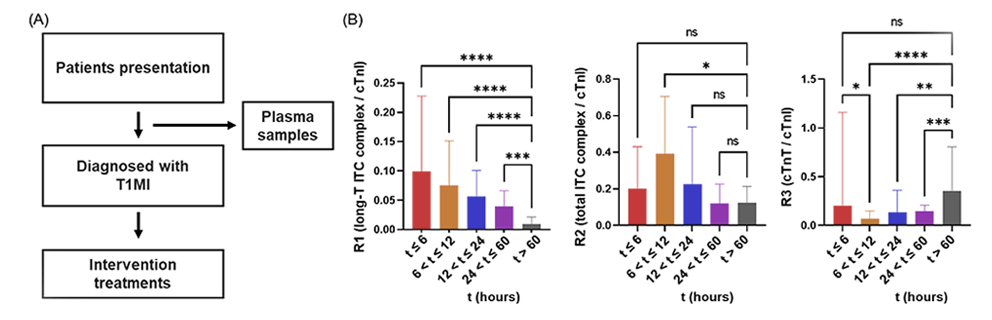
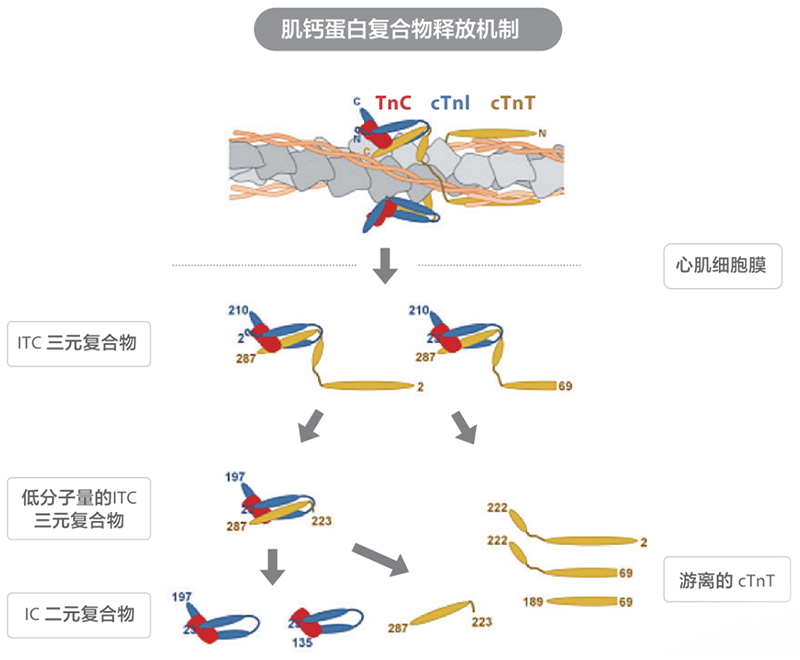
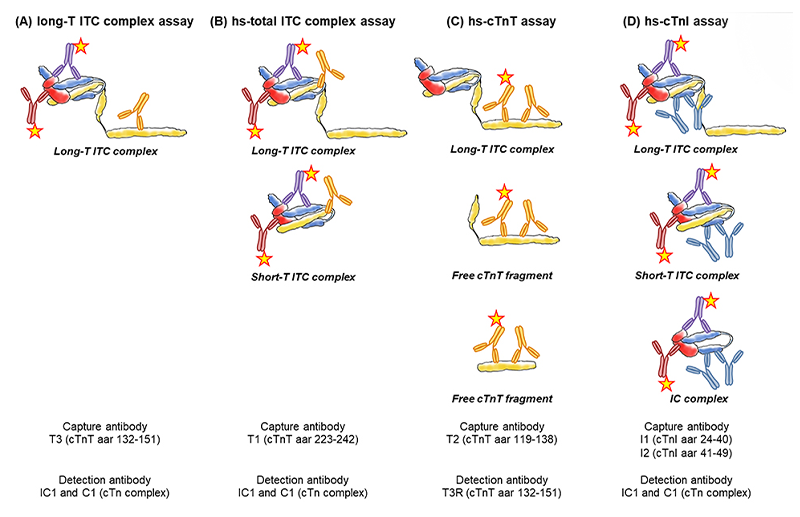
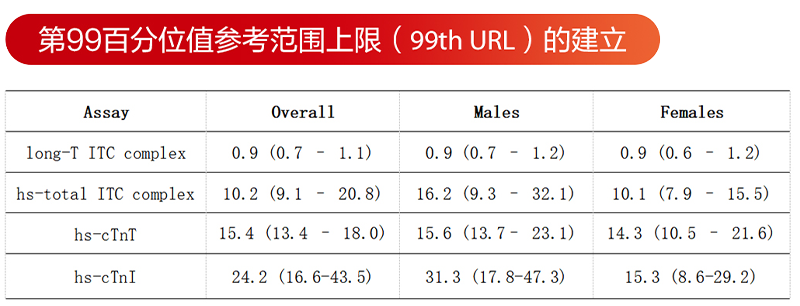
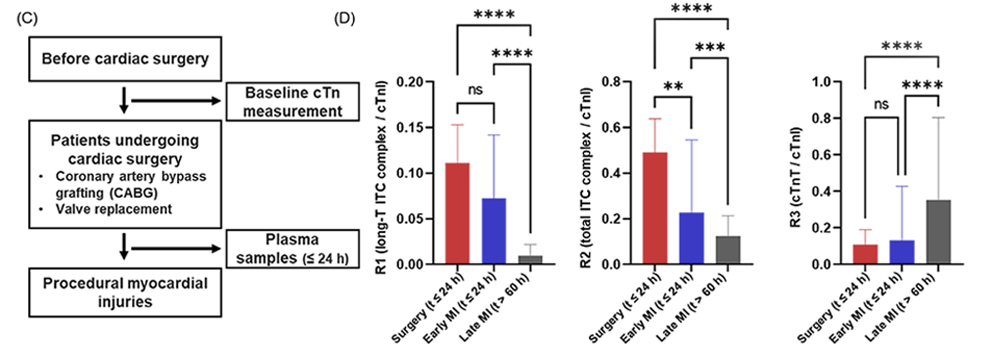
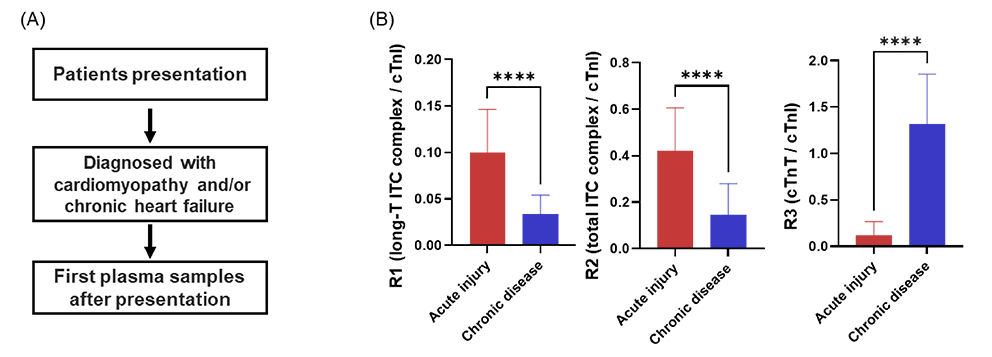
发表文章题目:
[1] Li L, Liu Y, Katrukha IA, et al. Design and Analytical Evaluation
of Novel Cardiac Troponin Assays Targeting Multiple Forms of the
Cardiac Troponin I-Cardiac Troponin T-Troponin C Complex and
Fragmentation Forms. Clin Chem. Published online December 19, 2024.
doi:10.1093/clinchem/hvae182
[2] Li L, Liu Y, Katrukha IA, et al. Characterization of Cardiac
Troponin Fragment Composition Reveals Potential for Differentiating
Etiologies of Myocardial Injury. Clin Chem. Published online December
17, 2024. doi:10.1093/clinchem/hvae200
引用资料:
[1] Katrukha IA, Katrukha AG. Myocardial injury and the release of
troponins I and T in the blood of patients. Clin Chem 2021;67:124-30.
[2] Damen SAJ, Cramer GE, Dieker H-J, Gehlmann H, Ophuis TJMO,
Aengevaeren WRM, et al. Cardiac troponin composition characterization
after non ST-elevation myocardial infarction: relation with culprit
artery, ischemic time window, and severity of injury. Clin Chem
2021;67:227-36.
[3] Airaksinen KEJ, Aalto R, Hellman T, Vasankari T, Lahtinen A,
Wittfooth S. Novel troponin fragmentation assay to discriminate
between troponin elevations in acute myocardial infarction and
end-stage renal disease. Circulation 2022;146:1408-10.
[4] Labugger R, Arrell DK, Van Eyk JE. Cardiac troponins: Exploiting
the diagnostic potential of disease-induced protein modifications. In:
Wu AHB, editor Cardiac markers Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2003. p.
125-38.
[5] 《心脏标志物 第2版》人民卫生出版社,2009 Alan
H.B.Wu原著;邹雄,潘柏申主译。