Interventional ultrasound has evolved rapidly in recent years, with extended applications in many fields. One example is ultrasound-guided ablation therapy for liver tumors. Under the guidance of ultrasound, the clinician inserts a needle electrode into the tumor, where the ablation zone can be heated up to about 100°C via electric current due to the frictional heat of polar molecules, causing coagulative necrosis of the tissue. As a safer and minimally invasive method compared to traditional surgeries, ultrasound-guided ablation therapy has been added to the guidelines for treating liver cancer in manycountries, providing another option for liver tumor patients.
Liver tumor ablation still faces many challenges, including the display of complex lesions before the procedure experience dependent treatment strategies, and the lack of spatial information for post-procedureevaluation, and so on.
- How to precisely localize the tumor before procedure?
- How to standardize the ablation strategy?
- How to instantly get a comprehensive evaluation of the ablation efficacy?
These are the problems Prof. Xie Xiaoyan’s team has been trying to solve. In the following article, Prof. Xie’s team and Mindray’s R&D team both take stock of the joint venture: how is the cooperation between the ultrasound department and an industry partner? How did the partnership come out?
The Department of Medical Ultrasoundat The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University is an advanced ultrasonic diagnosis and treatment center in China engaged in medical treatment, research and education. Prof. Xie Xiaoyan, head of the department and an expert in abdominal ultrasound and interventional ultrasound, has devoted herself to the research on tumor ablation for many years.


Guangzhou, China

2200-3000

Interventional ultrasound and tumor ablation, prenatal screening for fetal malformations, CEUS and diagnosis of hepatobiliary, pancreatic and splenic diseases
Led by Prof. Lyu Mingde, Prof. Xie and her team started trialing ablation treatment of liver cancer in southern China in 1990 and yielded positive results. However, some tough problems still remained unsolved. How to accurately insert a single needle right into the center of the tumor for ablation? When using multiple needles for ablation, how can the second and third needles be inserted precisely without being affected by the gas generated during the procedure, which fills the entire tumor? After ablation, how can efficacy be assessed more accurately than by the conventional method of looking at the ablatedlesion size? The team kept exploring. By a stroke of luck, they were inspired by GPS – with GPS, people can reach their destination regardless of the weather. If a tumor could be captured in a 3D image and then modeled into a map with GPS positioning, wouldn't it be possible to conduct precise needle insertion and get effective assessment of the ablation efficacy using the map as guidance?

Inspired by the idea, Prof. Xie and her team began to look for ways create a navigable "map" to position the tumor. They found that multimodality fusion between real time ultrasound and a map made from CT had already been used in treatment guidance. But given that CT involves a cumbersome process, was there a possibility to use ultrasound fusion to map the lesion?

Department of Medical Ultrasonics
The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University
Mindray Beijing R&D Center
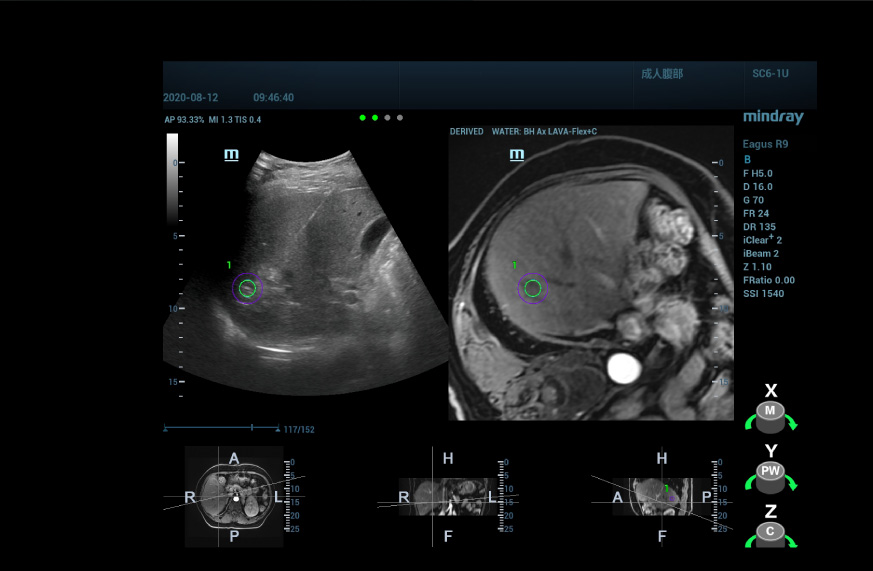
Locate lesions more precisely

By employing a multimodality fusion technique, using uHit Fusion from Mindraycan fuse the MRI information with the ultrasound image, allowing us to see the location of abnormally enhanced nodules shown by the MRI T1WI enhancement. With the supplemental spatial positioning information, apart from the MRI, we are able to locate the lesion with a high degree of confidence.
For the ultrasound/ultrasound fusion image, we obtain 3D ultrasound data of the lesion pre-procedure and fuse it with the real-time 2D image so that the information from the pre-procedurelesion assessment can be fully utilized, and the location and nature of the lesion can be confirmed by performing ultrasonography again.
For unavoidable respiratory movements and unexpected body movements during treatment, we have introduced respiratory compensation and movement correction functions to correct for position changes during fusion and make the ablation registration more accurate and stable.
Perform treatment more confidently
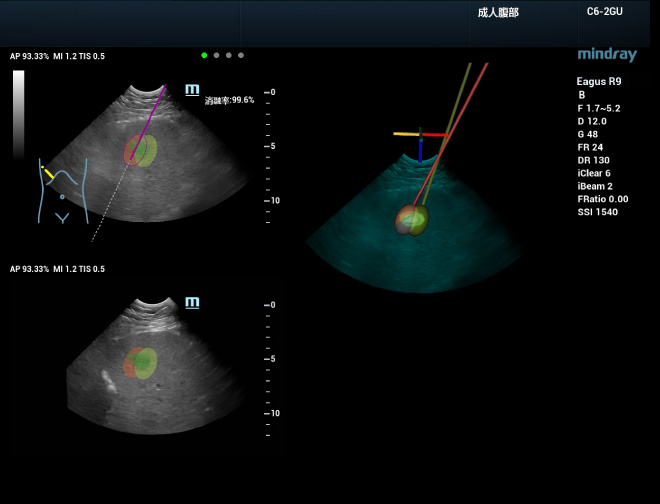
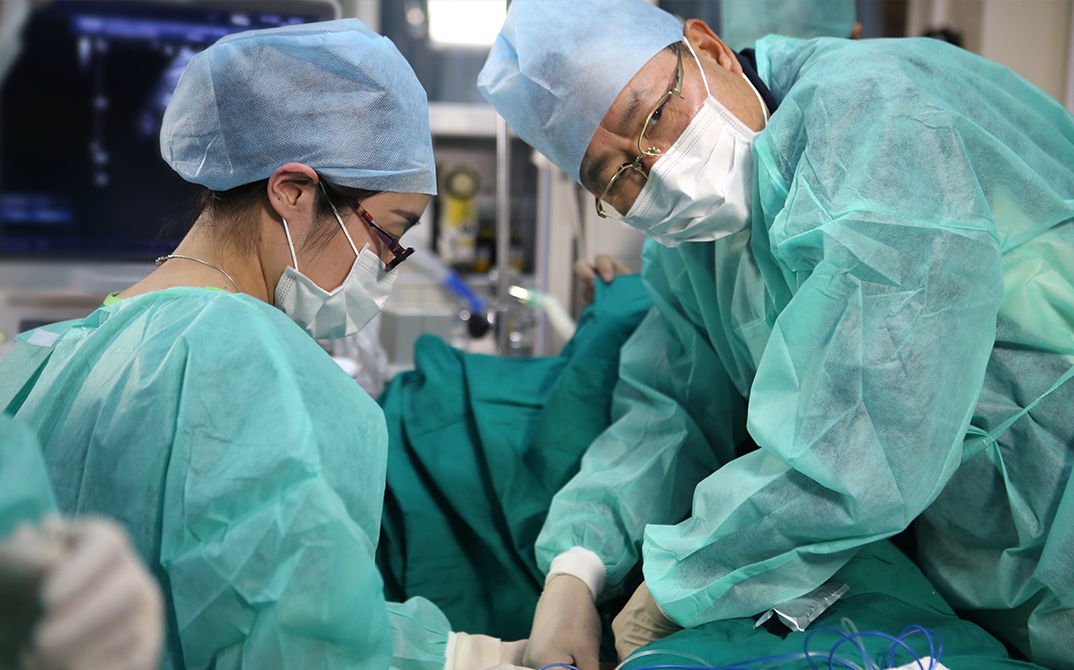
During 3D ablation planning, ablation simulation can be performed to develop an effective treatment strategy for large lesions that need to be ablated with several needles. First, set the ablation range for individual needles and then place the needles for ablation in the simulation. An optimum plan can be finalized by observing the real-time display of the coverage rate of the lesion. This process supports three-dimensional multi-angle display, which allows for intuitive and multi-dimensional observation of the ablation coverage for the whole tumor. The needle can then be guided into the real tumor according to the planned path, and the ablation coverage will be updated in real time with the actual needle insertion. Using uHit Fusion the whole ablation process can be better planned and standardized, thus reducing the operator’s dependency on experience.
Deliver clinical diagnosis more accurately
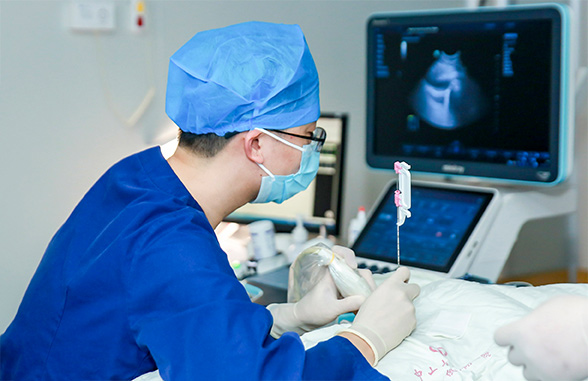
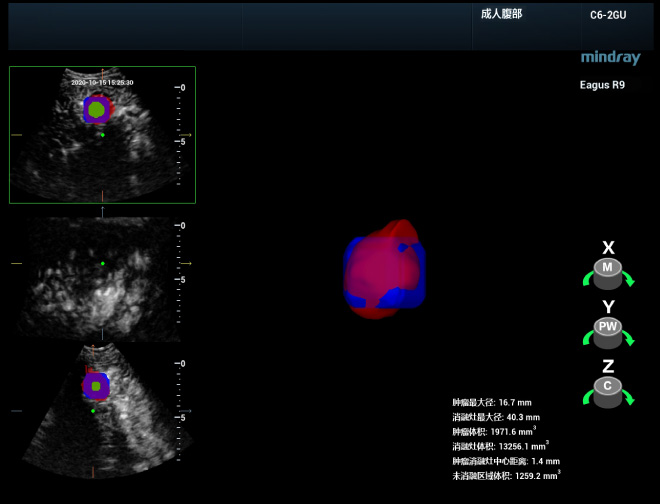
Conducting a comprehensive and immediate evaluation after ablation is vital for detecting residual tumors and performing supplementary treatment straight away, which helps improve the rate of complete ablation and avoid the occurrence of local advancement. Prof. Xie’s team can perform 3D ultrasonography of the ablation site immediately after the procedure and then fuse it with the 3D ultrasound data to get a complete picture of whether the ablation site covers the safe boundary of the lesion in the entire 3D space and whether there is any residual lesion or insufficient ablation. In addition, tomographic segmentation display and 3D volume reconstruction of this fusion image can be performed to visualize more clearly the spatial location of the area in need of complementary treatment and its relationship to the surrounding vital organs.
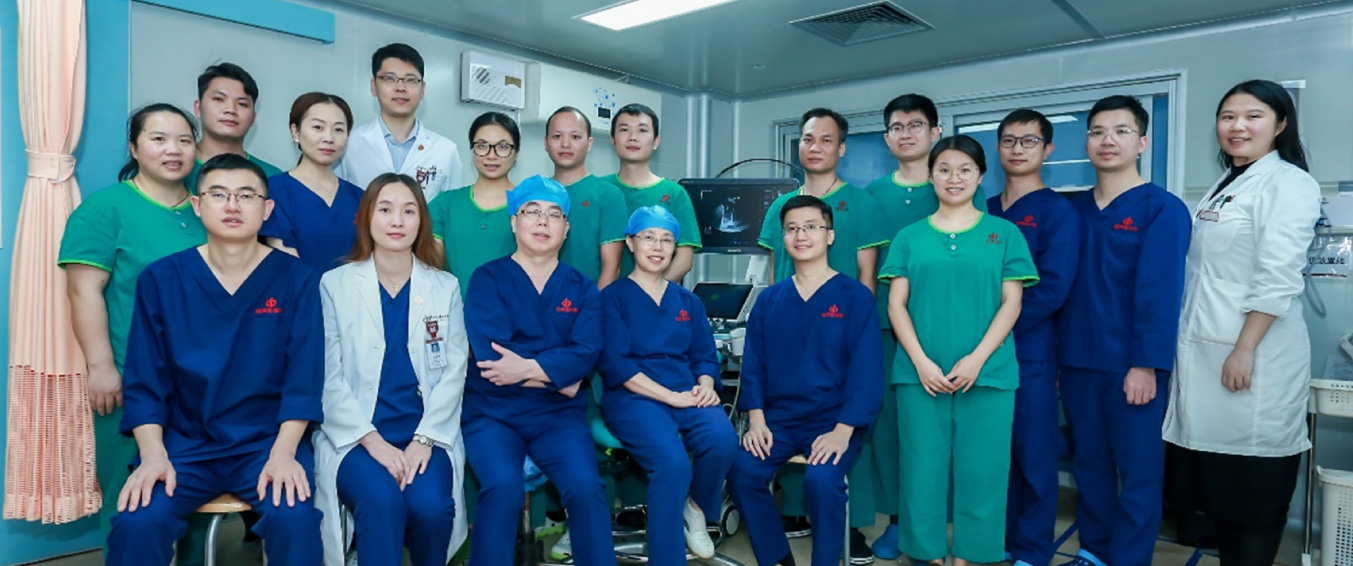

The hard-won ablation solution co-developed by Mindray and The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University is just one of the many success stories of the industry-academia-research collaboration between Mindray and hospital departments. We will continue to work together with medical professionals to translate cutting-edge technologies into effective clinical solutions, and explore the new boundaries of ultrasound diagnosis and treatment to effectively respond to patients' needs.