Le rôle de la rénine et de l'aldostérone dans l'aldostéronisme primaire
Mindray 2021-05-17

Rénine et aldostérone dans le SRAA
(Système rénine-angiotensine-aldostérone)
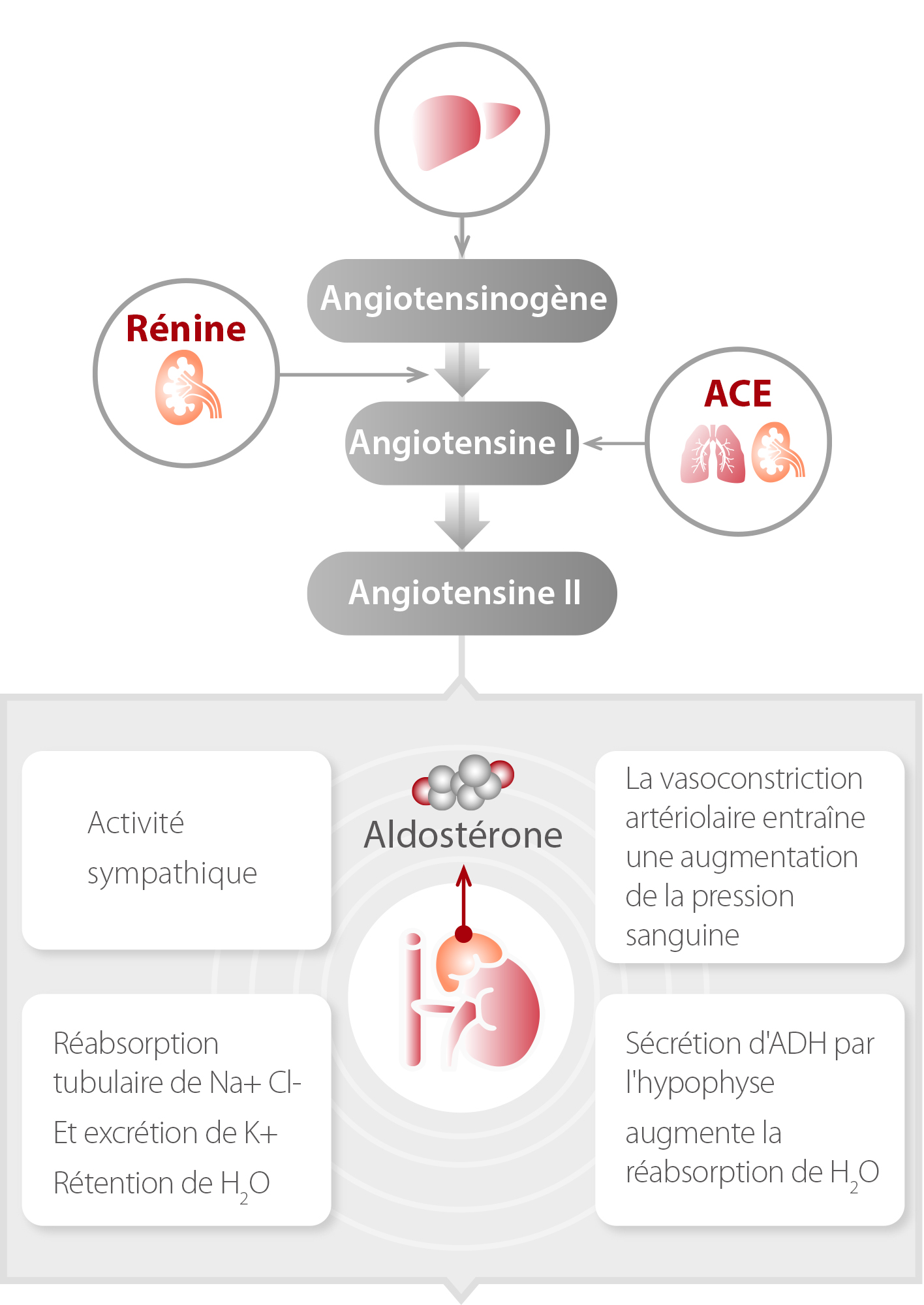
Direction différente de la rénine et de l'aldostérone dans l'hyperaldostéronisme primaire et secondaire
Le syndrome de l'aldostéronisme primaire a été décrit pour la première fois par Conn en 1955. Il se caractérise par une hypertension, une suppression de l'activité rénine plasmatique (ARP), une augmentation de la concentration d'aldostérone plasmatique (CAP) et des taux insuppressibles d'aldostérone dans le sang ou l'urine.
Les signes et les symptômes de l'AP ne sont pas spécifiques. Ils comprennent notamment:
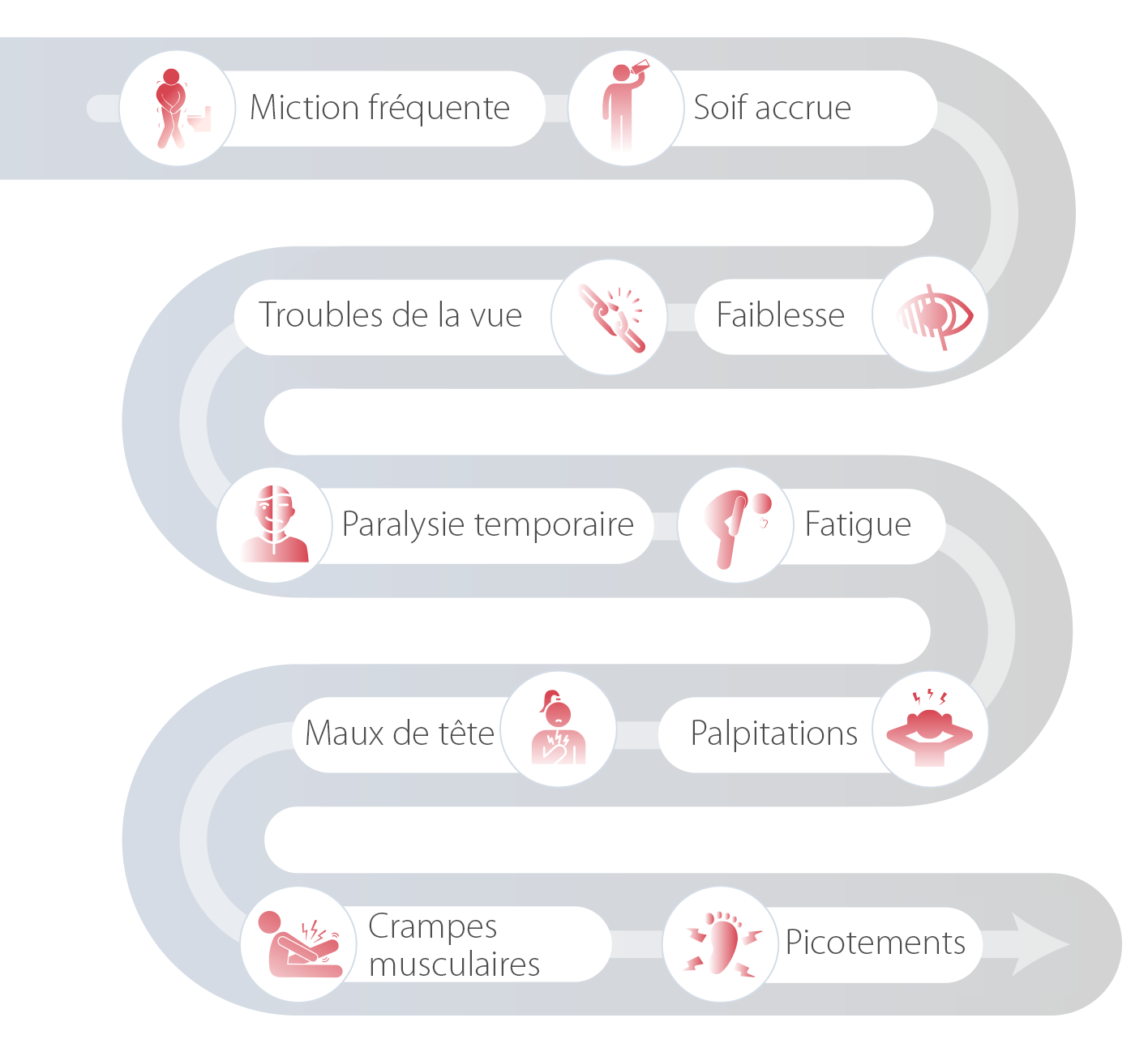
Le diagnostic de l'AP est insuffisant
Tous les patients souffrant d'hypertension devraient se faire tester
Le RAR est un outil utile pour la détection des PA
Le dépistage du RAR permet de multiplier par 10 le taux annuel de détection de l'aldostéronisme primaire.
Il est essentiel de distinguer le sous-type d'aldostéronisme primaire pour décider du traitement approprié
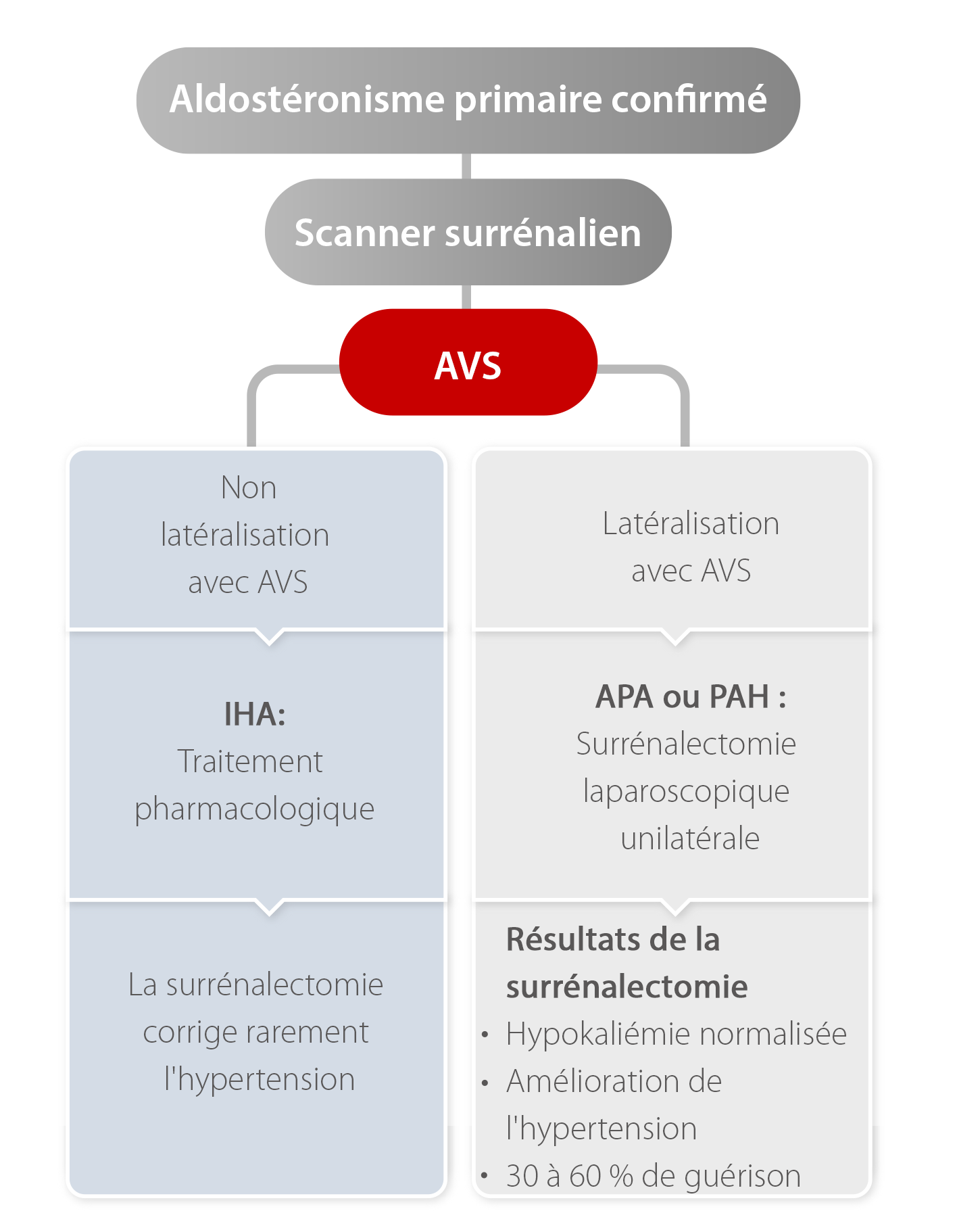
Algorithme de sous-typage
APA, adénome producteur d'aldostérone;
AVS, échantillonnage veineux surrénalien;
CT, tomodensitométrie;
IHA, hyperaldostéronisme idiopathique ; AP, aldostéronisme primaire;
HAP, hyperaldostéronisme primaire sur adénome.
En raison des limites de la tomographie par ordinateur, un prélèvement veineux surrénalien est nécessaire
Test de rénine et d'aldostérone Mindray

Références
[1] Young, WF (Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA). Diagnosis and treatment of primary aldosteronism: practical clinical perspectives (Review). J Intern Med 2019; 285: 126– 148.
[2] https://www.amazon.com/Secondary-Hypertension-Presentation-Diagnosis-Treatment/dp/ 1588291413> [Accessed 25 March 2021].
[3] <Effect of age on aldosterone/renin ratio (ARR) and comparison of screening accuracy of ARR plus elevated serum aldosterone concentration for primary aldosteronism screening in different age groups> Yin G, Zhang S Endocrine. 2012 Aug; 42(1):182-9.
[4] Williams textbook of endocrinology 13th edition
[5] Young WF, Stanson AW, Thompson GB, et al. Role for adrenal venous sampling in primary aldosteronism. Surgery. 2004;136:1227-1235




