
Authored By:Ren Min, He Ping
Hospital Name: Shanghai First Maternal and Infant Hospital
Instrument: Resona 7 system (Mindray Medical International, Shenzhen, China)

Editor's note:
Female pelvic floor dysfunction disease is an umbrella term for a series of pelvic floor structural and functional disorders, including stress urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, etc.,which will affect patients' quality of life and physical and mental health. So how can ultrasound assist in the diagnosis and treatment plan of pelvic floor diseases? Please see the following case:

Current medical history:
- Female
- Age 63
- self-conscious vaginal foreign body prolapse with frequent micturition and urgent micturition for more than 2 months
- POP-Q Score: Aa+3, Ba+4, C: +3, Ap-2, Bp+1, D-3, TVL7cm, h3.5cm and pb:2.5cm
- Previous history of myomectomy
- Birth History:1-0-1-1
Ultrasound Findings
The bladder neck is located 21.2mm above the pubic symphysis at rest, the uterus is located 27.0mm above, and the rectum is located 10.8mm above (see Figure 1).
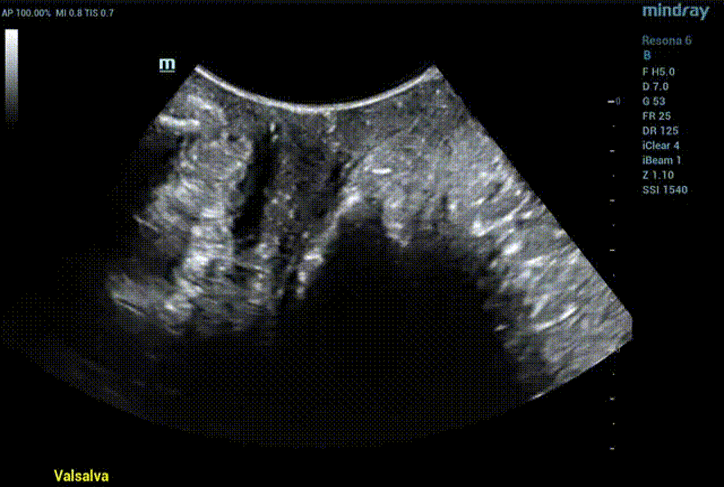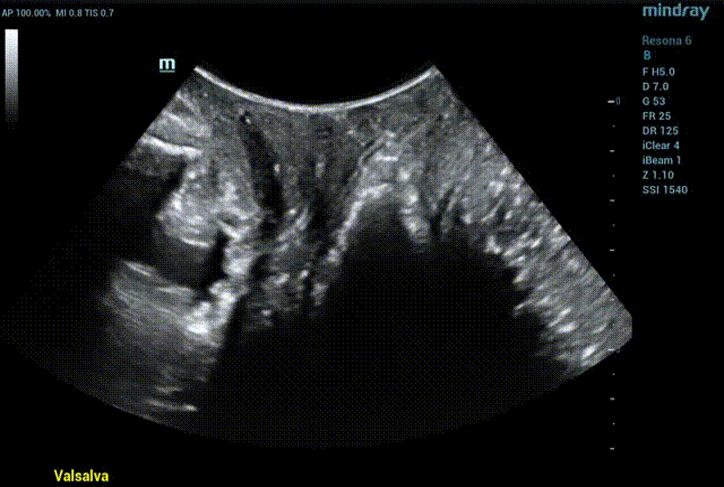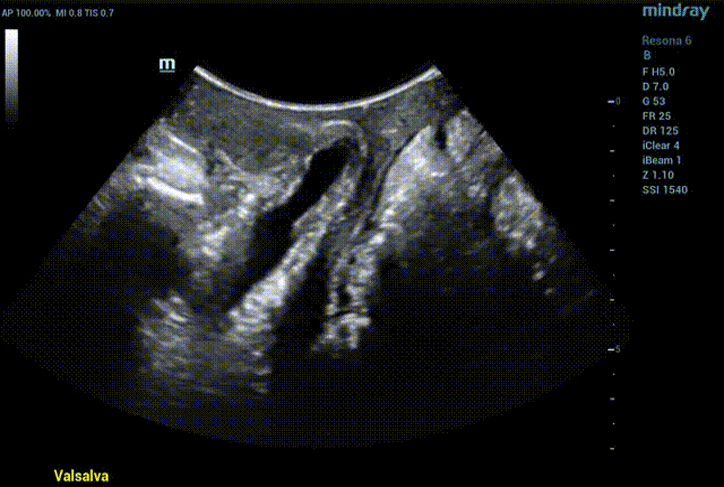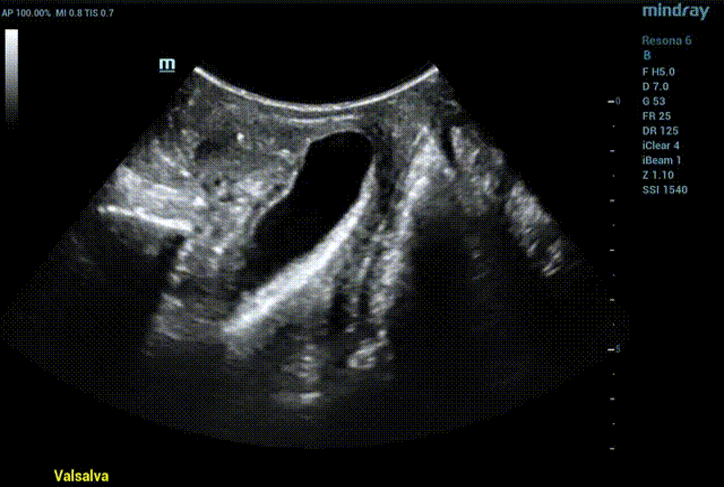
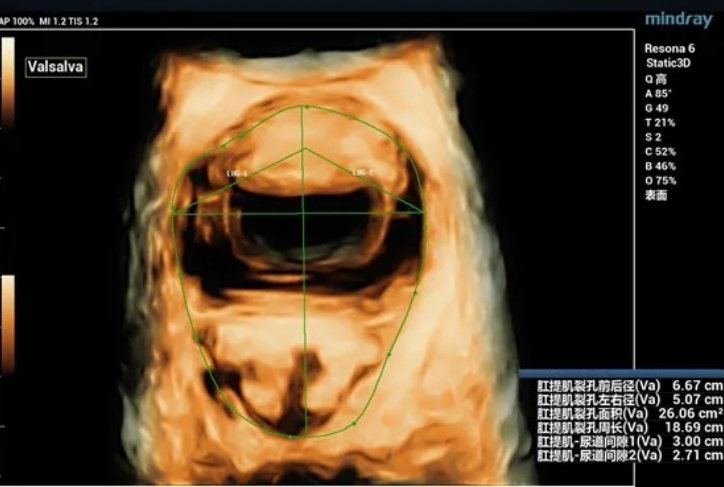
During maximal Valsalva maneuver, the bladder neck is 14mm below the pubic symphysis , the lowest point of bladder is 16.9mm below, the uterus is 7.3mm above and the rectum is 10.4mm below. The levator ani hiatus is 26.06cm2 (see Figure 2).
In the state of anal contraction, the levator ani is continuous, The internal and external anal sphincters are intact.
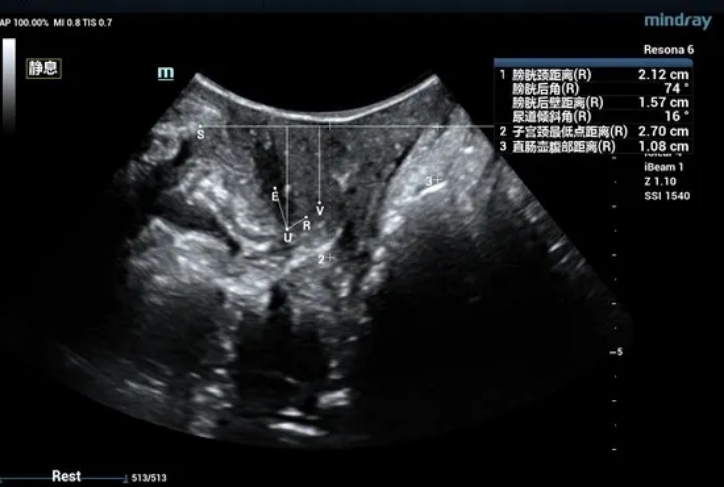
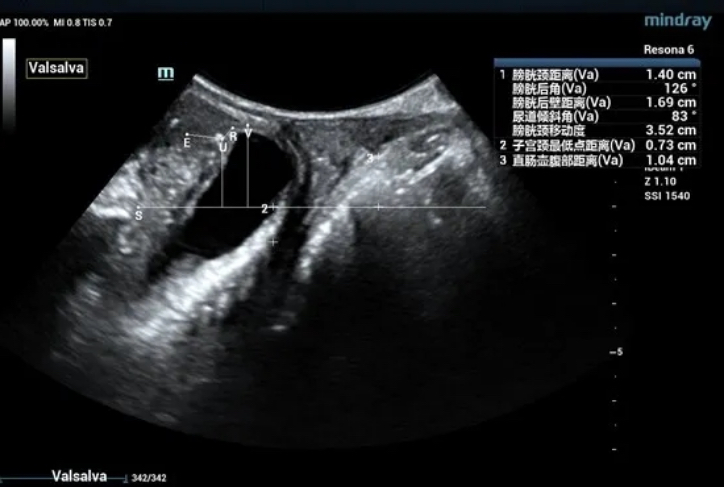
Ultrasound impression
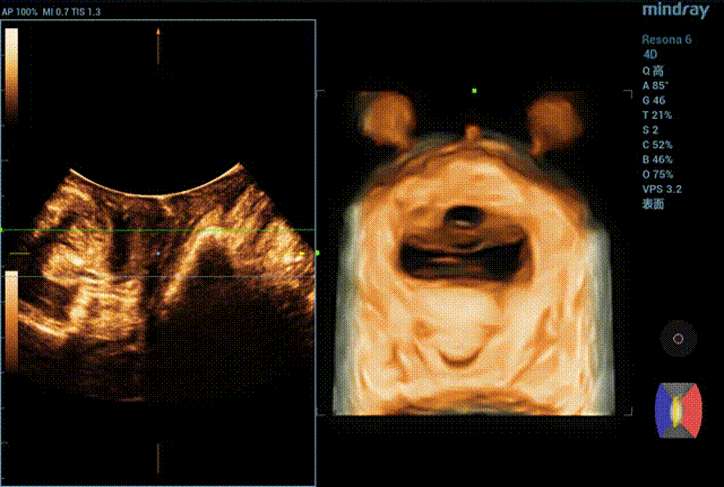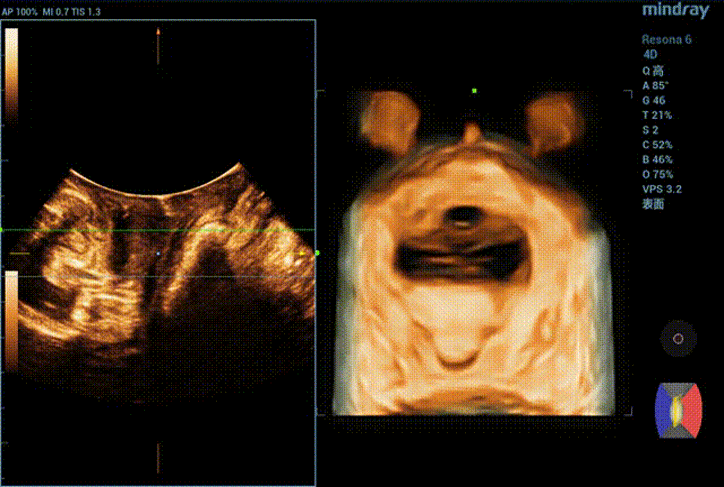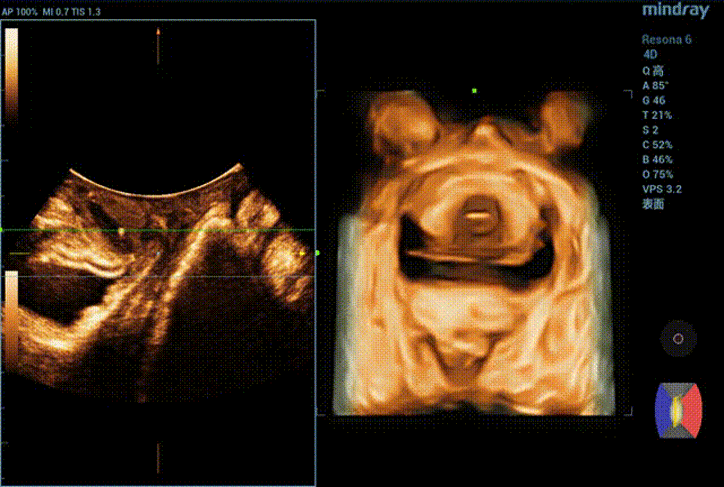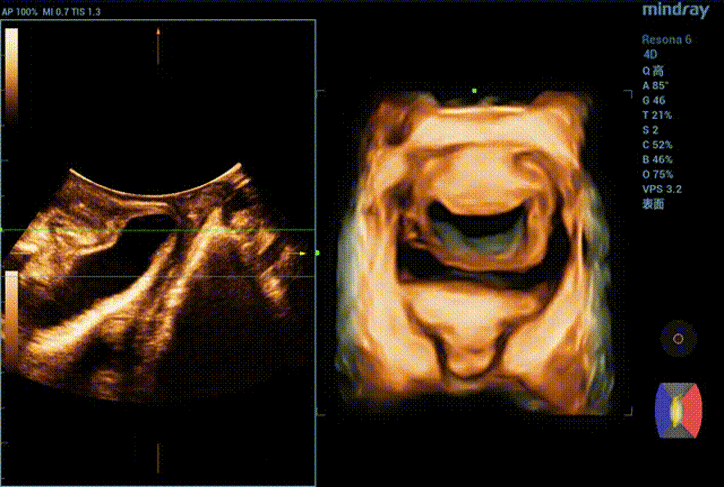
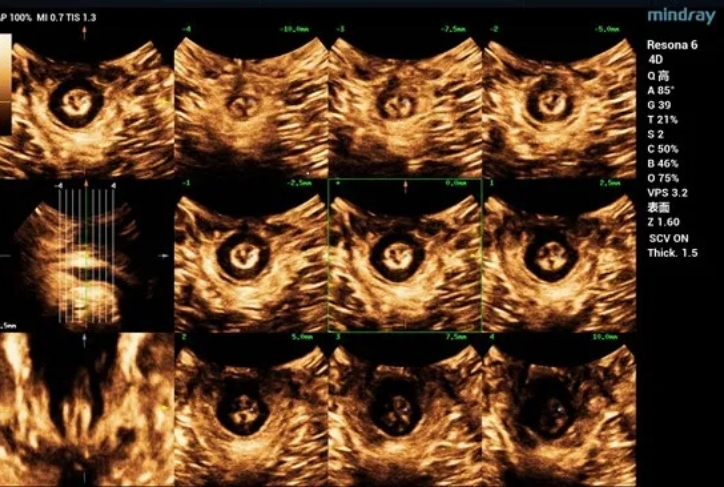
Obvious cystocele, increased mobility of bladder neck, increased urethral rotation angle, increased area of levator ani hiatus (see Figure 6 and Figure 7).
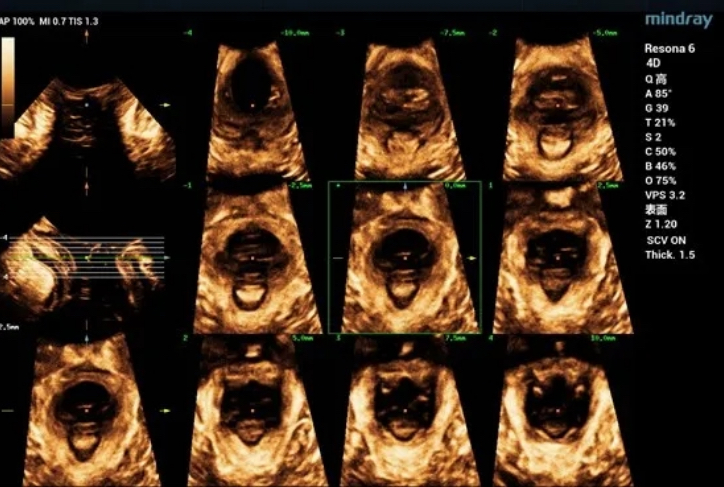
MRI diagnosis
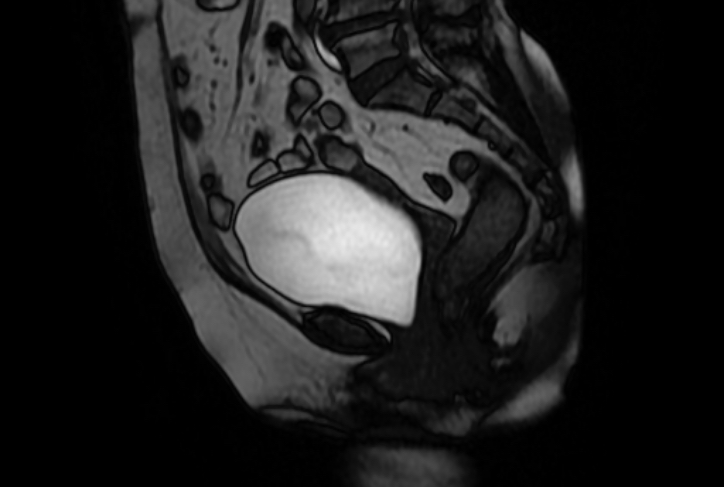
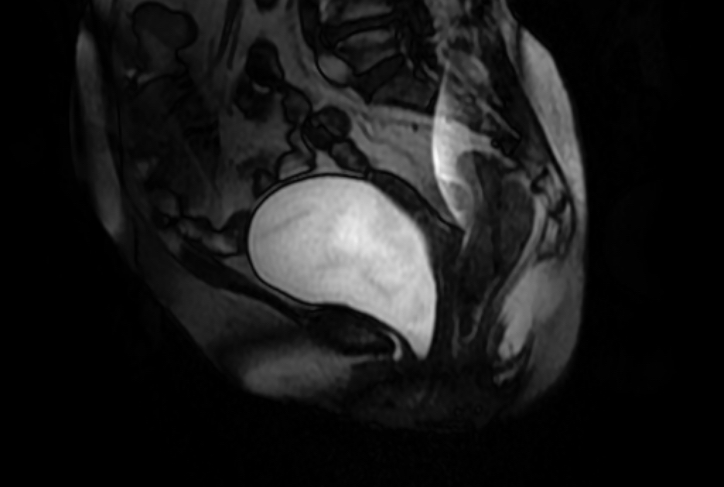
Preoperative Diagnosis: Vaginal anterior wall prolapse III° and vaginal posterior wall prolapse II°. Laparoscopic vaginal-presacral fixation, vaginal posterior wall repair, perineum plasty, hysterectomy plus both appendectomy were performed.
Intraoperative Diagnosis:Vaginal anterior wall prolapse III° vaginal posterior wall prolapse II°.

Female pelvic floor dysfunction disease is an umbrella term for a series of pelvic floor structural and functional disorders, including stress urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse,etc., which will affect patients' quality of life and physical and mental health.
Two-dimensional ultrasound can directly observe and measure pelvic floor structure, and understand the changes of pelvic organs in different states.
Three-dimensional ultrasound can measure the parameters of pelvic diaphragm hiatus in different planes. Tomography combines tomographic imaging with volumetric imaging to obtain cross-sectional image information similar to CT and MRI, thus realizing quantitative evaluation of levator ani injury. The degree of muscle injury can be quantitatively assessed by observing muscle movement in multiple planes, which is consistent with MRI in diagnosing muscle injury. It is currently a common method to evaluate the shape and function of pelvic floor muscles.
The standard for quantitative evaluation of ultrasound examination in this case referred to the Ultrasound in the Assessment of Pelvic Organ Prolapse published by Professor Hans Peter Dietz in 2019 on the Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics and Gynaecology.
Pelvic floor ultrasound and MRI are the commonly used imaging modality in clinic. MRI has high resolution for soft tissue and high reference value for the selection of surgical methods. Yet it is expensive in examination cost and time consuming Ultrasonic examination is convenient and economical, and it is an effective method for screening and diagnosing pelvic floor dysfunction diseases.
