Understanding Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA): Principles, Applications, and Advances
Mindray 2024-11-15

Brief Introduction to Immunoassays
Immunoassay is a biochemical test used to detect the specific analyte based on antigen-antibody reaction. The analyte may commonly be proteins, hormones, metabolites, tumour markers etc.
Immunoassays involve a variety of different labels to allow the detection of antibodies and antigens. Labels are typically chemical-linked or conjugated to the desired antibody or antigen. Immunoassays are indispensable tools in the in vitro diagnostics (IVD) industry to diagnose a plethora of disease conditions which play a crucial role in patient care and treatment strategies.
Based on the detection label type used it is mainly classified into the following types.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Radio Immunoassay (RIA)
- Fluorescence Immunoassay (FIA)
- Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA)
Overview of Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA)
Chemiluminescence Immunoassay is a sensitive & advanced technique used to determine the concentration of specific analytes in samples according to the intensity of the luminescence that the chemical reaction emits.
In this technique, an enzyme converts a highly sensitive substrate into a chemiluminescent signal, which is emitted as photons of light. This light is then amplified and detected by a photomultiplier tube (PMT), providing a precise measurement of the analyte’s concentration.
CLIA has a wide range of applications in IVD, Research and Pharma industries making it a versatile tool in laboratory medicine.

It is widely employed for:
- Thyroid function
- Cancer markers
- Reproductive hormones
- Cardiac markers
- Diabetic markers
- Infectious diseases
- Bone metabolism
- Anemia diagnosis
- Growth hormone systems
- Allergic reactions.
Compared to traditional techniques like RIA and FIA, CLIA offers several advantages, including:
- High sensitivity: It can detect even minute quantities of analytes.
- Wide assay menu: It can be adapted to measure a broad range of analytes.
- Stable results: It provides reliable and consistent results.
These attributes have made CLIA a preferred choice in the IVD industry, where accuracy and precision are paramount.
Section 1: What is Chemiluminescence Immunoassay?
Definition and basic principle
Chemiluminescence Immunoassay is a sensitive and precise analytical technique used to determine the concentration of specific analytes in the samples. It operates on the principle that certain chemical reactions emit light, a phenomenon known as Chemiluminescence.
In CLIA assay, first, the sample which contains antigen is mixed with a reagent containing labelled antibody to create a chemical complex. When a highly sensitive substrate is mixed with this chemical complex, it results in the production of light (Luminescence) which is further amplified and detected by the photomultiplier tube (PMT).
The amount of light detected by the photomultiplier tube is directly or indirectly proportional to the concentration of the analyte based on the assay type.

Comparison with other immunoassays like ELISA, RIA, and FIA
Comparison of CLIA with ELISA
ELISA or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is one of the earliest immunoassay methods used to detect and count certain antibodies, antigens, proteins or hormones in liquid samples. It involves a colorimetric detection process where the intensity of the color change is measured using a photometer. Although widely used, ELISA has many limitations when compared to advanced CLIA. This method involves manual processes, a limited assay menu with low sensitivity and is time-consuming. It requires a dedicated and well-trained person to process the samples.
Comparison of CLIA with RIA
RIA or Radio Immunoassay relies on the detection of radioactivity using a gamma counter. While it was a groundbreaking technique in its time, RIA has fallen out of favor today. This is due to the limited assay menu and involvement of radioisotope which is carcinogenic. CLIA is safer than RIA as it doesn’t involve the use of radioactive isotopes which can pose health risks.
Comparison of CLIA with FIA
FIA or Fluorescence Immunoassay analyzers detect fluorescence emission through a photodiode detector, which is also less suited for high-volume testing. When compared to CLIA, FIA is less suited for high-volume customers due to its limited assay menu. operate in batch mode and have a higher cost per test, making them less practical for large-scale applications compared to CLIA. CLIA typically offers higher sensitivity and a wider dynamic range.
Overall, CLIA has emerged as a preferred method for many immunoassay applications due to its sensitivity, specificity, and versatility. Its ability to provide accurate and reliable results has made it an invaluable tool in various fields, including clinical diagnostics, research, and drug development.
Section 2: CLIA Analyzers
Types of CLIA Analysers : Manual, Semi Automated and Automated
CLIA Analyzers come in various configurations to cater to different laboratory needs and testing volumes. It can be broadly categorized into three main categories:
Manual CLIA analyzers:
Manual CLIA analyzers offer flexibility and are cost-effective for smaller laboratories with lower testing volumes. It is suitable for specialized tests where automation is not necessary or is not feasible. However, it requires manual intervention from laboratory technicians at most of the steps. This includes adding reagents, mixing samples, incubating, and reading results which makes it labor-intensive & prone to human error.
Automated CLIA analyzers:
Automated CLIA analyzers are self-sufficient machines which can manage everything from sample loading to reagent dispensing to result reporting. These systems are designed to process large numbers of samples with maximum efficiency and high precision. The potential for high-throughput testing with minimal human intervention makes them an ideal choice for large laboratories, hospitals, reference labs etc.
Semi-automated CLIA analyzers:
Semi-automated CLIA analyzers combine elements of both manual and automated CLIA analyzers. In these analyzers, some of the steps are automated while some steps like sample preparation and result interpretation require manual interventions. It is generally used in medium-sized laboratories as it offers a balance between flexibility and efficiency and is cost-effective.
Key features and advantages of automated CLIA analyzers
CLIA analyzers have the following key features and advantages.
- CLIA analyzers are fully automated and have random access with varied throughput ranges of 100 to 200 to 400 to 900 tests per hour.
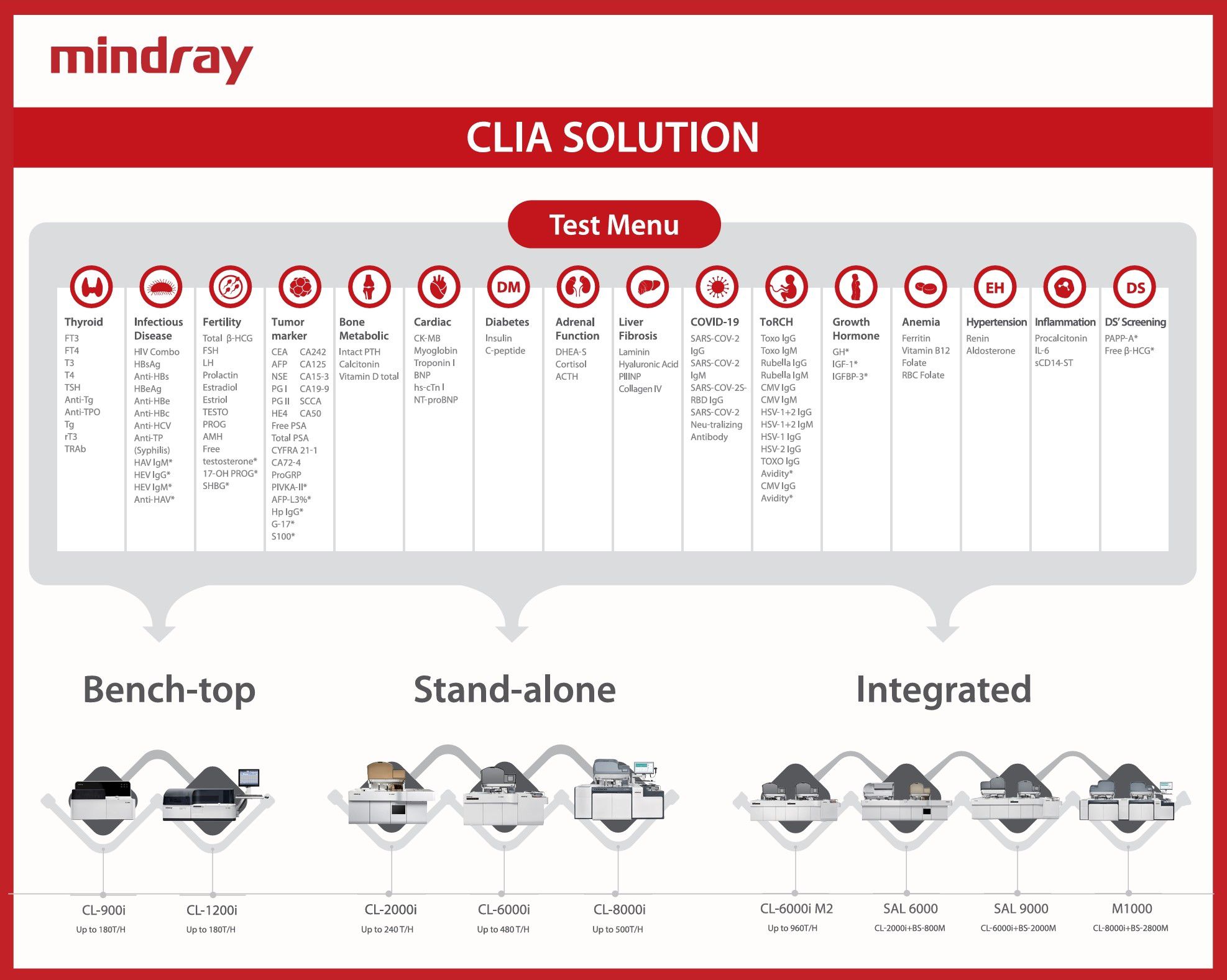
- The analyzer assay menu commonly includes Thyroid function tests, Fertility markers, Cancer markers, Cardiac Markers, Bone markers, Anemia panel, Infectious diseases, Diabetic profile and Liver fibrosis parameters.
- The analyzers are fully automated with a sample loading system that can simultaneously handle anywhere from 50 to 1000 samples without human intervention.
- The analyzer utilizes sensitive substrates like AMPPD, Acridinium Ester, Luminol etc.
- Reagent packs are available with varied pack sizes starting from 30 to 500 tests per pack, which suits low to high-customer segments.
- The reagents, controls, calibrators and consumables can be used with all the models of the same brand.
- The current CLIA analyzers in the market can be further integrated with Chemistry analyzers for effective utilization.
- Bi-directional LIS facility is available in CLIA analyzers.

Example of a popular analyzer
CL-900i Chemiluminescence Immunoassay System
CL-900i Chemiluminescence Immunoassay System is a popular choice for medium-sized and large-capacity laboratories. With the capability to handle up to 180 test per hour(T/H) and the flexibility to expand further, the CL-900i is engineered to excel in environments where speed, accuracy, and reliability are paramount.

What makes CL-900i a popular choice?
An exceptional throughput, accuracy, compact design and flexibility to integrate with other lab equipment makes it an ideal choice for laboratories with limited space but high- testing demands.
Unmatched Throughput: The CL-900i offers a throughput of up to 180 tests per hour, with 50 sample positions and 15 reagent positions, allowing it to handle a wide range of assays efficiently.
Reliable Results: The CL-900i is equipped with highly polished steel probes that feature a cone-head design and high-pressure interior washing. This minimizes carry-over, ensuring consistent and reliable results for patients.
Compact Design: Despite its impressive performance, the CL-6000i maintains a compact footprint, making it suitable for various lab environments. Its small size doesn't compromise on capacity or speed, delivering a perfect balance of performance and efficiency.
Seamless Integration: Seamlessly integrate with other lab systems to streamline workflows and optimize resource utilization. This enhances its scalability and makes it adaptable to the growing needs of laboratories.
Enhanced Sample Handling: The CL-900i comes with a patented sample basket design that ensures safe transportation and accommodates up to 600 sample positions. This provides significant capacity and long walk-away time, enabling lab technicians to focus on other critical tasks while the analyzer operates smoothly.
Section 3: Applications of CLIA
CLIA has a wide range of applications for detecting and monitoring various conditions. Some of the key applications include:
Infectious diseases
CLIA is extensively used in the detection of infectious diseases. It identifies various pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, etc., by detecting specific antigens or antibodies in the samples.
Hormone Levels
The accuracy and sensitivity of CLIA make it a preferred choice for assessing hormone imbalances. It is used to measure reproductive hormones, thyroid hormones, adrenal hormones etc.
Tumor Markers
CLIA plays a vital role in the screening and monitoring of tumor markers and cancer-specific antigens. Early detection of these markers can significantly improve patient outcomes by enabling timely intervention.
Metabolic disorders
CLIA is also employed in the diagnosis of metabolic disorders by measuring specific metabolites and enzymes like glucose, insulin, lipid profile etc.
Vitamin deficiency
The precision of CLIA ensures accurate monitoring of vitamin deficiencies like Vit D, Vit B12 etc.
HHH Marker
CLIA is also used for a triple H test used in the screening of HIV, HBV, and HCV infections.
Pregnancy marker
CLIA is used to detect pregnancy markers hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin). CLIA is commonly used to detect pregnancy markers such as hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin).
Use in thyroid function tests
Thyroid function test is the most common and high-volume parameter which is processed in any immunoassay analyzer.
Thyroid parameters can be classified based on disease conditions.
- Thyroid Function Test: T3, T4, FT3, FT4 and TSH
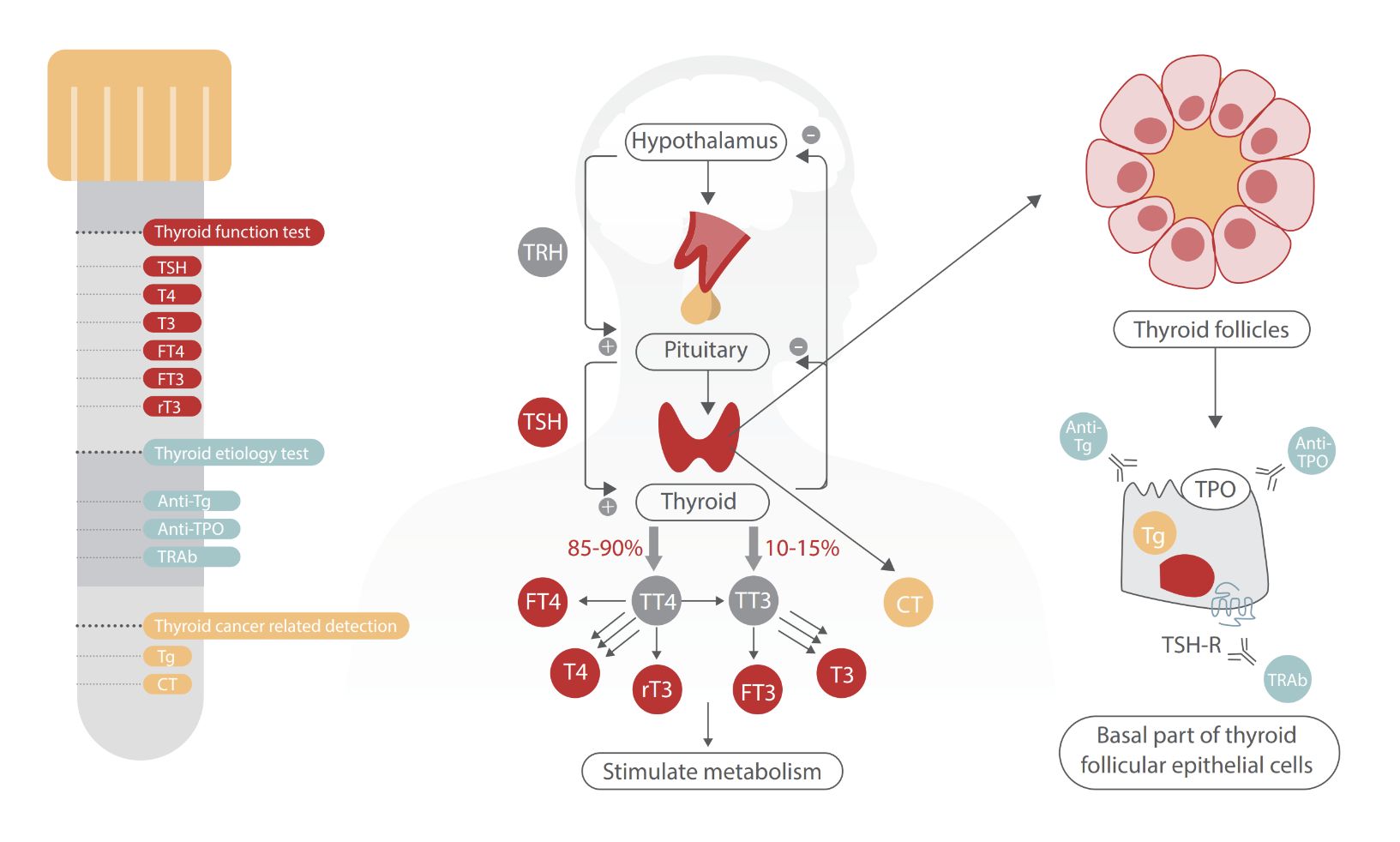
- Thyroid Autoimmune Disease: Anti TG, Anti TPO and TRAb
- Thyroid Cancer: TG and rT3
Above all parameters can be processed using CLIA analyzers both in serum and plasma. Among the above parameters, TSH plays very important role in the diagnosis and monitoring of these disease conditions. TSH parameter in CLIA analyzers is third generation assay with functional sensitivity of < 0.008 uIU/ml. Hence CLIA technology is the most preferred method to detect thyroid function tests.
Section 4: Advantages of CLIA
Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA) has emerged as a powerful technique in clinical diagnostics due to its numerous advantages which are as follows:
- Sensitivity: One of the significant advantages of CLIA is its high sensitivity. This allows the detection of very low concentrations of analytes.
- Specificity: CLIA is highly specific, minimizing the risk of false positive or negative results. This ensures accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Rapid Turnaround Time: CLIA provides quick results, which is crucial in clinical settings where timely diagnosis can significantly affect patient outcomes.
- Integration with Total Laboratory Automation (TLA): CLIA can be seamlessly integrated into TLA systems, further enhancing efficiency and reducing manual labor. This can improve laboratory workflows and reduce errors.
- Wide Assay Menu: CLIA offers a broad range of assays, allowing for the simultaneous detection of multiple analytes.
- Safe & Environment Friendly: CLIA is safer and more environmentally friendly for laboratory personnel. It eliminates the need for handling and disposing of hazardous radioactive substances, making it a preferred choice in modern laboratories.

Chemiluminescence Immunoassay is a method used to determine the concentration of specific analytes in the samples according to the intensity of the luminescence that the chemical reaction emits.
In Chemiluminescence technology first, the sample which contains antigen is mixed with a reagent containing labelled antibody to create a chemical complex.
When a highly sensitive substrate is mixed with this chemical complex, it results in the production of light (Luminescence) which is further amplified and detected by the Photomultiplier tube (PMT).
The amount of light detected by the photomultiplier tube is directly or indirectly proportional to the concentration of the analyte based on the assay type.
CLIA has a wide range of applications in IVD, Research and Pharma industry. It has many applications in laboratory medicine for diagnosing various diseases, including Thyroid function, Cancer markers, Reproductive hormones, cardiac markers, Diabetic markers, infectious diseases, bone metabolism, anaemia diagnosis, growth hormone systems and allergic reactions.
ELISA is the most conventional and traditional method which has many limitations on sensitivity, specificity, assay menu, manual interventions and turnaround time (TAT).
One of the major differences between ELISA and CLIA is the final detection method. In ELISA, the intensity of the color change is measured whereas in CLIA, the intensity of the emitted light (Luminescence) is measured through a photomultiplier tube (PMT) which provides highly sensitive and stable results when compared to ELISA.
Hence, CLIA is the most preferred method when compared to the conventional ELISA method due to its high sensitivity, high specificity, wide assay menu and improved TAT.
The cost of CLIA analyzers varies according to their throughput segment and additional features.
Yes. Thyroid function tests can be performed using CLIA technology.
The integration of chemistry and immunoassay into one system has captured the direct attention of large-scale clinical laboratories.
The integrated instruments offer the following benefits to large-scale Laboratories:
- Reduces the hardware footprint with more operational benefits.
- Single tube processing
- Broader test menu
- Increased sample loading capacity
- Increased walkaway time
- Reduction in the periodic maintenance
- Better planning on the reagent and consumables inventory