Understanding Anemia: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Solution Options with Mindray
Gaurav Kumar, Deputy Product Manager- CLIA, Mindray India

Anemia is a prevalent blood disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body doesn't have enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to its tissues. While anemia is a common condition, it can significantly impact an individual's quality of life if left untreated. In this article, let’s explore the various causes, symptoms, treatment, and Diagnosis options for anemia by Mindray. The global Anemia Market was valued at USD 7,832.8 million in 2023 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 7.3% over 2024-2030.
Causes of Anemia:
Anemia can be caused by several factors, including:
Iron Deficiency: This is the most common cause of anemia worldwide. Iron is essential for producing hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood. A lack of iron in the diet or poor absorption of iron by the body can lead to iron deficiency anemia.
Vitamin Deficiency: Deficiencies in vitamin B12 and folate (vitamin B9) can also cause anemia. These vitamins are necessary for the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. A diet lacking in these vitamins or conditions that affect their absorption, such as certain gastrointestinal disorders, can lead to vitamin deficiency anemia.
Chronic Diseases: Chronic conditions such as kidney disease, cancer, HIV/AIDS, and inflammatory diseases can interfere with the body's production of red blood cells, leading to anemia.
Genetic Disorders: Some individuals inherit genetic disorders that affect the production or structure of hemoglobin, such as sickle cell anemia and thalassemia.
Symptoms of Anemia:
The symptoms of anemia can vary depending on its underlying cause and severity.
Common symptoms include: Fatigue and weakness, Shortness of breath, Dizziness or lightheadedness, Pale skin, Cold hands and feet, Chest pain, Headaches, Irregular heartbeat, Brittle nails, Cognitive problems, such as difficulty concentrating.It's essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of these symptoms, as they can also be indicative of other health conditions.
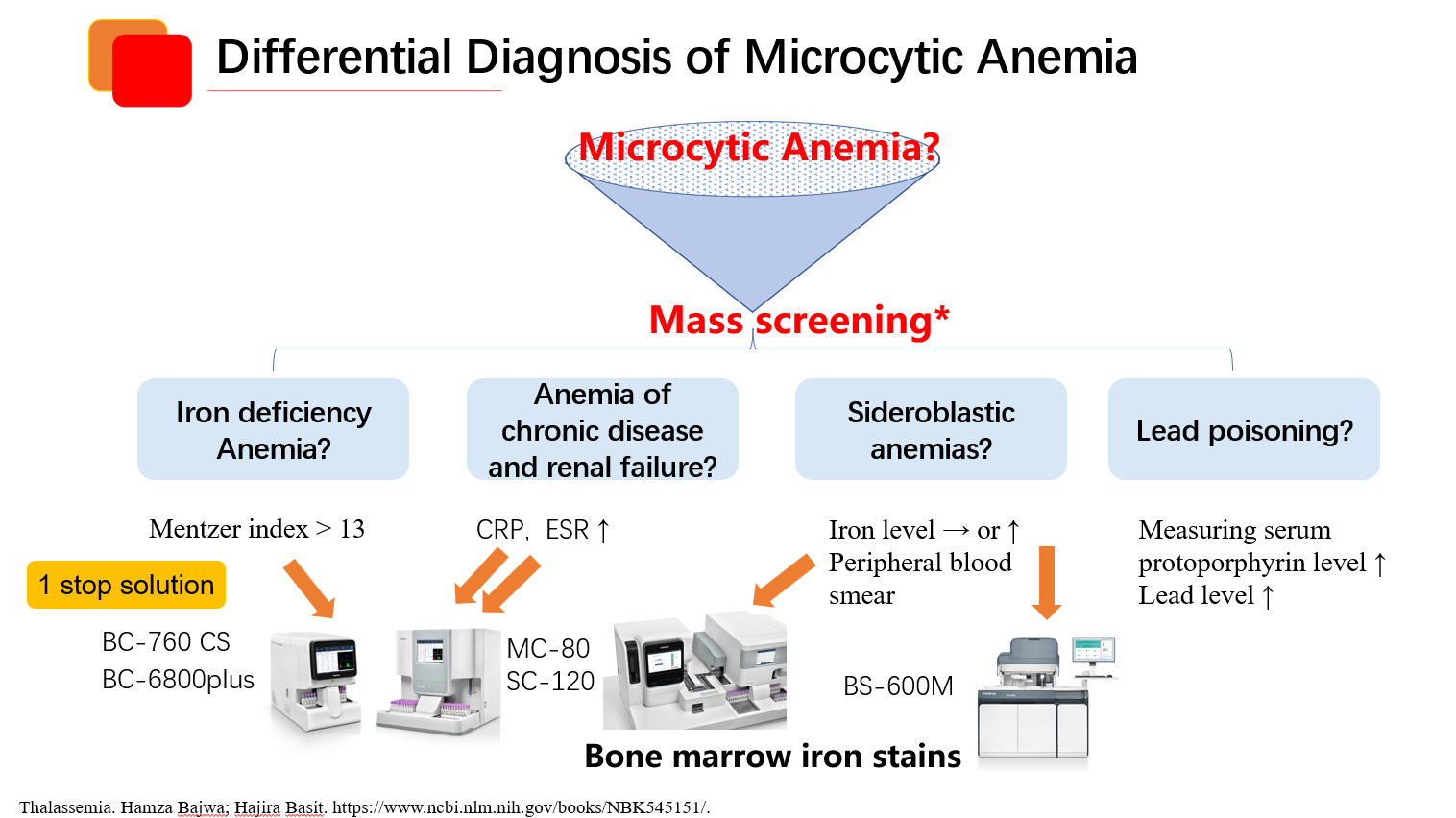
Mindray Solution for Anemia:
The Mindray Anemia Assay is versatile across all series of platforms, catering to a wide range of throughput needs, from moderate to high, ensuring flexibility and efficiency tailored to your requirements.
Mindray offers the Anemia Total Solution, providing efficient disease identification and treatment guidance. Our Anemia solution assay includes tests for Ferritin, Vitamin B12, Folate, and RBC Folate, boasting exceptional precision.
For Folate testing sample required is 80μL and is compatible with serum and plasma samples only. It maintains stability on the shelf for 12 months at 2~8℃. The expected values for Serum Folate range from 3.20 to 19.60 ng/mL and RBC Folate:119.47~822.63 ng/mL.
For Vitamin B12 testing sample required is 50μL of serum or plasma. It remains stable on the shelf for 12 months at 2~8℃. The expected values for Vitamin B12 range from 180 to 916 pg/mL.
For Ferritin testing sample required is only 15 μL of either serum or plasma. It remains stable on the shelf for 18 months at 2~8℃.
Expected values vary by gender: for males, the range is 27 to 375 ng/mL, and for females, it's 12 to 135 ng/mL.

For Vitamin B12 testing sample required is 50μL of serum or plasma. It remains stable on the shelf for 12 months at 2~8℃. The expected values for Vitamin B12 range from 180 to 916 pg/mL.
For Ferritin testing sample required is only 15 μL of either serum or plasma. It remains stable on the shelf for 18 months at 2~8℃. Expected values vary by gender: for males, the range is 27 to 375 ng/mL, and for females, it's 12 to 135 ng/mL.
Treatment:
Iron Supplementation: For iron deficiency anemia, iron supplements may be prescribed to replenish the body's iron stores. It's essential to follow the dosage and instructions provided by a healthcare professional, as excessive iron supplementation can have adverse effects.
Vitamin Supplements: Vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies can be treated with supplements or injections to restore normal levels of these vitamins in the body.
Treating Underlying Conditions: If anemia is caused by an underlying chronic disease or genetic disorder, treating the underlying condition is essential to manage the anemia effectively.
Blood Transfusion: In severe cases of anemia, particularly those caused by acute blood loss or chronic conditions, a blood transfusion may be necessary to replenish red blood cell levels quickly.
Dietary Changes: In cases where anemia is caused by nutritional deficiencies, making dietary changes to include iron-rich foods (such as red meat, leafy greens, and fortified and foods rich in vitamin B12 and folate (such as eggs, dairy products, and leafy greens) can help improve red blood cell production.
Conclusion:
Anemia is a common blood disorder that can have a significant impact on an individual's health and quality of life if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for anemia is essential for effective management and prevention. If you suspect you may have anemia, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes, many individuals with anemia can effectively manage their condition and improve their overall well-being.