Authored By: Yun XU, Lu CAI
Hospital Name: Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital
Instruments and Methods:
- Mindray Resona 7
- Probe SP5-1U
- A supine or lateral position should be taken

Patient Histroy:
- Female
- Age 26
- Complaint: been tired for over 20 years
Physical Examination Findings:
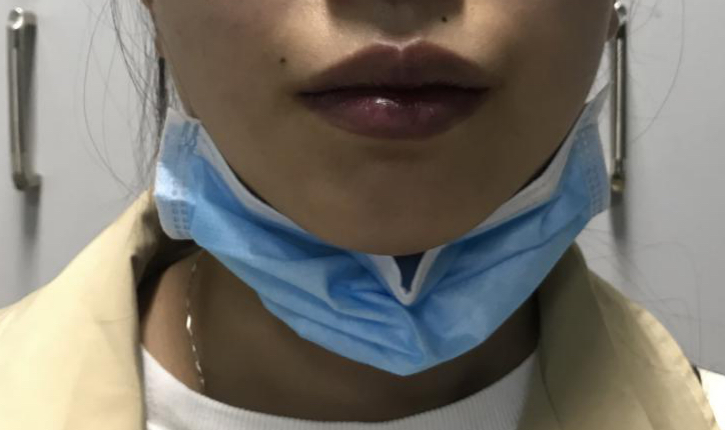
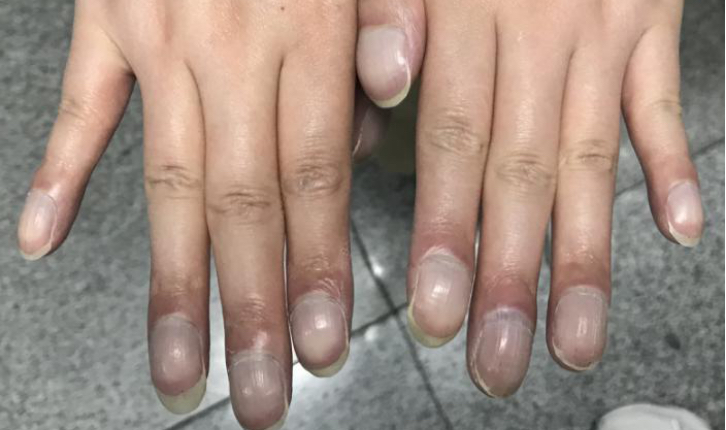
The patient's lips were purple and had distinct clubbed fingers.
Ultrasound findings:

The normal tricuspid valve structure was replaced by thick and dense hyperechoic tissue. RV: right ventricle, RA: right atrial, LV: left ventricle, LA: left atrial







Accordingly, this patient should be diagnosed TA, right ventricular dysplasia, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect and patent ductus arteriosus.

Tricuspid Atresia (TA) is an acyanotic congenital heart disease characterized by total agenesis of the tricuspid valve. That is, there is no communication between the right atrium and ventricle. The pathogenesis is not fully understood but maybe is due to the disruption of the normal development of the atrioventricular valves from the endocardial cushion. The incidence of TA accounted for 1% ~ 3% of congenital heart disease. It is the third most common cardiac malformation in cyanosis, after tetralogy of fallot and transposition of the great vessels.
Hemodynamics
TA, where blood flow does not enter the right ventricle from the right atrium, must be accompanied by other abnormalities.
Shunt of atrial level: blood from the right atrium enters the left atrium through anatrial septal defect or patent foramen ovale , blood oxygenation in the left ventricle are low, and the patient has cyanosis.
Ventricular level shunt: TA usually accompanied by ventricular septal defect. Most of the blood in the left ventricle enters the aorta during contraction, while the other part enters the right ventricle through a defect and returns to the left atrium through pulmonary circulation.
Arterial level shunt: left ventricular blood entering the aorta and through the patent ductus arteriosus to the pulmonary artery or through the bronchial artery into the lungs, right ventricular dysplasia, only a residual cavity.
Left ventricular dilatation: the left ventricular system receives both systemic and pulmonary blood, and the load is heavier, so the left ventricle is obviously enlarged.
Diagnosis
Echocardiography is the best tool for the diagnosis of TA. It is convenient, economical and effective. Two-dimensional echocardiography would show an inactive tricuspid valve with abnormal thickening and echogenicity, discordant sizes of the ventricular cavity with the left ventricle being larger than the right. and color flow doppler would show absent flow across the tricuspid valve. TA is often accompanied by other abnormalities, In this case, the diagnosis was TA with right ventricular dysplasia, patent ductus arteriosus,ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, and persistent left superior vena cava. The echocardiography can detect these abnormalities early, providing useful information for early diagnosis, operation planning, and evaluation of prognosis.
Treatment & prognosis
There are several subtypes of this disease with varied clinical presentations based on the degree of pulmonary blood flow. Surgical treatment of TA depends on its severity and the presence of other heart defects. This lesion carries a very high mortality rate if there is no intervention during the first year of life.
References:
1. Berg C , Lachmann R , Kaiser C , et al. Prenatal diagnosis of tricuspid atresia: intrauterine course and outcome.[J]. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology,2010, 35(2):183-190.
2. Sumal A S , Kyriacou H , Mostafa A M H A M .Tricuspid atresia: Where are we now?[J]. Journal of Cardiac Surgery,2020(1):1-9.
3. Brown J W , Heath D , Morris T L , et al.TRICUSPID ATRESIA[J]. British Heart Journal, 1956, 18(4):499.
4. 贾春红, 莫莉, 郑春华,等. 超声心动图诊断三尖瓣闭锁的价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2019, 35(05):38-40.
