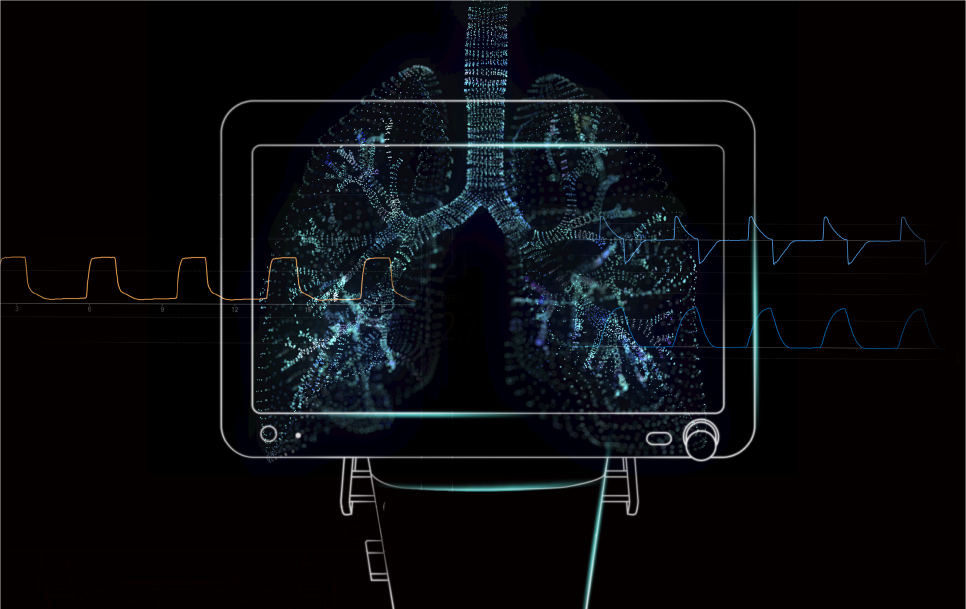
Europe is the epicenter of respiratory medicine in the world. The genesis of ventilation support theory began in Italy in the Renaissance period of the 16th century, along with Andreas Vesaliua's anatomical findings, while the knowledge about respiration and infectious diseases can be traced back to Hippocrates of ancient Greece. Today, it is home to the annual meeting of the European Respiratory Society (ERS), the largest respiratory summit in the world. Being admitted to major hospitals in Europe confirms its arrival in the top league of ventilator suppliers for a ventilator brand.
Many scholars believe that Western medicine originated in ancient Egypt and not in ancient Greece. This ancient Egyptian Ebers Papyrus, written around 1550 B.C., records probably the earliest inhalation therapy in human history.

The Bible records that the Prophet Elisha raising the son of the Shunamite by mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration.


Hippocrates in ancient Greece coined the term epidemic and introduced the concept of diagnosis, treatment, and healing of acute respiratory diseases such as pneumonia, pleurisy, pleural effusion, and upper respiratory obstruction in a medical treatise whose influence lasted.

Many scholars believe that Western medicine originated in ancient Egypt and not in ancient Greece. This ancient Egyptian Ebers Papyrus, written around 1550 B.C., records probably the earliest inhalation therapy in human history.

The Bible records that the Prophet Elisha raising the son of the Shunamite by mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration.

Hippocrates in ancient Greece coined the term epidemic and introduced the concept of diagnosis, treatment, and healing of acute respiratory diseases such as pneumonia, pleurisy, pleural effusion, and upper respiratory obstruction in a medical treatise whose influence lasted.
Facing the brutal impact of COVID-19 since 2020, many countries in Europe have seen multiple epidemiological peaks, causing significant pressure on hospital admissions and a severe shortage of medical ventilators. At those times, Mindray received product supply requests from many countries and customer's hospitals. Mindray made every effort to mobilize all resources to ensure the supply of ventilators and provided remote and offline clinical and operational maintenance support to assist European medical staff in treating COVID-19 patients. Many medical institutions and clinical experts recognized this effort.




There can be significant developments during the course of a pandemic. The respiratory medicine community has been the first to bear the brunt of the pandemic brought by the high transmissibility of the COVID-19 virus and rapid deterioration of the condition of patients. Medical professionals have deepened their discussion on ventilators' ease of use, efficiency, and pulmonary protection characteristics. In the future, achieving a balance between the safety and efficiency of the clinical application of ventilators and further lowering the barriers to ventilator use and training will be the issues that cannot be disregarded during intensive care ventilator development in the post-epidemic era.
Safety and Efficiency: From Dilemma to Coupling
The French writer Gustave Flaubert once said: "Science and art break up at the foot of the mountain and meet at the summit." Mechanical ventilation therapy is the art of "coupling" - ventilation modes coupled with clinical treatment demands, work of ventilators coupled with the patient's spontaneous breathing effort, parameterization coupled with the patient's pulmonary mechanical indices, timing of intubation and extubation coupled with the patient's vital signs et cetera. Behind the coupling is the dilemma between efficiency and safety.
However, with the help of IoT, algorithms, AI, and other advanced technologies, the medical world is also witnessing a watershed moment. In the future, the innovation of ventilators will focus on medical informatization and individual machine intelligentization to continuously relieve the burden on medical staff and provide patients with more accurate treatments to achieve better recovery.
By focusing on the concept of accurate lung protection, Mindray has striven to provide clinical decision support to the entire process of intubation - measurement and evaluation - ventilation support - extubation, to improve clinical safety. Based on bedside data integration with the backing from advanced algorithms, the ventilator decision-support tools help clinicians evaluate patient indicators more comprehensively. By identifying the patient's respiratory motions and evaluating lung re-expansion more accurately, the clinicians can select the most suitable treatments to facilitate recovery.










Of course, more powerful devices and more information do not mean increased requirements for operators. Instead, ventilators are moving toward smart closed-loop ventilation, just like smart cars being on the way to autonomous driving. By progressively achieving "automatic identification" of the patient's breathing pattern and "automatic adjustment" of ventilation parameters, the smart ventilators improve clinical efficiency and ventilator-patient synergy. With the help of smart ventilators, caregivers can better address many "conditions" in acute, anesthetized, and intensive care scenarios and reduce repeated adjustments of ventilation modes and parameters to guarantee patients' safety better.
By focusing on the concept of accurate lung protection, Mindray has striven to provide clinical decision support to the entire process of intubation - measurement and evaluation - ventilation support - extubation, to improve clinical safety. Based on bedside data integration with the backing from advanced algorithms, the ventilator decision-support tools help clinicians evaluate patient indicators more comprehensively. By identifying the patient's respiratory motions and evaluating lung re-expansion more accurately, the clinicians can select the most suitable treatments to facilitate recovery.
Of course, more powerful devices and more information do not mean increased requirements for operators. Instead, ventilators are moving toward smart closed-loop ventilation, just like smart cars being on the way to autonomous driving. By progressively achieving "automatic identification" of the patient's breathing pattern and "automatic adjustment" of ventilation parameters, the smart ventilators improve clinical efficiency and ventilator-patient synergy. With the help of smart ventilators, caregivers can better address many "conditions" in acute, anesthetized, and intensive care scenarios and reduce repeated adjustments of ventilation modes and parameters to guarantee patients' safety better.
Sharing, Communicating, Brainstorming and… INNOVATING!
The maturation of ancient Greek philosophy resulted from extensive and frequent cultural exchanges between the Mediterranean civilizations. As portrayed in Raphael's classic work of the utopia constructed in The Academy of Athens, progress comes from deep discernment about the unknown and integration of experience. In the complex field of intensive care medicine, we increasingly require a more professional communication platform.
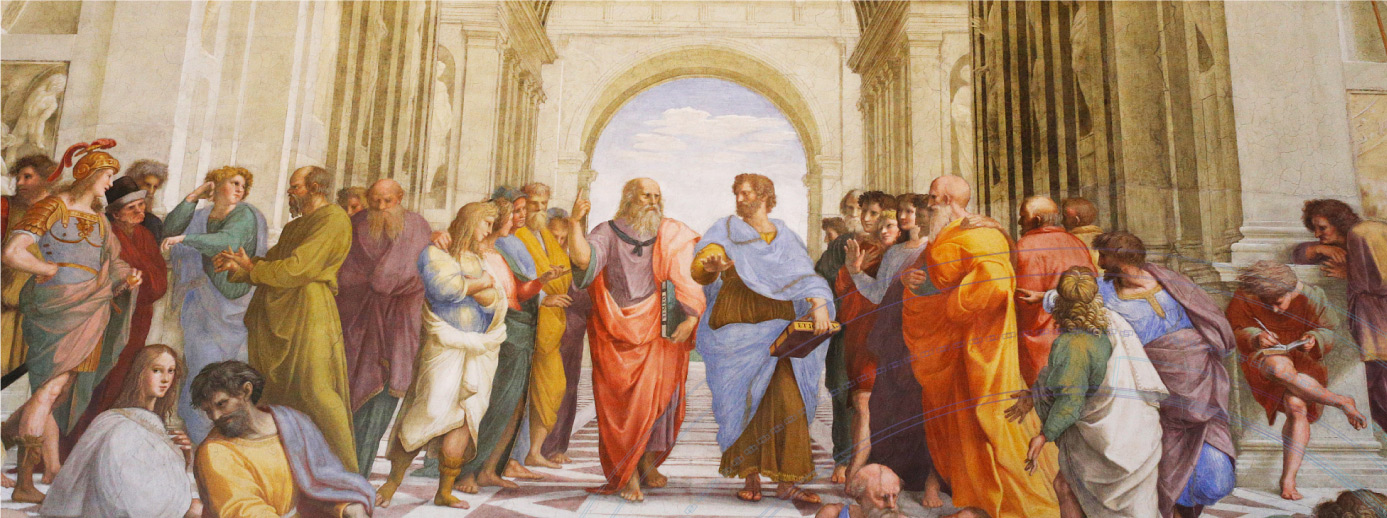

On the global medical frontline, Mindray has found that the clinical ventilation therapy routines in different countries and hospitals vary from one to another. Meanwhile, individual patient differences have also allowed doctors to gain additional insights during their clinical practices. In 2018, Mindray set out to create an "Academy of Athens" for acute, anesthetized, and intensive care, and the M-academy was born. It is a community for academic opinions, standard consensus, and information regarding rare and intractable diseases. It also enables mechanical ventilation treatment theory and practical experience to deposit training notes for respiratory medicine talents.
Mindray invites global experts to give webinars on various medical topics related to mechanical ventilation.


Mindray’s global ventilator proactive service plan.

Mindray shares the ventilator clinical application lectures via M-academy.
In addition to training and academic support, Mindray's user service team has launched a "Global Ventilator Support Program" to support clinical practices. While instructing users to operate and maintain the ventilators better, Mindray has also actively collected clinical use feedback to improve ventilators. For example, based on different use habits in different countries and regions, Mindray has modified and improved parts and breather valves, tubes, and other consumables of ventilators in order to make these devices more ergonomic, thus enabling medical staff to focus on patient care.

Mindray invites global experts to give webinars on various medical topics related to mechanical ventilation.

Mindray’s global ventilator proactive service plan.

Mindray shares the ventilator clinical application lectures via M-academy.
In addition to training and academic support, Mindray's user service team has launched a "Global Ventilator Support Program" to support clinical practices. While instructing users to operate and maintain the ventilators better, Mindray has also actively collected clinical use feedback to improve ventilators. For example, based on different use habits in different countries and regions, Mindray has modified and improved parts and breather valves, tubes, and other consumables of ventilators in order to make these devices more ergonomic, thus enabling medical staff to focus on patient care.
The value of innovation lies in enabling people to make better products and achieve better results. What is more invaluable is the wisdom and discernment to satisfy our endless imagination about the origin of life. Medical pioneers have done groundbreaking research to lay a solid foundation for modern medicine with sheer perseverance and painstaking hard work. Today, Mindray has inherited the enthusiasm and persistence of the pioneers to explore the informatization and intelligentization of ventilators. With data support platforms and more advanced data processing methods, Mindray has formed a closed data loop of treatments and clinical indications in order to improve the safety and ease of use of ventilators, giving more people access to high-quality ventilator treatments.