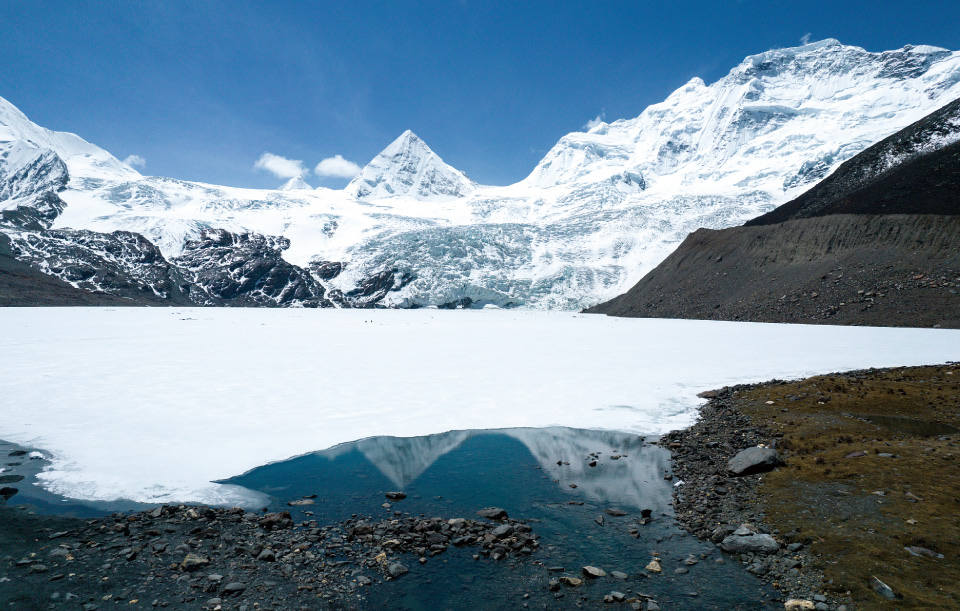
Located in the hinterland of China's Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Naqu's climate is chilly, low on oxygen, and predominantly dry, with about 100 windy days a year. It is also the source of the Yangtze and Nujiang Rivers, among others. Due to the lack of heat and water required for vegetation to grow, lush forests are rarely seen across this vast landscape, where the air only has half the oxygen content compared with at sea level. As one of the largest pastures in China, it's home to generations of herders.

Average altitude
Average altitude

Thanks to the economic growth and improvements in transportation, Naqu Town, once a sparsely populated village, has now grown into a thriving transportation and economic hub. However, its infrastructure is still lagging behind areas with lower altitudes due to the harsh environment, and unfortunately, rapid population growth is putting pressure on its healthcare system. In the event that a ventilator fails, the service staff have to make an arduous journey to get a new one, which demands a lot of manpower and time. Medical professionals do not get the equipment and supplies they need in a timely and effective manner, leading to delays in patient treatment.
Average altitude of Naqu
Population of Naqu
Land area of Naqu
Natural population growth rate
Common lung diseases in Naqu:
Tuberculosis, pneumonia, asthma, and lung cancer




Altitude of El Alto
Altitude of La Paz
El Alto-La Paz is located in the eastern part of the Bolivian Altiplano. Las Paz is the highest capital city in the world. Owing to its high altitude, it enjoys an unusual subtropical highland climate with rainy summers and dry winters. La Paz is an important political, administrative, economic, and sporting center of Bolivia, as well as a cultural city in Latin America, with a rich and diverse historical heritage left over from the colonial period. El Alto is the second largest city in Bolivia and the highest major city in the world. The metropolitan area has an unusual subtropical plateau climate with rainy summers and dry winters. In spite of its high altitude, the majority of Bolivians still choose to live in El Alto-La Paz where the economy is booming.
Population of metropolitan area
Altitude of La Paz
Altitude of El Alto
Percentage of population that is undernourished in Bolivia
Percentage of Bolivia's GDP spent on
healthcare (2018 data)
Diseases with the highest mortality rate in Bolivia: Coronary heart disease, lower respiratory tract infection, stroke
Bolivia has vigorously reformed its healthcare system in recent years, but overall it still lags behind most countries in Latin America. In 2019, there was only one doctor for every 1,000 residents. This shortage of medical professionals combined with a lack of professional health knowledge and a weak healthcare system meant Bolivia was severely hit by COVID-19. As Bolivia’s second largest metropolitan area, El Alto-La Paz bears responsibility for providing medical care for both the local and national population. In the post-pandemic era, there is an urgent need for ventilators that are reliable and easy to use. In fact, it can be a matter of life or death for residents on the plateau.

Mindray's R&D team took into account all the factors that could affect the ventilator in the process of research and development. In the face of the harsh plateau environment, the team analyzed its impact on the ventilator's materials and specification requirements for key components (valves, turbines, sensors), the key algorithm control performance, monitoring performance, maintenance of the system, and its alarms (such as air pressure and temperature changes, oxygen concentration monitoring, the gas output of the turbine).
The turbine is the power source for the flow and pressure outputs of the ventilator. The outputs are influenced by altitude, as the air becomes thinner higher up. As a therapeutic medical device, ventilators need to be reliable to prevent patients' conditions from deteriorating. This means that the rated output of the turbine needs to be turned up for ventilation at higher altitudes. But this leads to another problem: the heat caused by the increased power will shorten the service life of the turbine. To this end, by simulating different altitude environments, output pressures, turbine speeds, and temperatures, Mindray's R&D team finally succeeded in using active heat sinks to dissipate heat from the turbine, extending the service life of the turbine while ensuring reliable performance.
The monitoring of ventilator parameters plays an integral role in guaranteeing a patient's safety, and the monitoring of both tidal volume and oxygen concentration can be affected by high altitudes. Compared with areas at low altitude, the ventilator sensor can deviate by more than half in a low pressure environment at high altitude. This will cause high risks and non-controllability in therapeutic devices such as ventilators. To ensure an accurate monitoring of tidal volume and oxygen concentration, the R&D team set up an altitude compensation algorithm, enabling accurate gas delivery for patients. In view of the importance of altitude compensation, the R&D team set up dual atmospheric pressure sensors to optimize the monitoring of the ventilator at high altitudes. This means monitoring data can be backed up for mutual inspection and the altitude can be automatically calculated by the monitored atmospheric pressure, which ultimately ensures the accuracy and safety of altitude monitoring.
After designing and developing the ventilator adapted to high altitudes, the R&D team fully simulated and tested it in low-temperature and low-pressure environments to ensure it met the specifications and performance requirements. The device was able to work normally and meet clinical requirements at an altitude of up to 5,000 meters. And a ventilator that could function properly on high-altitude plateaus was born.
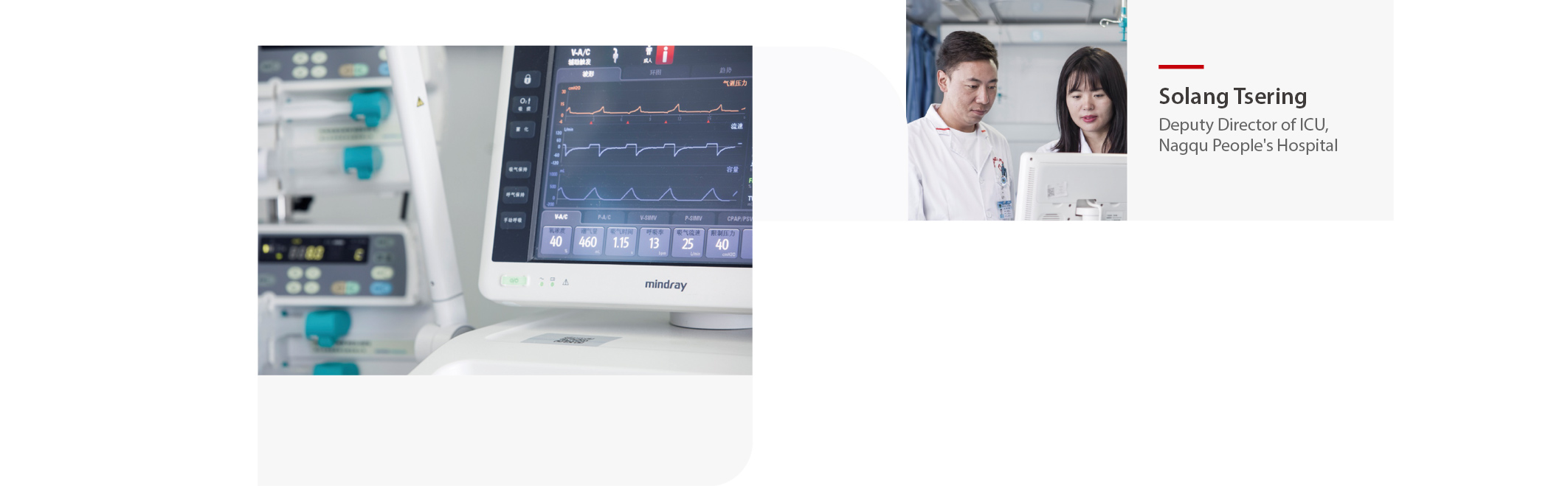
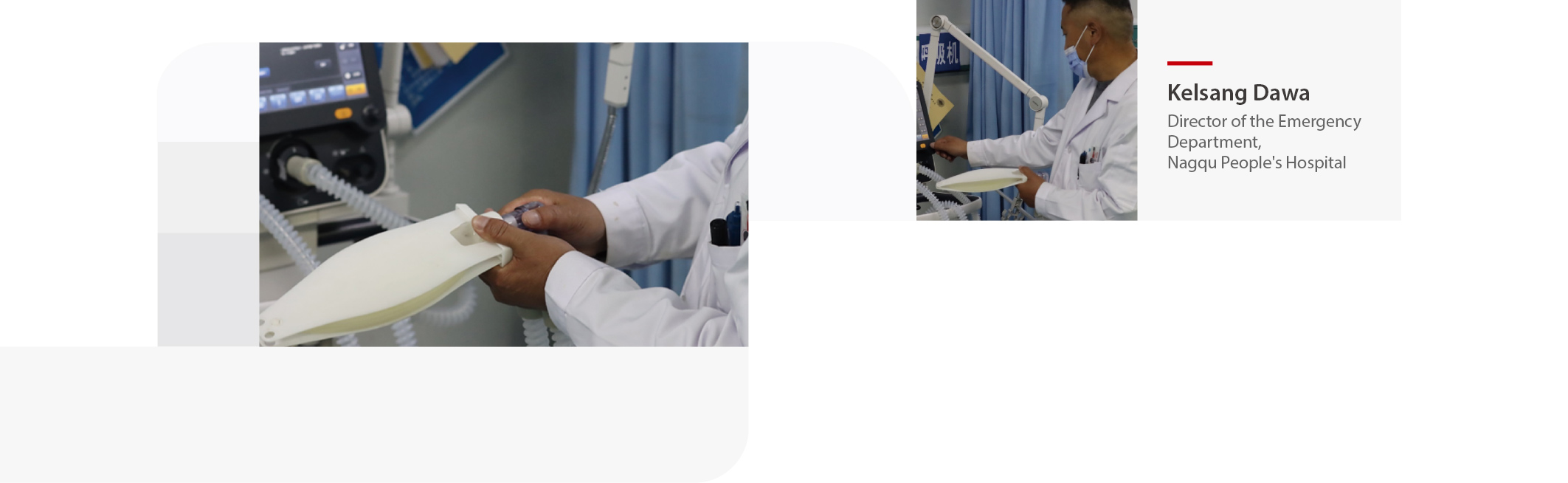
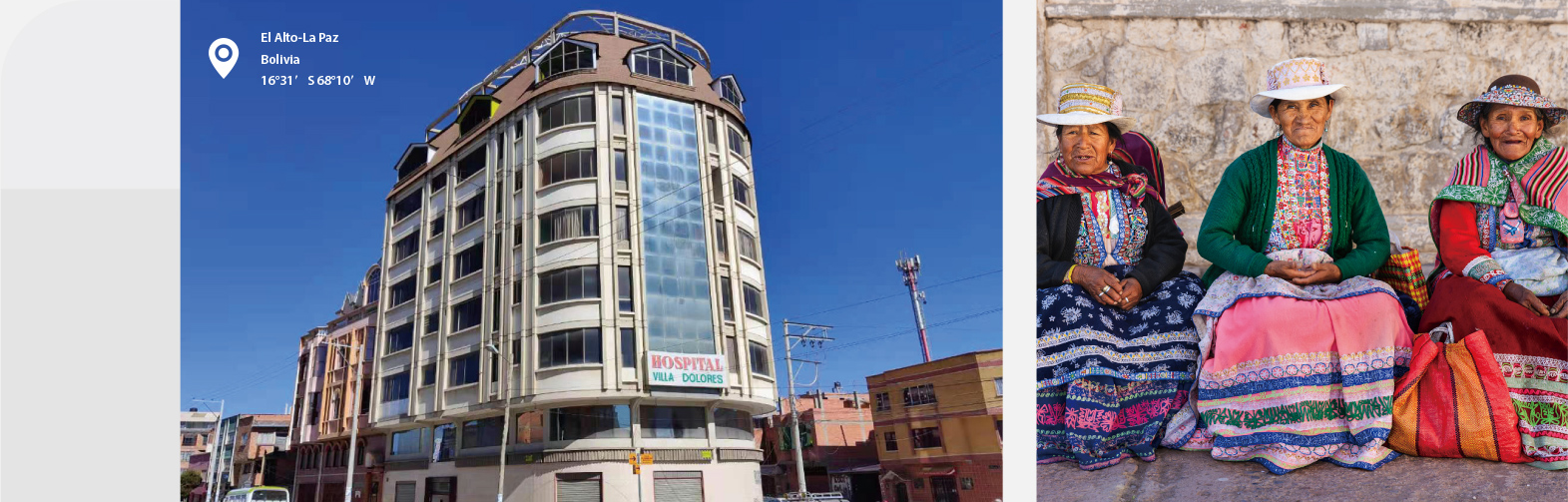
Located in Seni District, Naqu City, Nagqu People's Hospital is the only Grade A tertiary hospital in northern Tibet that integrates medical treatment, emergency care, prevention, health care, scientific research, and teaching. It is a lifeline for the 500,000 local residents.

Villa Dolores Hospital is located in El Alto, 4150 meters above sea level. The hospital currently has 60 beds, including 13 ICU beds. As a level 3 hospital by Bolivian hospital standards, Villa Dolores is committed to providing timely and reliable care for patients in the region.

Mindray is committed to bringing high-quality care to every corner of the world. Whether Naqu or El Alto-La Paz, we always align with our customers and strive to develop medical technology that can be successfully adapted to local environments.
In addition to providing devices, we pay extra attention to the special needs of healthcare professionals in remote areas for services and training. We make full use of online and offline channels to provide local medical staff with comprehensive, professional and detailed training and user services.
As we bring breath to new heights, there is warmth in places high and cold.