Detect potential abnormalities or complications
- Guide procedures like amniocentesis
Additionally, clinicians rely on ultrasound to support gynecological health. The visualization of reproductive organs can help healthcare providers evaluate conditions like ectopic pregnancies, uterine fibroids, some cancers, and ovarian cysts. Ultrasound also delivers real-time, dynamic images of breast tissue, which can support adjunct assessments and guidance.
Renal, Hepatobiliary, and Abdomen
Ultrasound technology allows for detailed visualization of pelvic and abdominal structures and tissues. Its use is widespread for potentially identifying:
- Kidney stones and gallstones
- Cirrhosis, fatty liver disease, and other liver conditions
- Appendicitis
- Pancreatic anomalies
- Abdominal aneurysms
- Prostate abnormalities
Vascular
Ultrasound plays a critical role in vascular care by providing real-time, noninvasive visualization of blood vessels and blood flow. It is commonly used to diagnose arterial and venous disease, detect blockages or clots, assess blood flow abnormalities, and monitor disease progression or treatment outcomes. Because it is safe, repeatable, and does not rely on radiation or contrast agents, ultrasound is often the first-line imaging modality for both diagnostic evaluation and procedural guidance in vascular applications such as the following:
- Carotid artery disease
- Peripheral arterial disease (PAD)
- Renal artery stenosis
- Aneurysms
- Arterial occlusion or thrombosis
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Chronic venous insufficiency
- Varicose veins
Musculoskeletal
A musculoskeletal diagnostic ultrasound evaluates tendons, ligaments, joints, and muscles. It is common in orthopedics and sports medicine to assess injuries like ligament sprains and muscle tears. The technology is also used to help guide procedures like biopsies or injections to deliver medication to a targeted area. Other conditions ultrasound can support the detection of include:
- Fluid in the joints
- Tendinitis and carpal tunnel syndrome
- Masses in soft tissue
Interventional Medicine and Anesthesia
Ultrasound technology provides the detailed visualizations needed for professionals in interventional medicine and anesthesia. Imaging helps guide procedures like:
- Biopsies for precision tissue extraction
- Drainage of excess fluids
- Placement of lines and nerve blocks
- Cardiac catheterizations
Urology
Urologists rely on ultrasound to help them assess potential patient conditions for next steps. They are routinely used in diagnostic imaging to:
- Evaluate bladder volume
- Visualize abnormalities within the scrotum that could contribute to infertility challenges
- Examine the internal structure of the prostate and identify potential lesions within it
- Provide procedural guidance for prostate interventions
Pediatrics
Pediatricians regularly turn to ultrasound since it is non-invasive and doesn't expose the patient to ionizing radiation. The technology can offer value in any of the use cases above, but also supports specialized pediatric applications, such as:
- Monitoring liver size and fluid retention in newborns with hemolytic disease
- Identifying and characterizing congenital abnormalities
- Detecting and locating intussusception
- Assessment of kidney and bladder conditions
- Imaging of fetal cranium to evaluate brain hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, and ventricular enlargement
- Musculoskeletal imaging for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), soft-tissue masses or fluid collections, and joint effusions
How Ultrasound Complements Other Imaging Methods
One of the most important clinical uses of ultrasound is its ability to complement other imaging methods for a more holistic visualization.
Ultrasound and X-Ray
With its use of high-frequency sound waves, ultrasound is suitable for imaging soft tissues, like muscles and most organs. Conversely, X-ray offers detailed imaging of denser tissues and bones and detects air in the chest and abdomen. Used together, the two methods provide a complementary visualization to support clinical diagnosis and next steps.
Ultrasound and Computed Tomography
Unlike the real-time dynamic assessment of ultrasound, a CT scan offers cross-sectional visualization with detailed anatomic context of bone, calcification, and soft tissue. These capabilities make it useful for whole-body or regional imaging. If an ultrasound identifies an abnormality, a CT scan can further characterize its extent in surrounding tissues. Pairing the two helps support assessment and treatment programs.
Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Similar to CT, MRI can visualize soft and dense tissue alike and provide high-contrast images of deeper structures that are challenging to image with ultrasound. This capability makes it especially useful for bone and bone marrow. The high-resolution MRI images and real-time ultrasound data are often combined by clinicians in applications like guided biopsies due to the complementary nature of visualization.
Ultrasound and Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine uses radiopharmaceuticals to provide images at a molecular level, visualizing metabolic processes to evaluate organ function. This functional analysis may help detect disease at early stages, where structural impacts that an ultrasound could reveal are not yet evident. The complementary information of each method helps give medical providers a clearer understanding of the patient's condition to support diagnosis and treatment plans.
Why Trust Mindray North America for Ultrasound Systems?
As one of the top three ultrasound developers in the U.S., Mindray offers ultrasound systems that support consistent image quality and efficient workflows across various clinical applications. Our mission is clear — advance medical technologies to make healthcare more accessible. Part of that vision means continuously improving our systems and innovating with advanced solutions like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) that help promote standardization, repeatability, and efficiency.
Our history as a trusted partner to healthcare providers spans over three decades. Today, we continue partnering with medical professionals nationwide for accessible solutions that put healthcare within reach.