Hemabook Chapter 14: Exploring Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): A Comprehensive Guide: Part A
BY Mindray 2023-10-25
In the dynamic landscape of modern medicine, diagnostic tools are pivotal in early detection, monitoring, and managing various health conditions. Among these tools, the Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) emerges as an invaluable ally for healthcare providers. This comprehensive guide embarks on an exploration of ESR, delving deep into this diagnostic tool,offering an in-depth understanding of its role in healthcare. Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), as determined by the Westergren method, is a valuable diagnostic tool in the realm of hematology. It measures the rate at which red blood cells (RBCs) gracefully settle at the bottom of a specialized tube, typically filled with anticoagulated blood, over the course of one hour. This process is observed in millimeters (mm), and it unfolds as a dynamic indicator of the interactions between blood components.
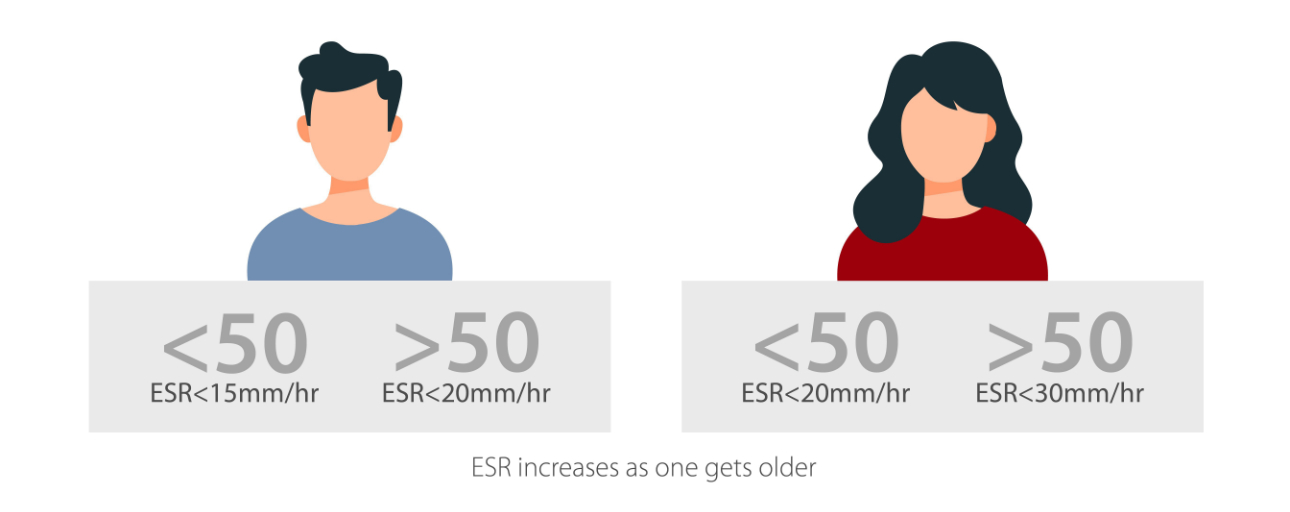
ESR is expressed in millimeters per hour (mm/hr), and it serves as a vital parameter in medical diagnostics. The understanding of what constitutes normal ESR values is pivotal in clinical practice:
ESR range for men
In the case of men, the normal ESR range typically falls within 0 to 15 mm/hr.
ESR range for women
The normal ESR spectrum is slightly broader for women, spanning from 0 to 20 mm/hr.
These normal ESR values provide a benchmark against which healthcare providers can gauge the health status of individuals. Any deviation from these established ranges can serve as an alert, indicating potential health issues that warrant further investigation and diagnostic procedures.
It's important to note that while ESR is a valuable diagnostic parameter, it is a non-specific test, meaning that it doesn't pinpoint the exact cause of any abnormalities. Rather, it acts as an indicator of an underlying issue that requires further assessment. In this way, ESR plays a crucial role in health evaluation, prompting healthcare professionals to delve deeper into a patient's medical history and symptoms to arrive at a precise diagnosis and develop a suitable treatment plan.
Understanding the nuances of ESR and its significance in hematology is pivotal in modern healthcare. It ensures that medical professionals can leverage this test effectively, facilitating the accurate diagnosis of underlying conditions and promoting the well-being of patients. In the ever-evolving field of modern medicine, diagnostic tools play a pivotal role in the early detection, monitoring, and management of various health conditions. One such tool is the Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR). This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of ESR and its vital role in modern healthcare while optimizing it for SEO.
What does Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) mean?

Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) is a blood test that measures the rate at which red blood cells settle in a vertical tube over a specific period. While it's not a disease-specific diagnostic tool, ESR serves as a sensitive indicator of inflammation within the body.
This section provides a comprehensive understanding of ESR, defining it and emphasizing its significance as a widely used diagnostic test. ESR is a versatile and indispensable tool in the realm of medicine. It not only provides crucial information about inflammation but also raises a red flag for various health issues.
To fully appreciate the importance of ESR in modern medicine, it's essential to understand its historical roots. ESR was first introduced in the early 20th century as a cost-effective and straightforward method to assess inflammation within the body. Over time, it has evolved into a widely used diagnostic tool, playing a pivotal role in healthcare. This historical context not only showcases the journey of ESR but also highlights its enduring relevance.
The historical evolution of ESR underscores its vital role in healthcare. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a fundamental diagnostic tool, ESR's journey is a testament to its contribution to medical science.
How is ESR Measured?
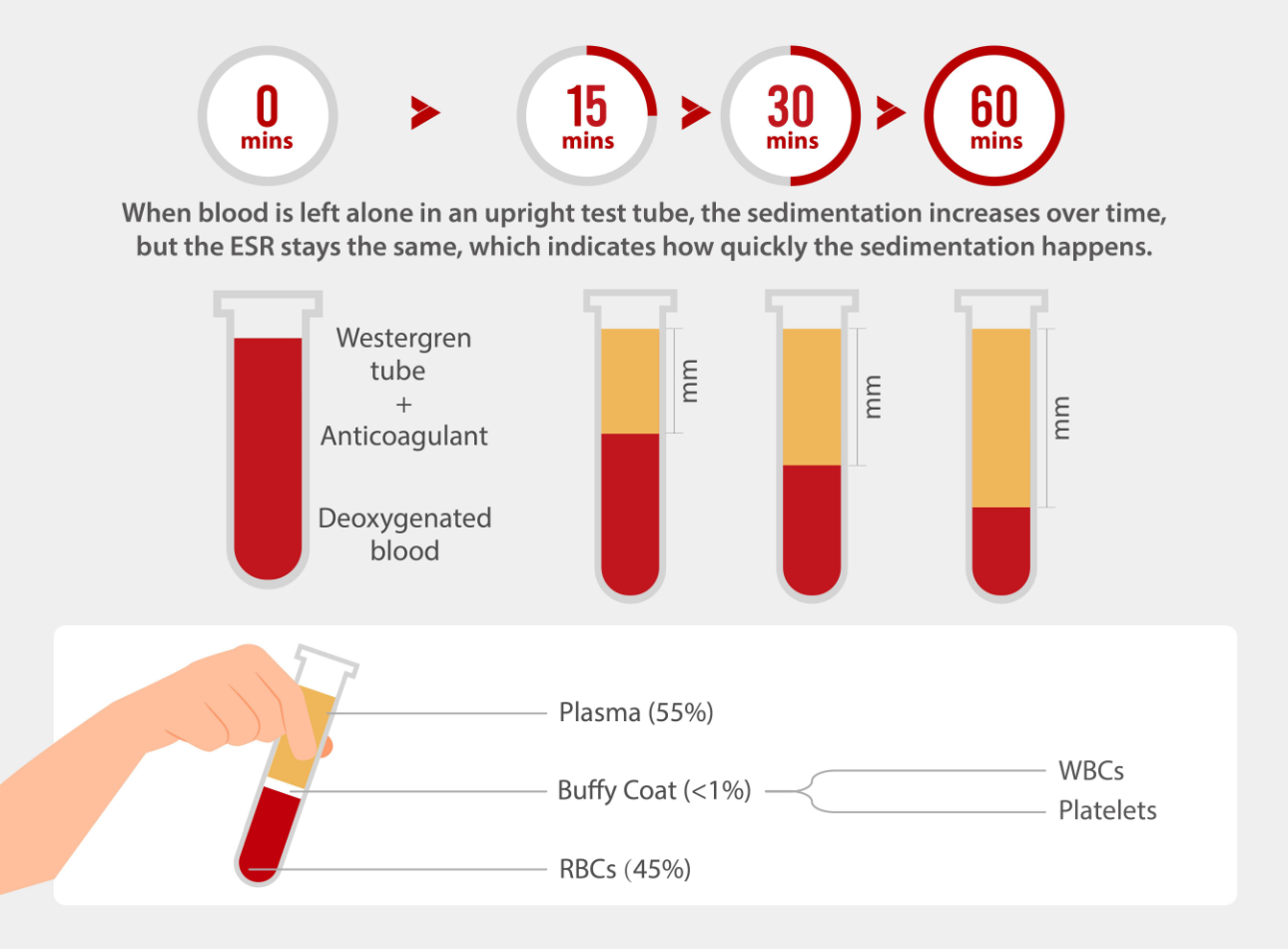
ESR is measured through a relatively simple process that involves drawing a small amount of blood from a vein, typically in the arm. This collected blood is placed in a tall, thin tube, and an anticoagulant is added to prevent clotting. The tube is then placed in an upright position, allowing the red blood cells to settle over a specific timeframe, with the rate of settling measured in millimeters per hour (mm/h).
This section provides an in-depth explanation of the testing process, making it easy for readers to understand how this diagnostic tool works. The ESR testing process is straightforward yet effective. By understanding how it works, both healthcare providers and patients can appreciate the simplicity and significance of this test.
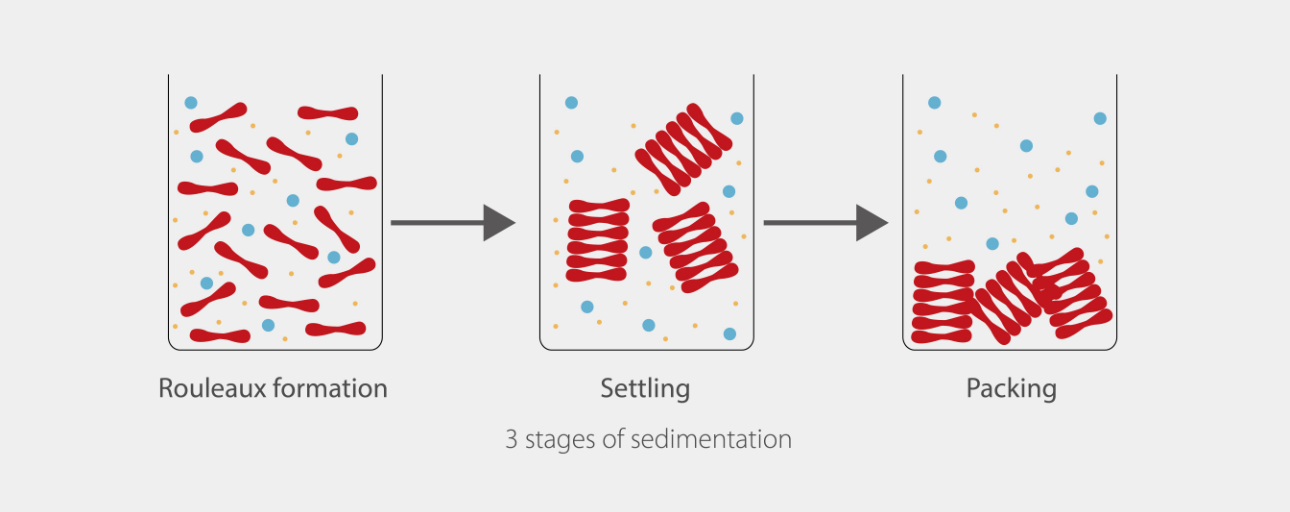
Factors Affecting ESR Results
The Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) is a dynamic diagnostic tool that provides insights into a person's health. However, ESR levels are not set in stone; they can be influenced by various health conditions and factors. In this section, we embark on a comprehensive journey through the conditions and influences that can affect ESR levels.
1. Infections: ESR levels can surge in response to infections, be they bacterial, viral, or fungal. When the body's immune system goes into overdrive to combat these invaders, red blood cells tend to clump together more, leading to higher ESR rates. This makes ESR a valuable indicator of ongoing infections.
2. Inflammatory Disorders: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and giant cell arteritis are characterized by chronic inflammation. This persistent inflammation can result in elevated ESR levels, underscoring the importance of ESR as a marker of inflammatory activity in such disorders.
3. Autoimmune Diseases: Disorders where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, like multiple sclerosis, Crohn's disease, and Hashimoto's thyroiditis, can lead to elevated ESR. The presence of these autoimmune diseases is often reflected in increased ESR values.
4. Tumors: Certain cancers, particularly lymphomas and multiple myeloma, can trigger an elevation in ESR rates. The presence of these cancers can thus be an important consideration when interpreting ESR results.
5. Pregnancy: ESR levels tend to rise during pregnancy, primarily due to changes in blood composition and the body's physiological adaptations to support the growing fetus. This is considered a normal variation in ESR values during pregnancy.
6. Anemia: While anemia typically results in lower red blood cell counts, certain types of anemia, such as hemolytic anemia, can contribute to increased ESR. In these cases, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells can influence ESR values.
7. Chronic Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can also affect ESR levels. The kidneys play a role in maintaining blood composition, and any dysfunction in this process can influence ESR values.
8. Thyroid Conditions: Both hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid) can influence ESR rates. Thyroid hormones have a broad impact on the body, including blood composition, which can indirectly affect ESR levels.
9. Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can cause elevated ESR. Understanding the medication history of a patient is crucial for accurate interpretation of ESR results.
10. Age and Gender: ESR levels are not uniform across all age groups and genders. In general, ESR tends to be slightly higher in women compared to men.
Additionally, ESR rates tend to increase with age. These age and gender variations in ESR values are considered normal and are important reference points when interpreting results.
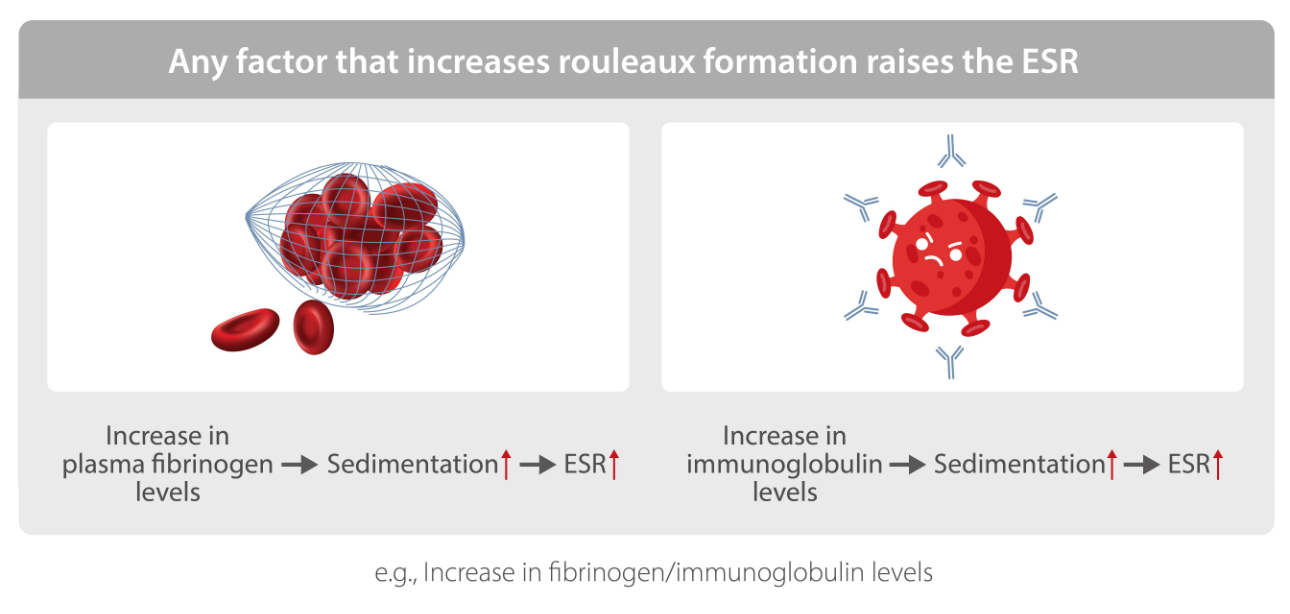
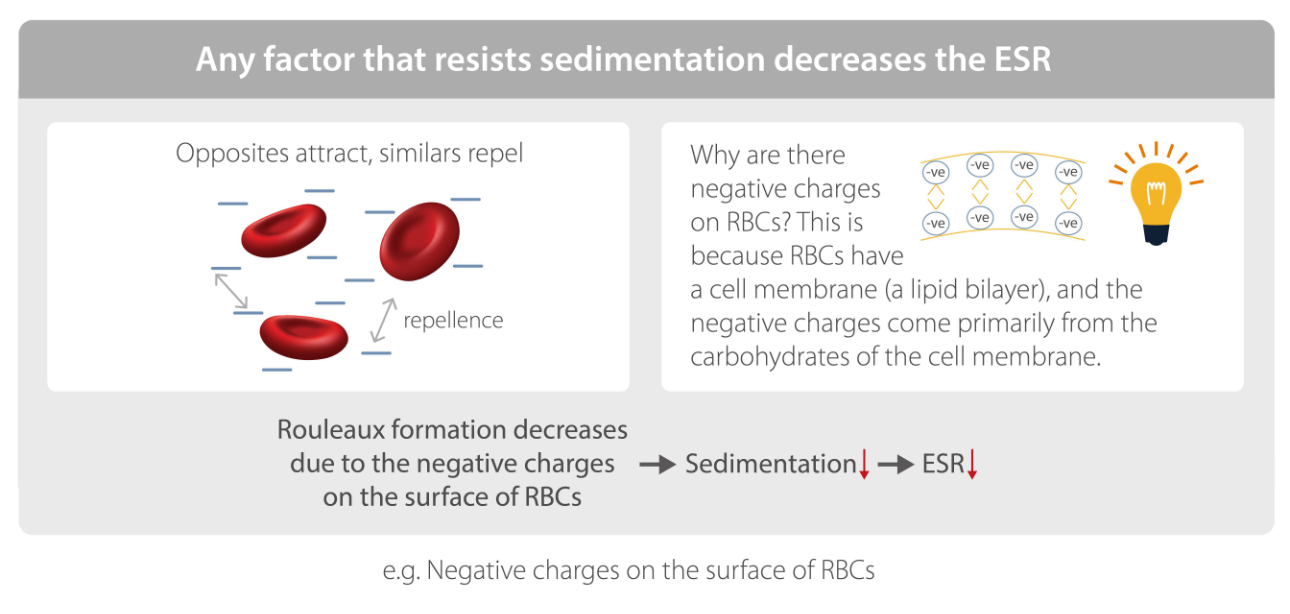
What Do ESR Results Mean?
In this section, we delve into the critical aspect of interpreting ESR results. We discuss the normal range of ESR, which can vary slightly between laboratories but generally falls within specific limits for men and women. Elevated ESR levels are investigated, emphasizing that an elevated result is not a specific diagnosis but an indicator of potential health issues. This section helps readers understand the significance of ESR values and what they might imply.
Understanding ESR results is a fundamental aspect of medical diagnostics. By comprehending the meaning behind ESR values, both healthcare providers and patients can appreciate the significance of this diagnostic tool.
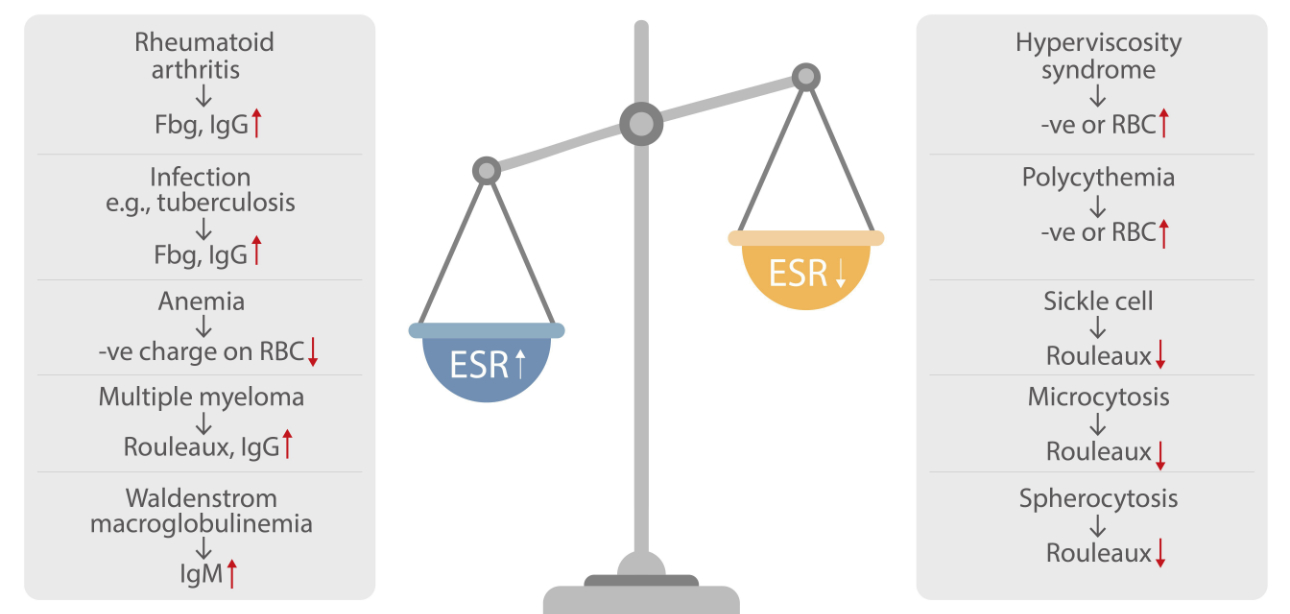
Interpreting Elevated ESR
When ESR results are elevated, it's essential to consider various potential underlying causes. Infections, inflammation, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and tissue damage are discussed in detail, providing readers with a comprehensive overview of the conditions that can lead to elevated ESR levels. This section enables healthcare providers and patients to recognize the red flags that elevated ESR results may present. Interpreting elevated ESR results is a complex process that involves considering a range of potential underlying causes. By understanding these causes, healthcare providers can make more informed decisions regarding patient care.
1. Infection: In cases of infection, the body's immune system releases proteins that can cause red blood cells to clump together, thereby increasing the ESR.
2. Inflammation: Inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus, can lead to elevated ESR levels.
3. Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like systemic vasculitis or polymyalgia rheumatica can result in elevated ESR, indicating the need for further evaluation.
4. Cancer: Some cancers, particularly multiple myeloma or lymphoma, can cause increased ESR.
5. Tissue Damage: Conditions involving tissue damage, such as burns or heart attacks, can also lead to elevated ESR, highlighting the importance of considering various health factors.
6. Low ESR: While less common, a low ESR can also provide valuable information. It may indicate conditions such as polycythemia, a disorder where the body produces too many red blood cells.

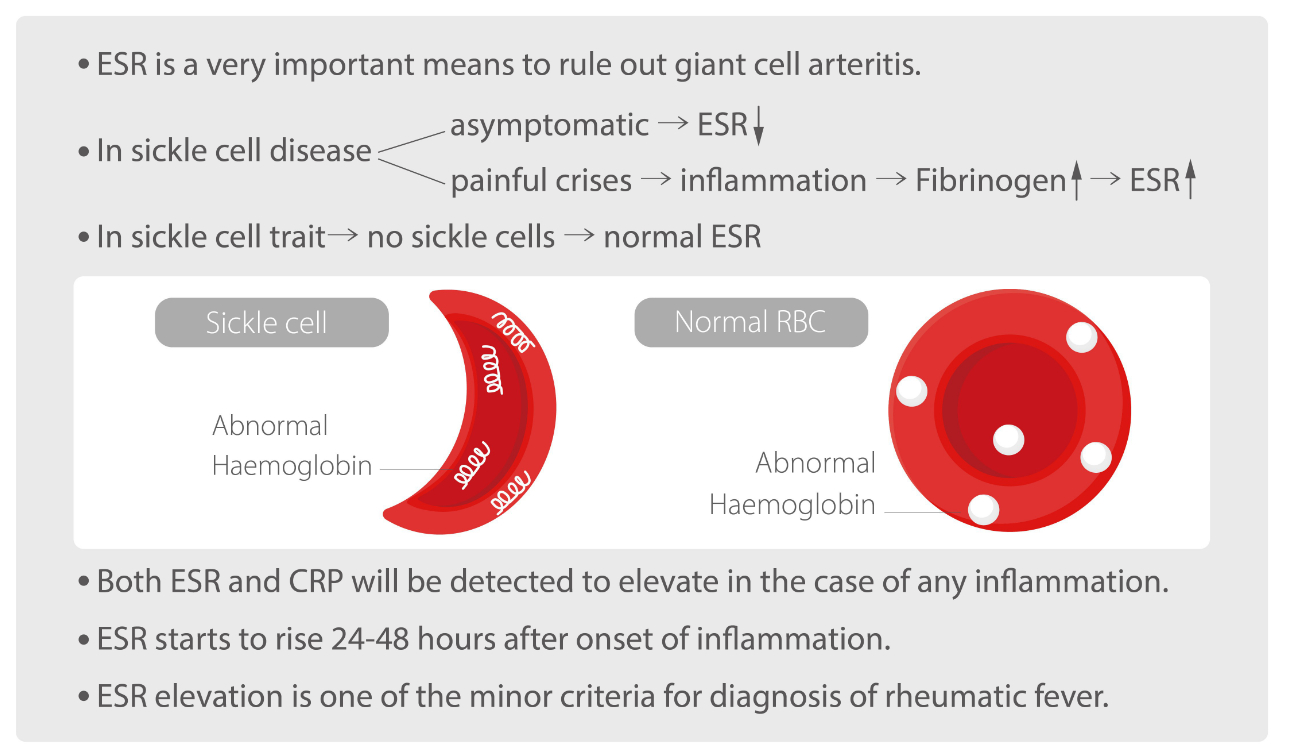
The Need for Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Testing: A Comprehensive Examination
The Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) test, when used in conjunction with a Complete Blood Count (CBC) test, unfolds as a powerful diagnostic duo that offers profound insights into an individual's health. This section delves into the multifaceted need for ESR testing, underscoring its pivotal role in healthcare.
Understanding ESR and Its Synergy with CBC
1. Comprehensive Inflammation Marker: ESR is the measure of how quickly red blood cells settle in a vertical tube over time. When combined with a CBC, which provides intricate details about blood cell counts and types, it unveils a holistic view of the body's inflammatory response. This synergy paints a comprehensive picture of inflammation and its potential underlying causes.
2. Identification of Infection: While a CBC can hint at infection through changes in white blood cell counts, ESR further bolsters this diagnosis. It detects elevated sedimentation rates induced by heightened inflammation during infections, providing vital confirmation and a more complete clinical understanding.
3. Monitoring Chronic Conditions: For individuals battling chronic conditions like autoimmune disorders or specific cancers, the amalgamation of ESR and CBC results offers an invaluable tool for monitoring disease progression and evaluating the effectiveness of ongoing treatments. This combination equips healthcare providers with the ability to make timely adjustments to care plans.
4. Health Status Evaluation: ESR results, when considered in conjunction with CBC values, contribute to a meticulous health assessment. This in-depth evaluation aids healthcare professionals in identifying concealed health issues and facilitating early intervention, potentially preventing further complications.
5. Treatment Effectiveness: The CBC delves into the specifics of blood cell types and levels, while the ESR test reflects the body's inflammation levels. Together, they create a dynamic duo for gauging the effectiveness of treatment in managing underlying conditions. This approach provides quantitative data to ascertain whether treatment regimens are yielding the desired results.
6. Diagnostic Aid: Elevated ESR values, when accompanied by specific CBC findings, can serve as a potent diagnostic aid. The synergy between these two tests can raise red flags about potential health concerns, prompting further investigation and targeted diagnostic tests for precise identification. This early detection can be pivotal in the context of serious health conditions.

The Integration of ESR and CBC
In recognition of the indispensable nature of ESR and CBC tests, Mindray's BC-700 series Hematology Analyzer takes a significant stride. It seamlessly integrates an automatic ESR module within a comprehensive hematology analyzer. This innovation empowers healthcare professionals to generate both CBC and ESR results within a single test, accomplishing this feat in a mere 1.5 minutes. This advanced integration ensures efficiency, accuracy, and expeditious health insights, benefiting both patients and healthcare providers.
In sum, the ESR test, when joined with the CBC test, forms a formidable alliance in the realm of diagnostics. This combination empowers healthcare professionals to paint a clearer, more comprehensive picture of an individual's overall health. Armed with this knowledge, they can make well-informed decisions, craft personalized treatment plans, and, ultimately, improve patient care and outcomes. The integration of ESR and CBC tests signifies a leap forward in diagnostic technology, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare processes.
Conclusion
In the realm of medical diagnostics, the Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) stands as an enduring sentinel, ever watchful for signs of inflammation and health anomalies. As we conclude our journey through the intricacies of ESR, it's essential to appreciate the pivotal role this diagnostic tool plays in modern healthcare.
ESR, born from the simplicity of a vertical tube test, has evolved into a sophisticated indicator, capable of flagging potential health concerns and guiding healthcare providers on the path to timely intervention. Its historical significance and continued relevance underscore its enduring value.
Interpreting ESR results, whether within the normal range or elevated, requires a keen understanding of the multifaceted factors that influence its outcome. Infections, inflammation, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and tissue damage are all potential instigators of change in ESR levels. Recognizing these red flags empowers healthcare providers and patients to make informed decisions regarding further evaluation and care.
This comprehensive guide has shed light on the intricacies of ESR, from the historical roots to its contemporary applications, offering a wealth of information for healthcare providers and patients alike. By understanding ESR, we not only decode test results but also enhance our grasp of our own well-being.
As you navigate the landscape of healthcare, may this knowledge serve as a beacon, guiding you toward better health and a deeper understanding of your body's signals. ESR, in all its simplicity, remains a steadfast companion in this journey, watching, waiting, and providing essential insights into your health.
With ESR as an ally, we march forward with a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of our bodies, and a greater readiness to face health challenges with knowledge and resilience.
References
[1] Aldo F.F.R, Luiz J.S. Alteration in the Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate in Dengue Patients: Analysis of 1,398 Cases The Brazilian journal of infectious
diseases: an official publication of the Brazilian Society of Infectious Diseases Med 2009;12(6):472-5.
[2]. https://labtestsonline.org.uk/tests/erythrocyte- sedimentation-rate-esr
[3]. https://labs.selfdecode.com/blog/erythrocyte- sedimentation-rate-esr-high-low-levels-how-to-decrease-it/
[4]. ICSH recommendations for measurement of erythrocyte sedimentation rate. International Council for Standardization in Haematology (Expert Panel on
Blood Rheology). J Clin Pathol. 1993 Mar;46(3):198-203. [PMC free article] [PubMed]